adb,全稱 Android Debug Bridge,是 Android 的命令行調試工具,可以完成多種功能,如跟蹤系統日志,上傳下載文件,安裝應用等。
支持兩種ADB鏈接方式:USB和網絡連接。
USB方式
網絡方式
-
網絡ADB
-
查看RK3399Pro的IP地址,PC端通過網絡訪問。例:
-
adb connect + IP adb shell
首先參照安裝 RK USB 驅動一節安裝好驅動。然后到 http://adbshell.com/download/download-adb-for-windows.html 下載 adb.zip,解壓到C:\adb以方便調用。 打開命令行窗口,輸入:
cd C:\adb adb shell
如果一切正常,就可以進入adb shell,在設備上面運行命令。
-
安裝 adb 工具:
sudo apt-get install android-tools-adb -
加入設備標識:
mkdir -p ~/.android vi ~/.android/adb_usb.ini # 添加以下一行 0x2207 -
加入 udev 規則:
sudo vi /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules # 添加以下一行: SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="2207", MODE="0666" -
重新插拔 USB 線,或運行以下命令,讓 udev 規則生效:
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules sudo udevadm trigger -
重新啟動 adb 服務器
sudo adb kill-server adb start-server 連接管理
列出所有連接設備及其序列號
adb devices 如果有多個連接設備,則需要使用序列號來區分:
export ANDROID_SERIAL=<設備序列號> adb shell ls 多設備下連接指定設備
adb -s 序列號 shell 可以通過網絡來連接 adb:
# 讓設備端的 adbd 重啟,并在 TCP 端口 5555 處監聽 adb tcpip 5555 # 此時可以斷開 USB 連接 # 遠程連接設備,設備的 IP 地址是 192.168.1.100 adb connect 192.168.1.100:5555 # 斷開連接 adb disconnect 192.168.1.100:5555 獲取系統日志 adb logcat
-
用法
adb logcat [選項] [應用標簽] -
示例
# 查看全部日志 adb logcat # 僅查看部分日志 adb logcat -s WifiStateMachine StateMachine 運行命令 adb shell
獲取詳細運行信息 adb bugreport
adb bugreport用于錯誤報告,里面包含大量有用的信息。
-
示例
adb bugreport # 保存到本地,方便用編輯器查看 adb bugreport >bugreport.txt root 權限
如果 TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT 使用的是 userdebug 模式,要獲得 root 權限,需要先運行:
adb root 讓 adb 的設備端切換到 root 權限模式,這樣 adb remount 等需要 root 權限的命令才會成功。
安裝應用 adb install
-
用法:
adb install [選項] 應用包.apk 選項包括:
-l forward-lock -r 重新安裝應用,保留原先數據 -s 安裝到 SD 卡上,而不是內部存儲 -
示例:
# 安裝 facebook.apk adb install facebook.apk # 升級 twitter.apk adb install -r twitter.apk 如果安裝成功,工具會返回成功提示 “Success”;失敗的話,一般是以下幾種情況:
-
INSTALL_FAILED_ALREADY_EXISTS: 此時需要用 -r 參數來重新安裝。
-
INSTALL_FAILED_SIGNATURE_ERROR: 應用的簽名不一致,可能是發布版和調試版簽名不同所致。如果確認 APK 文件簽名正常,可以用 adb uninstall 命令先卸載舊的應用,然后再安裝。
-
INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE: 存儲空間不足,需要檢查設備存儲情況。
卸載應用 adb uninstall
-
用法:
adb uninstall 應用包名稱 -
示例:
adb uninstall com.android.chrome 應用包名稱可以用以下命令列出:
adb shell pm list packages -f 運行結果是:
package:/system/app/Bluetooth.apk=com.android.bluetooth 前面是 apk 文件,后面則是對應的包名稱。
命令行幫助信息 adb help
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31 -a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection -d - directs command to the only connected USB device returns an error if more than one USB device is present. -e - directs command to the only running emulator. returns an error if more than one emulator is running. -s <specific device> - directs command to the device or emulator with the given serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL environment variable. -p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or a relative/absolute path to a product out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'. If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT environment variable is used, which must be an absolute path. -H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost) -P - Port of adb server (default: 5037) devices [-l] - list all connected devices ('-l' will also list device qualifiers) connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified. disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device. Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified. Using this command with no additional arguments will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices. device commands: adb push [-p] <local> <remote> - copy file/dir to device ('-p' to display the transfer progress) adb pull [-p] [-a] <remote> [<local>] - copy file/dir from device ('-p' to display the transfer progress) ('-a' means copy timestamp and mode) adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed (-l means list but don't copy) (see 'adb help all') adb shell - run remote shell interactively adb shell <command> - run remote shell command adb emu <command> - run emulator console command adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections. the format is a list of lines with the following format: <serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n" adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections forward specs are one of: tcp:<port> localabstract:<unix domain socket name> localreserved:<unix domain socket name> localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name> dev:<character device name> jdwp:<process pid> (remote only) adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote> - same as 'adb forward ' but fails if <local> is already forwarded adb forward --remove <local> - remove a specific forward socket connection adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport adb install [-l] [-r] [-d] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <file> - push this package file to the device and install it ('-l' means forward-lock the app) ('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data) ('-d' means allow version code downgrade) ('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage) ('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already) adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device ('-k' means keep the data and cache directories) adb bugreport - return all information from the device that should be included in a bug report. adb backup [-f <file>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<packages...>] - write an archive of the device's data to . If no -f option is supplied then the data is written to "backup.ab" in the current directory. (-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves in the archive; the default is noapk.) (-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion (aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default is noobb.) (-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.) (-all means to back up all installed applications) (-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes system applications; the default is to include system apps) (<packages...> is the list of applications to be backed up. If the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the command line will be included even if -nosystem would ordinarily cause them to be omitted.) adb restore <file> - restore device contents from the <file> backup archive adb help - show this help message adb version - show version num scripting: adb wait-for-device - block until device is online adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number> adb get-devpath - prints: <device-path> adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port networking: adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB. Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection. <tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1 [parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ] <localdir> can be interpreted in several ways: - If <directory> is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated. - If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition is updated. environmental variables: ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values 1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given. ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed. 編譯 Android 對機器的配置要求較高:
官方推薦 Ubuntu 14.04 操作系統,經測試,Ubuntu 12.04 也可以編譯運行成功,只需要滿足 http://source.android.com/source/building.html 里的軟硬件配置即可。編譯環境的初始化可參考 http://source.android.com/source/initializing.html 。
-
安裝 OpenJDK 8:
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk 提示:安裝 openjdk-8-jdk,會更改 JDK 的默認鏈接,這時可用:
$ sudo update-alternatives --config java $ sudo update-alternatives --config javac 來切換 JDK 版本。SDK 在找不到操作系統默認 JDK 的時候會使用內部設定的 JDK 路徑,因此,為了讓同一臺機器可以編譯 Android 5.1 及之前的版本,去掉鏈接更方便:
$ sudo /var/lib/dpkg/info/openjdk-8-jdk:amd64.prerm remove -
Ubuntu 12.04 軟件包安裝:
sudo apt-get install git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ g++-multilib mingw32 tofrodos gcc-multilib ia32-libs \ python-markdown libxml2-utils xsltproc zlib1g-dev:i386 \ lzop libssl1.0.0 libssl-dev -
Ubuntu 14.04 軟件包安裝:
sudo apt-get install git-core gnupg flex bison gperf libsdl1.2-dev \ libesd0-dev libwxgtk2.8-dev squashfs-tools build-essential zip curl \ libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev pngcrush schedtool libxml2 libxml2-utils \ xsltproc lzop libc6-dev schedtool g++-multilib lib32z1-dev lib32ncurses5-dev \ lib32readline-gplv2-dev gcc-multilib libswitch-perl \ libssl1.0.0 libssl-dev Android SDK 源碼包比較大,可以通過如下方式獲取Android8.1源碼包:
-
下載
[下載SDK]完成后先驗證一下 MD5 碼:
$ md5sum /path/to/rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.001 $ md5sum /path/to/rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.002 $ md5sum /path/to/rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.003 70dd51416594d36e140d2eef0738e270 rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.001 ac8234b94df1b812afd6a4c8c42976cb rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.002 68b2da1653aed2d9d80871d7ad21272d rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.003 確認無誤后,就可以解壓:
cd ~/proj/ 7z x ./rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4_android8.1_20190430.7z.001 -oAIO-RK3399ProJD4 cd ./AIO-RK3399proJD4 git reset --hard -
更新
以下為從 gitlab 處更新的方法:
#1. 進入SDK根目錄 cd ~/proj/AIO-RK3399ProJD4 #2. 下載遠程bundle倉庫 git clone https://gitlab.com/TeeFirefly/rk3399pro-oreo-bundle.git .bundle #3. 若下載倉庫失敗,則可以從下方百度云下載[bundle壓縮包]并解壓到SDK根目錄,解壓指令如下: 7z x rk3399pro-oreo-bundle.7z -r -o. && mv rk3399pro-oreo-bundle/ .bundle/ #4. 更新SDK,并且后續更新不需要再次拉取遠程倉庫,直接執行以下命令即可 .bundle/update #5. 按照提示已經更新內容到 FETCH_HEAD,同步FETCH_HEAD到firefly分支 git rebase FETCH_HEAD 百度云下載[bundle壓縮包]
HDMI顯示編譯
./FFTools/make.sh -d rk3399pro-firefly-aiojd4 -j8 -l rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4-userdebug ./FFTools/mkupdate/mkupdate.sh -l rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4-userdebug 手動編譯AIO-3399ProJD4
編譯前執行如下命令配置環境變量:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar -
編譯kernel:
cd ~/proj/AIO-RK3399ProJD4/kernel/ make ARCH=arm64 firefly_defconfig make -j8 ARCH=arm64 rk3399pro-firefly-aiojd4.img -
編譯uboot:
cd ~/proj/AIO-RK3399ProJD4/u-boot/ ./make.sh rk3399pro -
編譯android:
cd ~/proj/AIO-RK3399ProJD4/ source build/envsetup.sh lunch rk3399pro_firefly_aioJD4-userdebug make -j8 ./mkimage.sh 編譯完可以用Firefly官方的腳本打包成統一固件,執行如下命令:
./FFTools/mkupdate/mkupdate.sh update 打包完成后將在rockdev/Image-rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4/下生成統一固件:update.img
在 Windows 下打包統一固件 update.img 也很簡單,將編譯生成的文件拷貝到 AndroidTool 的 rockdev\Image 目錄中,然后運行 rockdev 目錄下的 mkupdate.bat 批處理文件即可創建 update.img 并存放到 rockdev\Image 目錄里。
編譯的時候執行 ./mkimage.sh 會重新打包 boot.img 和 system.img, 并將其它相關的映像文件拷貝到目錄 rockdev/Image-rk3399pro_firefly_aiojd4/ 中。以下列出一般固件用到的映像文件:
-
boot.img :Android 的初始文件映像,負責初始化并加載 system 分區。
-
kernel.img :內核映像。
-
misc.img :misc 分區映像,負責啟動模式切換和急救模式的參數傳遞。
-
parameter.txt :emmc的分區信息
-
recovery.img :急救模式映像。
-
resource.img :資源映像,內含開機圖片和內核的設備樹信息。
-
system.img :Android 的 system 分區映像,ext4 文件系統格式。
-
trust.img :休眠喚醒相關的文件
-
MiniLoaderAll.bin :Loader文件
-
uboot.img :uboot文件
-
oem.img :預置媒體資源及數據包
-
vendor.img :產品標識和驅動
請參照 如何升級固件 一文來燒寫分區映像文件。
如果使用的是 Windows 系統,將上述映像文件拷貝到 AndroidTool (Windows 下的固件升級工具)的 rockdev\Image 目錄中,之后參照升級文檔燒寫分區映像即可,這樣的好處是使用默認配置即可,不用修改文件的路徑。
update.img 方便固件的發布,供終端用戶升級系統使用。一般開發時使用分區映像比較方便。
定制 Android 固件,有兩種方法:
-
改源碼,然后編譯生成固件。
-
在現有固件的基礎上進行裁剪。
前一種方法,可以從各個層面去定制 Android,自由度大,但對編譯環境和技術要求比較高,參見《編譯 Android8.1 固件》一文。現在介紹后一種方法,分為解包、定制和打包三個階段。主機操作系統為 Linux,采用的工具為開源軟件。
統一固件 release_update.img,內含啟動加載器 loader.img 和真正的固件數據 update.img
release_update.img |- loader.img `- update.img update.img 是個復合文件,內含多個文件,由 package-file 描述。一個典型的 package-file 為:
# NAME Relative path package-file package-file bootloader Image/MiniLoaderAll.bin parameter Image/parameter.txt trust Image/trust.img uboot Image/uboot.img misc Image/misc.img resource Image/resource.img kernel Image/kernel.img boot Image/boot.img recovery Image/recovery.img system Image/system.img backup RESERVED #update-script update-script #recover-script recover-script -
package-file
-
update.img 的打包說明文件,update.img 里也含有一份 package-file。
-
Image/MiniLoaderAll.bin
-
啟動加載器,即 bootloader。
-
Image/parameter.txt
-
參數文件,可以設定內核啟動參數,里面有重要的分區信息。
-
Image/trust.img,trust.img 是U-Boot作為二級loader 的打包。
-
Image/misc.img
-
misc 分區的映像,用來控制 Android 是正常啟動,還是進入急救模式(Recovery Mode)。
-
Image/kernel.img
-
Android 內核。
-
Image/resource.img
-
資源映像,內有內核開機圖片和內核設備樹信息(Device Tree Blob)。
-
Image/boot.img
-
Android 內核的內存啟動盤(initrd),是內核啟動后最先加載的根文件系統,包含重要的初始化動作,一般不需要改動。
-
Image/recovery.img
-
Android 急救模式的映像,內含內核和急救模式的根文件系統。
-
Image/system.img
-
對應于 Android 的 /system 分區,是以下的定制對象。
解包,就是提取 release_update.img 里的 update.img, 然后解壓出內含 package-file 所聲明的多個文件。打包,則是個逆過程,將 package-file 將所列的多個文件合成 update.img,加進 loader.img,最終生成 release_update.img 。
git clone https://github.com/TeeFirefly/rk2918_tools.git cd rk2918_tools make sudo cp afptool img_unpack img_maker mkkrnlimg /usr/local/bin -
解壓 release_update.img
$ cd /path/to/your/firmware/dir $ img_unpack AIO-3399ProJD4_Android8.1.0_HDMI_190509.img img rom version: 6.0.1 build time: 2016-10-27 14:58:18 chip: 33333043 checking md5sum....OK -
解壓 update.img
$ cd img $ afptool -unpack update.img update Check file...OK ------- UNPACK ------- package-file 0x00000800 0x000002AC Image/MiniLoaderAll.bin 0x00001000 0x0004394E Image/parameter.txt 0x00045000 0x00000368 Image/trust.img 0x00045800 0x00400000 Image/uboot.img 0x00445800 0x00400000 Image/misc.img 0x00845800 0x0000C000 Image/resource.img 0x00851800 0x00038800 Image/kernel.img 0x0088A000 0x012D2014 Image/boot.img 0x01B5C800 0x0017893C Image/recovery.img 0x01CD5800 0x00866B8C Image/system.img 0x0253C800 0x41A9110C Image/vendor.img 0x43FCE000 0x1206E0A0 Image/oem.img 0x5603C800 0x00058094 RESERVED 0x00000000 0x00000000 UnPack OK! -
查看 update 目錄下的文件樹
$ cd update/ $ tree . ├── Image │ ├── boot.img │ ├── kernel.img │ ├── MiniLoaderAll.bin │ ├── misc.img │ ├── oem.img │ ├── parameter.txt │ ├── recovery.img │ ├── resource.img │ ├── system.img │ ├── trust.img │ ├── uboot.img │ └── vendor.img ├── loader.img ├── package-file └── RESERVED 1 directory, 15 files 這樣,固件就解包成功了,下面就開始定制吧。
打包
首先要檢查一下 system.img 的大小,對照 parameter 文件的分區情況(可參考文檔Parameter 文件格式,作必要的大小調整。例如,parameter.txt 文件里的 system 分區大小,可以找到 CMDLINE 一行,然后找到 system 字符串:
0x00200000@0x000B0000(system) @ 前面就是分區的大小,單位是 512 字節,這樣該 system 分區的大小就是:
$ echo $(( 0x00200000 * 512 / 1024 / 1024))M 1024M 只要 system.img 的大小不超過 1024M,parameter 文件就不用更改。如果分區不用更改,可以直接用燒寫工具將新的 system.img 燒寫到開發板的 system 分區上做試驗。否則,需要制作新固件并燒寫后再行測試。以下是打包成統一固件 update.img 所需要的步驟:
-
合成 update.img :
# 當前的目錄仍然為 update/ ,內有 package-file, package-file 所列的文件均存在 # 將參數文件拷貝一份到 paramter, 因為 afptool 默認要用到 $ cp Image/parameter.txt parameter $ afptool -pack . ../update_new.img ------ PACKAGE ------ Add file: ./package-file Add file: ./Image/MiniLoaderAll.bin Add file: ./Image/parameter.txt Add file: ./Image/trust.img Add file: ./Image/uboot.img Add file: ./Image/misc.img Add file: ./Image/resource.img Add file: ./Image/kernel.img Add file: ./Image/boot.img Add file: ./Image/recovery.img Add file: ./Image/system.img Add file: ./Image/vendor.img Add file: ./Image/oem.img Add file: ./RESERVED Add CRC... ------ OK ------ Pack OK! -
合成 release_update.img :
$ img_maker -rk33 loader.img update_new.img release_update_new.img generate image... append md5sum... success! release_update_new.img 即為最終生成的可燒寫的統一固件文件。
固件的版本在哪設置
在 parameter 文件中找到下行并修改即可,注意版本號為數字,中間兩個點號不能省略。
FIRMWARE_VER: 8.1 -
嵌入式主板
+關注
關注
7文章
6102瀏覽量
36329 -
安卓
+關注
關注
5文章
2155瀏覽量
58742 -
Firefly
+關注
關注
2文章
543瀏覽量
8471
發布評論請先 登錄
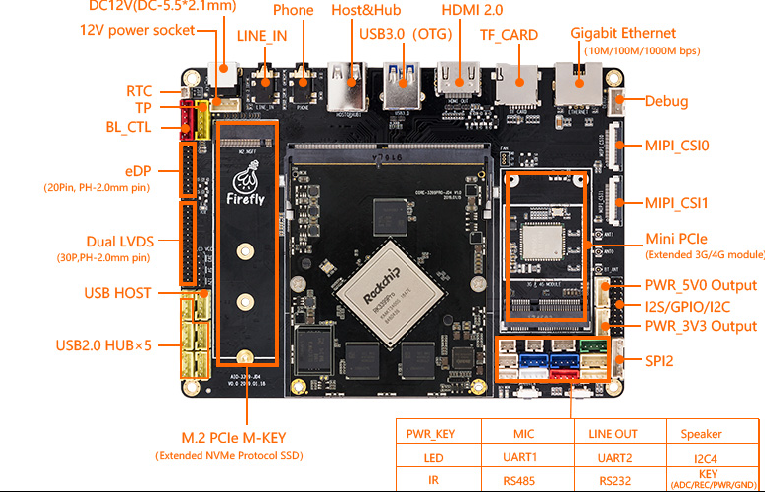
fireflyCORE-3399PRO主板JD4接口定義
fireflyCORE-3399PRO主板JD4燒寫固件簡介
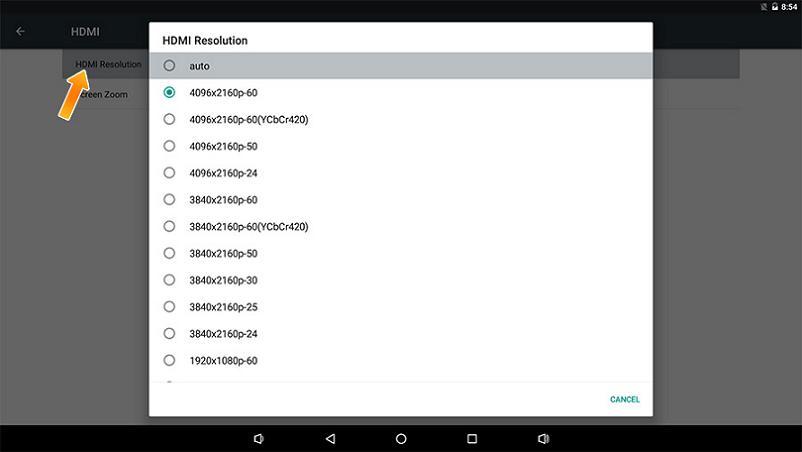
fireflyCORE-3399PRO主板JD4產品簡介
fireflyCORE-3399主板JD4--FAQs方案
fireflyCORE-3399主板JD4--Android工具簡介
fireflyCORE-3399主板JD4產品簡介
Core 3399Pro JD4工具AndroidTool Release v2.54文件包

Core 3399Pro JD4工具AndroidTool Release v2.63文件包

Core 3399Pro JD4 AndroidTool Release v2.71文件包

Core 3399Pro JD4 Android 8.1 SDK源碼

Core 3399Pro JD4 Android 9.0 SDK源碼

Core 3399Pro JD4固件Android 8.1固件

Core 3399Pro JD4 Android 9.0固件資料

Core 3399 JD4固件Android 7.1系統




















評論