Randomw Forest算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn),該系列文章主要是對(duì)常見的機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)算法的實(shí)現(xiàn)。
完整的筆記和代碼以上傳到Github,地址為(覺得有用的話,歡迎Fork,請(qǐng)給作者個(gè)Star):
https://github.com/Vambooo/lihang-dl
隨機(jī)森林 Random Forest
隨機(jī)森林是對(duì)多棵樹組合對(duì)樣本訓(xùn)練預(yù)測的一種分類器,它是Bagging方法的最流行的版本之一。
可以理解為隨機(jī)森林是個(gè)體模型為決策樹的Bagging算法。
隨機(jī)森林由Breiman提出的一種分類算法,它使用Bootstrap重采樣技術(shù),從原始訓(xùn)練樣本集中有放回的重復(fù)隨機(jī)抽取n個(gè)樣本生成新的樣本集合,以此作為訓(xùn)練集來訓(xùn)練決策樹。然后按照上述步驟生成m棵決策樹組合而成隨機(jī)森林。
隨機(jī)森林算法

Random Forest算法案例 python實(shí)現(xiàn)
(代碼可以左右滑動(dòng)看)
第一步:構(gòu)建數(shù)據(jù)(這里用make_blobs()來構(gòu)建聚類數(shù)據(jù))
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=3000, centers=2, random_state=42, cluster_std=1.0)
n_samples是待生成的樣本的總數(shù);
n_features是每個(gè)樣本的特征數(shù);
centers表示類別數(shù);
cluster_std表示每個(gè)類別的方差。
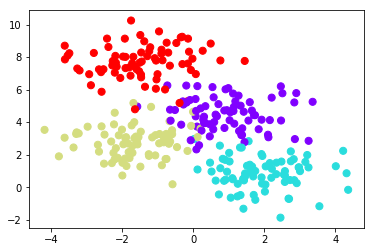
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=300, centers=4, random_state=0, cluster_std=1.0)plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='rainbow');
定義樹的可視化方法
def visualize_tree(estimator, X, y, boundaries=True, xlim=None, ylim=None, ax=None): ax = ax or plt.gca() # 繪制訓(xùn)練點(diǎn) ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=30, cmap='viridis', clim=(y.min(), y.max()), zorder=3) ax.axis('tight') ax.axis('off') if xlim is None: xlim = ax.get_xlim() if ylim is None: ylim = ax.get_ylim() # 擬合估計(jì)器 estimator.fit(X, y) xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(*xlim, num=200), np.linspace(*ylim, num=200)) Z = estimator.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # 將結(jié)果放入到帶顏色的圖中 n_classes = len(np.unique(y)) Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) contours = ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.3, levels=np.arange(n_classes + 1) - 0.5, cmap='viridis',zorder=1) ax.set(xlim=xlim, ylim=ylim) # 繪制決策邊界 def plot_boundaries(i, xlim, ylim): if i >= 0: tree = estimator.tree_ if tree.feature[i] == 0: ax.plot([tree.threshold[i], tree.threshold[i]], ylim, '-k', zorder=2) plot_boundaries(tree.children_left[i], [xlim[0], tree.threshold[i]], ylim) plot_boundaries(tree.children_right[i], [tree.threshold[i], xlim[1]], ylim) elif tree.feature[i] == 1: ax.plot(xlim, [tree.threshold[i], tree.threshold[i]], '-k', zorder=2) plot_boundaries(tree.children_left[i], xlim, [ylim[0], tree.threshold[i]]) plot_boundaries(tree.children_right[i], xlim, [tree.threshold[i], ylim[1]]) if boundaries: plot_boundaries(0, xlim, ylim)
定義分類器的可視化方法
def visualize_classifier(model, X, y, ax=None, cmap='rainbow'):
ax = ax or plt.gca()
# 繪制訓(xùn)練點(diǎn) ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=30, cmap=cmap,
clim=(y.min(), y.max()), zorder=3) ax.axis('tight')
ax.axis('off') xlim = ax.get_xlim() ylim = ax.get_ylim()
# 擬合估計(jì)器 model.fit(X, y)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(*xlim, num=200),
np.linspace(*ylim, num=200))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]).reshape(xx.shape)
# 將擬合結(jié)果繪制在帶顏色的圖中
n_classes = len(np.unique(y))
contours = ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.3,
levels=np.arange(n_classes + 1) - 0.5,
cmap=cmap,
zorder=1)
ax.set(xlim=xlim, ylim=ylim)
#定義可設(shè)置深度的決策樹分類器def depth_tree(depth=5): clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=depth, random_state=0) visualize_tree(clf, X, y)
深度為1的決策樹分類器,分類效果
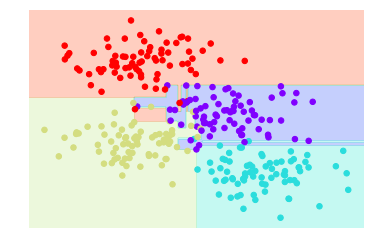
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifiertree = DecisionTreeClassifier().fit(X, y)visualize_classifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), X, y)
深度為5的決策樹分類器,分類效果
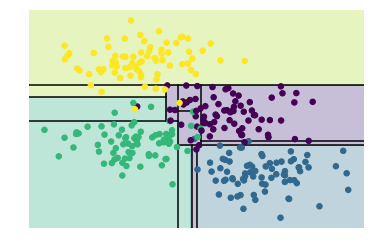
depth_tree(depth=5)
深度為10的決策樹分類器,分類效果
depth_tree(depth=10)
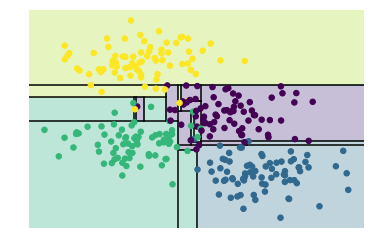
深度為15的決策樹分類器,分類效果
depth_tree(depth=15)

如上圖,當(dāng)決策樹的深度不斷增加時(shí),會(huì)出現(xiàn)不同的分類區(qū)域,比如當(dāng)depth=10時(shí),在黃色和藍(lán)色之間存在一條紫色區(qū)域,這塊數(shù)據(jù)應(yīng)該是噪聲或者特定采樣的結(jié)果,這塊不能歸為紫色一類,這種現(xiàn)象其實(shí)就是過擬合。
可以通過組合多個(gè)分類器(這里是決策樹分類器)來減少這個(gè)種過擬合的影響。這也是Bagging的思想。
下面就是使用Bagging來組合100個(gè)DecisionTreeClassifier來進(jìn)行測試。其中使用80%的數(shù)據(jù)來隨機(jī)化數(shù)據(jù)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier tree = DecisionTreeClassifier()bag = BaggingClassifier(tree, n_estimators=100, max_samples=0.8, random_state=1) bag.fit(X, y)visualize_classifier(bag, X, y)
也可以直接使用Scikit-learn中已定義好的RandomForestClassifier來實(shí)現(xiàn)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=0)visualize_classifier(model, X, y);
-
機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
66文章
8406瀏覽量
132563 -
python
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
56文章
4792瀏覽量
84628 -
隨機(jī)森林
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
22瀏覽量
4268
原文標(biāo)題:機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)筆記系列(十四) | Random Forest算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn)
文章出處:【微信號(hào):AI_class_vip,微信公眾號(hào):人工智能學(xué)研社】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
Python的Apriori算法和FP-Growth算法是什么
Python實(shí)現(xiàn)k-近鄰算法
BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn)
大數(shù)據(jù)分析到底需要多少種工具_(dá)大數(shù)據(jù)分析總結(jié)
蟻群算法python編程實(shí)現(xiàn)
Python基礎(chǔ)教程之《Python機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)—預(yù)測分析核心算法》免費(fèi)下載
多元統(tǒng)計(jì)分析:R與Python的實(shí)現(xiàn)
Python實(shí)現(xiàn)所有算法-基本牛頓法
基于Python實(shí)現(xiàn)隨機(jī)森林算法





 Random Forest算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn)案例分析
Random Forest算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn)案例分析










評(píng)論