概述
LSM303分支板結(jié)合了磁力計(jì)/羅盤模塊和三軸加速度計(jì),構(gòu)成了緊湊的導(dǎo)航子系統(tǒng)。 I2C接口與3.3v和5v處理器兼容,并且兩個(gè)引腳可以由其他I2C設(shè)備共享。結(jié)合L3GD20等3軸陀螺儀,您將擁有完整的IMU(慣性測量單元)所需的所有傳感器,以用于空中,陸地或海洋導(dǎo)航。
在本教程中,我們將向您展示如何將LSM303連接到Arduino,CircuitPython開發(fā)板或Blinka支持的設(shè)備,以及如何使用它來測量相對于地球磁場的方向以及在三個(gè)軸上的加速度。
新版LSM303AGR的一個(gè)重要功能是它包括一個(gè) STEMMA QT 連接器,無需焊接即可使用。 只需將STEMMA QT插入公頭連接線,即可將其連接到帶有母頭的面包板或開發(fā)板,重新參加比賽!您甚至可以使用STEMMA QT電纜將其與其他STEMMA QT分支連接起來
i》
工作原理:
傳感器組成硅晶片上的微機(jī)械結(jié)構(gòu)。有一些用于測量X,Y和Z軸上的加速度和磁場的結(jié)構(gòu)
加速度測量
這些結(jié)構(gòu)被多晶硅彈簧懸掛,當(dāng)它們在X,Y和/或Z軸上受加速度作用時(shí),它們可以偏轉(zhuǎn)。撓曲會(huì)導(dǎo)致固定板和連接到懸掛結(jié)構(gòu)的板之間的電容發(fā)生變化。每個(gè)軸上的電容變化都會(huì)轉(zhuǎn)換為與該軸上的加速度成比例的輸出電壓。
磁場測量
這些結(jié)構(gòu)與加速度計(jì)的結(jié)構(gòu)相似,但是用微觀線圈蝕刻。勵(lì)磁電流流經(jīng)線圈,由于磁場而產(chǎn)生的洛倫茲力使結(jié)構(gòu)發(fā)生偏轉(zhuǎn)。偏轉(zhuǎn)再次轉(zhuǎn)換為與該軸上的磁場強(qiáng)度成比例的輸出電壓。
我擁有哪個(gè)LSM303?
現(xiàn)在有兩個(gè)由Adafruit制造的LSM303突破口! Schnikes!它們的功能幾乎相同,但又有足夠的差異,以至于它們需要磁力計(jì)的不同驅(qū)動(dòng)器。為什么只有磁力計(jì)?好吧,我要告訴你一個(gè)小秘密:LSM303是兩個(gè)傳感器貼在同一個(gè)盒子里!
因?yàn)閮蓚€(gè)封裝都具有相同的加速度傳感器,且寄存器布局相同,所以我們可以使用兩者都使用相同的加速度計(jì)驅(qū)動(dòng)器。磁力計(jì)盡管都具有相同的I2C地址(0x1E),但寄存器布局卻完全不同,這意味著它們各自需要自己的驅(qū)動(dòng)程序庫。
因此,您將需要知道你有哪個(gè)版本。這是區(qū)分兩個(gè) Adafruit 突破的一種高度科學(xué)的方法:
LSM303AGR是黑色的,說“ LSM303AGR”不同于
LSM303DLHC是藍(lán)色并且說“ LSM303DLHC”
復(fù)雜,我知道,但我相信您。下面概述了更多細(xì)微的差異
LSM303AGR
adafruit塊上的新孩子是LSM303AGR。這是對LSM303系列的更新,該系列體積更小,內(nèi)部裝有不同的磁力計(jì)芯片。我們的突破如下:
除了體積更小,更容易丟失籌碼外,還有其他一些區(qū)別。芯片本身暴露了磁力計(jì)(INTM)的中斷引腳(也許是內(nèi)置的新型磁力計(jì)傳感器的功能?)以及加速度計(jì)和磁力計(jì)的芯片選擇引腳( CSA 和 CSM )。
兩者之間的另一個(gè)令人興奮的區(qū)別是增加了兩個(gè) STEMMA QT 連接器,每個(gè)連接器的一側(cè)板。這樣一來,您無需焊接即可使用該傳感器,并且可以與其他STEMMA QT傳感器鏈接。
請注意,雖然LSM303AGR分支具有CS引腳,但它僅支持3線SPI,而我們無法使用它。喜歡冒險(xiǎn)的人可以參考數(shù)據(jù)表并嘗試一下!歡迎PR;)
LSM303/LSM303DLHC
AdafruitLSM303分支使用LSM303 DLHC ,看起來像這樣:
》
與LSM303AGR相比,您可以看到傳感器本身(中間的黑色矩形)實(shí)際上更大。此外,引腳的順序不同,并且LSM303DLH公開了 DRDY (數(shù)據(jù)就緒)引腳。
插腳

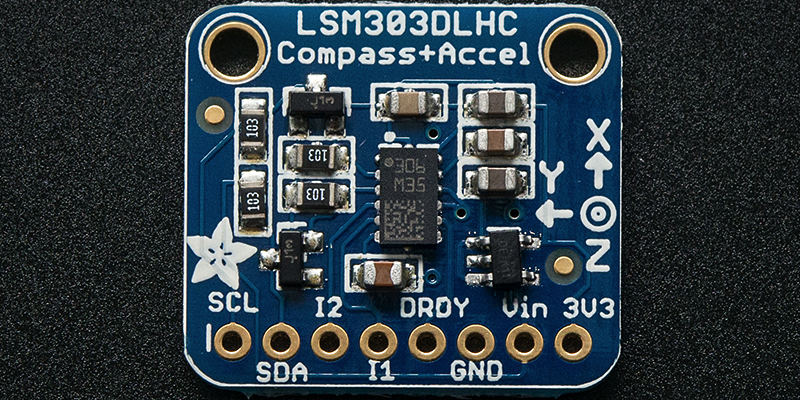
電源引腳
Vin -這是電源引腳。由于傳感器芯片使用的是3.3 VDC,因此我們在板載了一個(gè)穩(wěn)壓器,該穩(wěn)壓器將采用3-5VDC的電壓并將其安全地向下轉(zhuǎn)換。要為電路板供電,請為其提供與微控制器邏輯電平相同的功率-例如,對于像Arduino這樣的5V微控制器,請使用5V
3Vo -這是穩(wěn)壓器的3.3V輸出,如果您愿意,可以從中獲得100mA的電流。
GND -電源和邏輯的公共接地
I2C邏輯引腳
SCL -I2C時(shí)鐘引腳,連接到微控制器的I2C時(shí)鐘線。該引腳經(jīng)過電平轉(zhuǎn)換,因此您可以使用3-5V邏輯,并且該引腳上具有 10K上拉。
SDA -I2C數(shù)據(jù)引腳,連接到微控制器的I2C數(shù)據(jù)線。該引腳經(jīng)過電平轉(zhuǎn)換,因此您可以使用3-5V邏輯,并且該引腳上具有 10K上拉。
STEMMA QT- ,這些連接器允許您可以連接到具有 STEMMA QT 連接器的開發(fā)板或具有各種關(guān)聯(lián)附件的其他東西的連接器
其他通用引腳
IA1 -加速度計(jì)的第一個(gè)中斷引腳。僅限3V邏輯
IA2-加速度計(jì)的第二個(gè)中斷引腳。僅3V邏輯
LSM303AGR僅限
INTM -磁力計(jì)的中斷引腳。僅限3V邏輯
CSA-加速度計(jì)的CS引腳。僅限3V邏輯
CSM-磁力計(jì)的CS引腳。僅限3V邏輯
請注意,雖然LSM303AGR突破口具有CS引腳,僅支持我們無法使用的3線SPI。喜歡冒險(xiǎn)的人可以參考數(shù)據(jù)表并嘗試一下!歡迎PR;)
僅適用于LSM303DLH
DRDY -這是數(shù)據(jù)就緒引腳。僅限3V邏輯
程序集
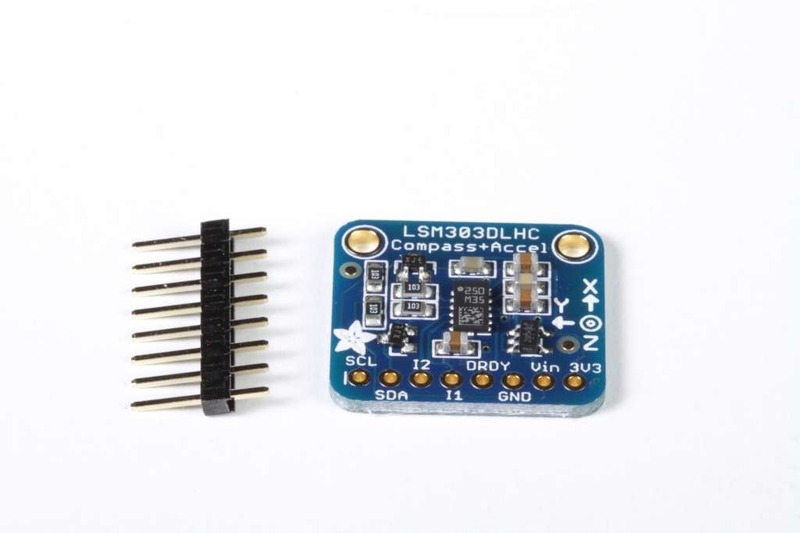
電路板組裝:所有表面安裝組件都已預(yù)先焊接到電路板上。您可以將連接直接焊接到板上,也可以安裝標(biāo)題欄(已提供)以簡化在面包板上的使用。

放置頁眉,如有必要,將頁眉切成一定長度,然后將長針向下插入面包板。
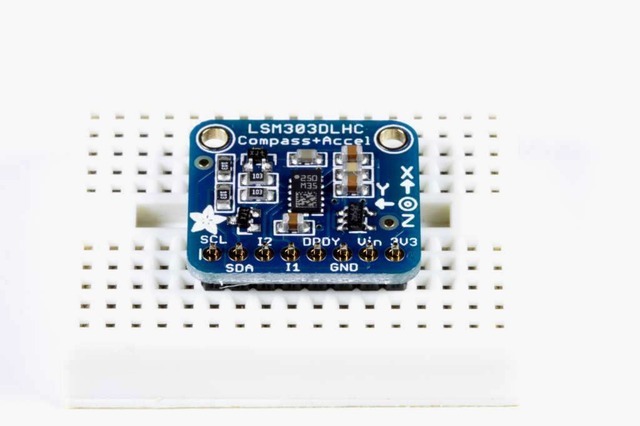
放置板子將板子放在排針頂部。支撐必要的背面,以便在焊接之前將電路板弄平。
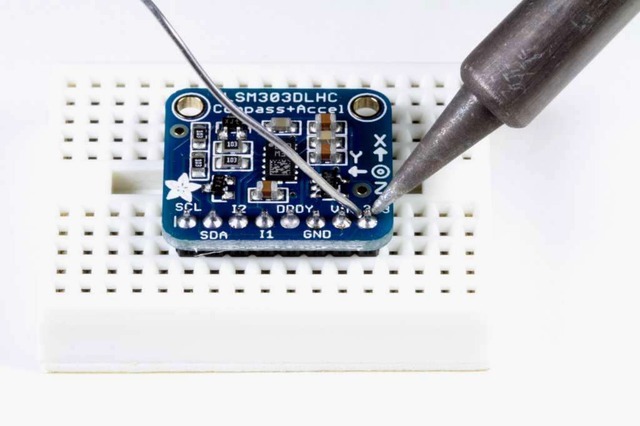
然后焊接!焊接每個(gè)引腳以確保良好的電氣連接。
如果您是焊接新手,請查閱我們的出色焊接指南。
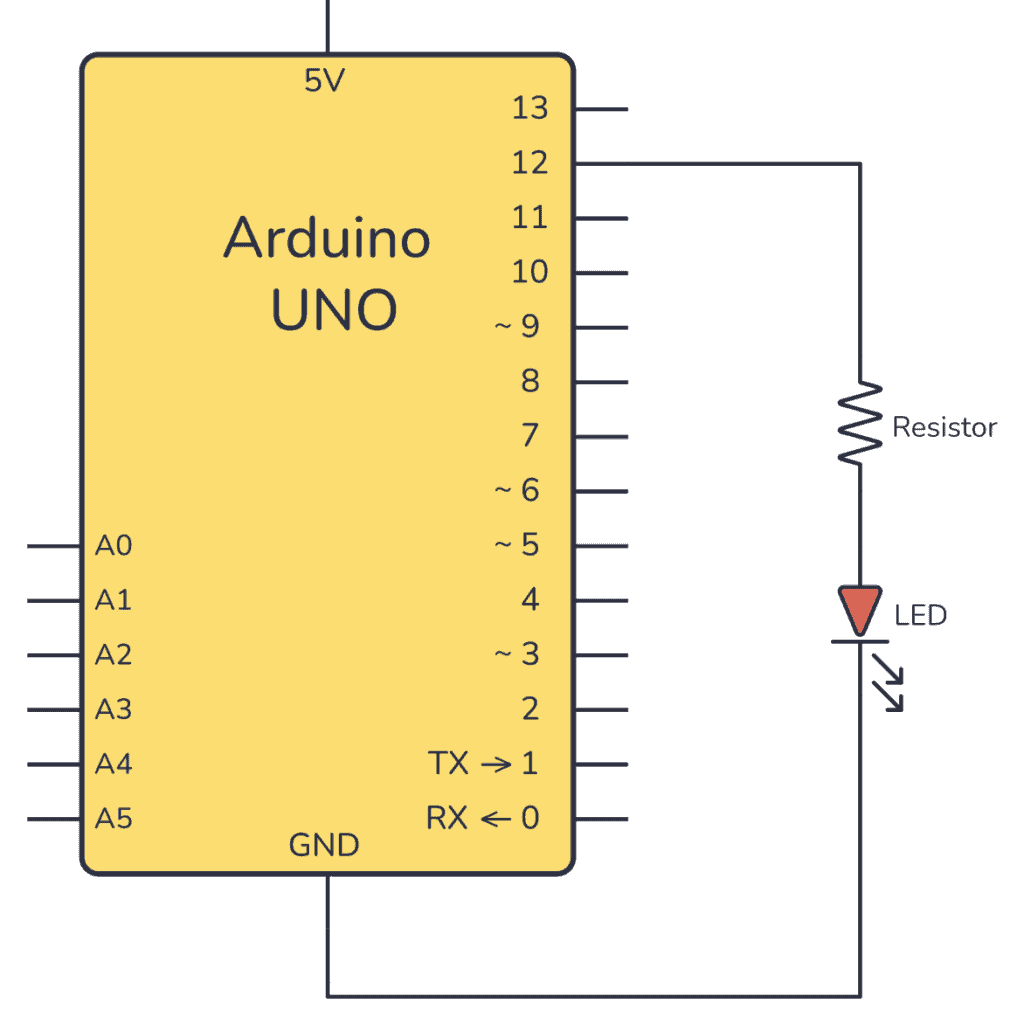
Arduino
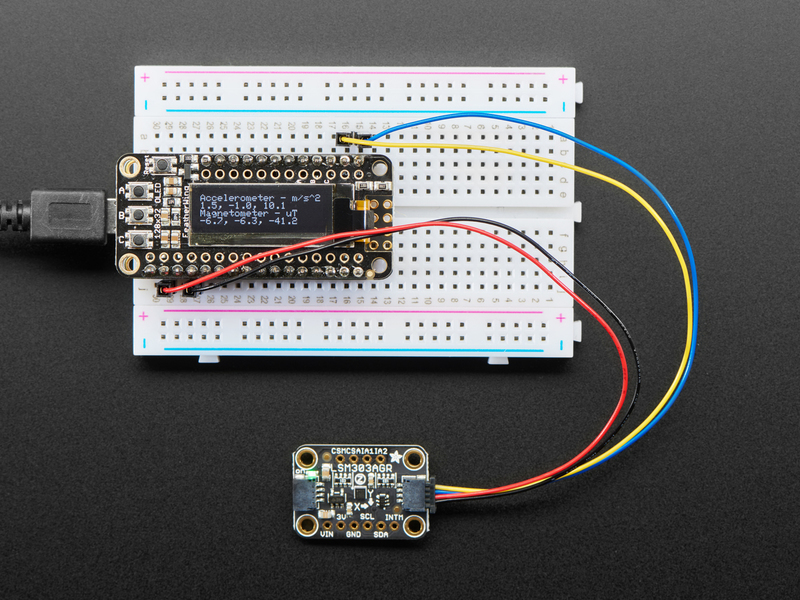
Arduino接線
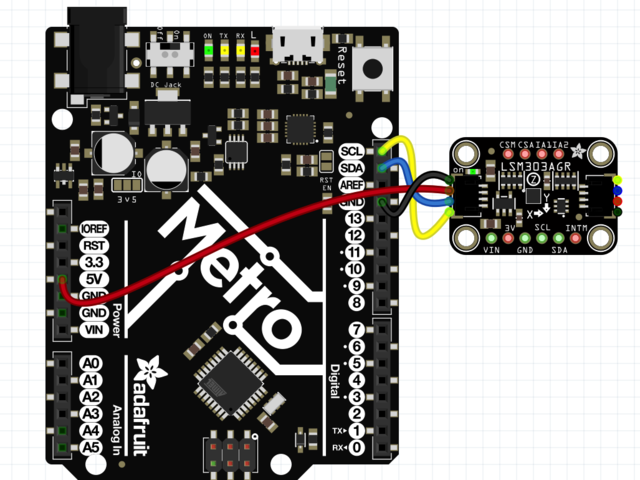
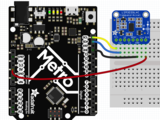
Connect 板載VCC(紅線)5V Arduino板(Uno等),則將strong》改為 Arduino 5V 。如果您的板為 3V, 相反。
連接板子 GND(黑線)到 Arduino GND
將板 SCL(黃線)連接到 Arduino SCL
連接板 SDA(藍(lán)線)到 Arduino SDA
ul》
安裝庫
要開始使用LSM303,您需要安裝加速度計(jì)庫,并板的磁力計(jì)庫。另外,您將需要Adafruit_Sensor庫以及Adafruit_BusIO庫,該庫允許它以與其他類似傳感器一致的方式返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)。可以使用Arduino IDE中的庫管理器安裝所有庫:
在繼續(xù)之前,請確保您知道傳感器的版本,
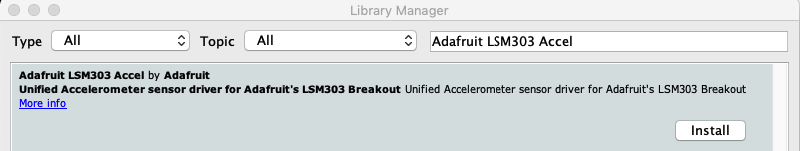
安裝加速計(jì)庫
點(diǎn)擊管理庫。.. 菜單項(xiàng),搜索 Adafruit LSM303 Accel ,然后選擇 Adafruit_LSM303_Accel 庫:
安裝磁力計(jì)庫
最后,您需要在LSM303中安裝磁力計(jì)庫。確保下載適用于您的分組討論板的正確驅(qū)動(dòng)程序。
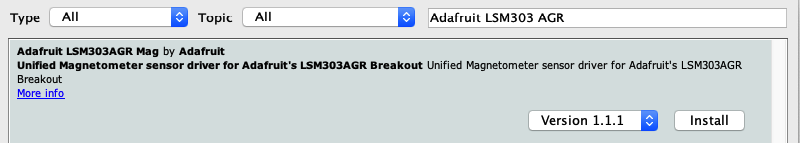
LSM303AGR
在庫管理器中搜索 Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag 庫:
LSM303/LSM303DLHC
在庫管理器中搜索 Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag 庫:
安裝幫助程序庫
對 Adafruit BusIO 庫執(zhí)行相同的過程:
最后,對 Adafruit Unified Sensor 庫:

加速度計(jì)演示
第一個(gè)演示將向您展示如何獲得加速度計(jì)最有效的讀數(shù):測量加速度!
打開文件-》示例-》 Adafruit LSM303 Accel -》 accelsensor 并上傳到與傳感器連接的Arduino。
將草圖上傳到板上并打開Serial Monitor(工具-》 Serial Monitor )以 115200波特。您應(yīng)該看到啟動(dòng)時(shí)打印的當(dāng)前配置設(shè)置的值,然后是與X,Y和Z軸類似的加速度讀數(shù):

Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified 傳感器Adafruit_LSM303_Accel庫中的類報(bào)告X,Y和Z軸加速度計(jì)的讀數(shù)直接以米/秒為平方。庫中的accelsensor示例代碼從傳感器讀取并將加速度讀數(shù)打印到串行監(jiān)視器中。
在靜止?fàn)顟B(tài)下,傳感器不應(yīng)報(bào)告任何加速度,除非是由于重力(大約9.8米/秒平方)。通過計(jì)算重力矢量相對于X,Y和Z軸的角度,該設(shè)備可以用作傾角儀。
基本磁力計(jì)讀數(shù)
第一個(gè)演示將向您展示如何獲得加速度計(jì)最有效的讀數(shù):測量加速度!
LSM303AGR
打開文件-》示例-》 Adafruit LSM303AGR Mag -》磁傳感器并上傳到您的Arduino接線端
LSM303/LSM303DLH
打開文件-》示例-》 Adafruit LSM303DLH Mag -》磁傳感器,然后
將草圖上傳到您的電路板上,并以 115200波特打開串行監(jiān)視器(工具-》串行監(jiān)視器)。您應(yīng)該看到啟動(dòng)時(shí)打印的當(dāng)前配置設(shè)置的值,然后是X,Y和Z軸的磁場讀數(shù),類似于:

磁力儀庫中的傳感器類報(bào)告X,Y和Z軸磁力儀讀數(shù)直接在微型Teslas中。 magsensor 示例代碼從傳感器讀取并將微型特斯拉讀數(shù)打印到串行監(jiān)視器。
在沒有任何強(qiáng)磁場的情況下,傳感器讀數(shù)應(yīng)反映地球的磁場(介于20到60微特拉斯之間)。當(dāng)傳感器保持水平時(shí),通過計(jì)算磁場相對于X和Y軸的角度,該設(shè)備可用作指南針。
計(jì)算指南針航向
要將microTesla讀數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換為0-360度指南針航向,我們可以使用atan2()函數(shù)來計(jì)算由Y和X軸讀數(shù)定義的向量的角度。結(jié)果將以弧度為單位,因此我們將其乘以180度并除以Pi以將其轉(zhuǎn)換為度。
LSM303AGR
打開文件-》示例-》 Adafruit LSM303AGR Mag -》羅盤,并上傳到與傳感器連接的Arduino。
LSM303/LSM303DLH
打開文件-》示例-》 Adafruit LSM303DLH Mag -》羅盤,并通過傳感器連接到Arduino。
將草圖上傳到板上并打開串行監(jiān)視器(工具-》串行監(jiān)視器),位于 115200波特。您將看到航向計(jì)算打印到串行監(jiān)視器。如果在傳感器運(yùn)行時(shí)旋轉(zhuǎn)傳感器,則會(huì)看到航向更改:

加速度計(jì)演示代碼
下載:Project Zip 或 accelsensor.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified accel = Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified(54321);
void displaySensorDetails(void) {
sensor_t sensor;
accel.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.print(“Sensor: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print(“Driver Ver: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print(“Unique ID: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print(“Max Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(“ m/s^2”);
Serial.print(“Min Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(“ m/s^2”);
Serial.print(“Resolution: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(“ m/s^2”);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
delay(500);
}
void setup(void) {
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial)
; // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(“Accelerometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!accel.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the ADXL345 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
accel.setRange(LSM303_RANGE_4G);
Serial.print(“Range set to: ”);
lsm303_accel_range_t new_range = accel.getRange();
switch (new_range) {
case LSM303_RANGE_2G:
Serial.println(“+- 2G”);
break;
case LSM303_RANGE_4G:
Serial.println(“+- 4G”);
break;
case LSM303_RANGE_8G:
Serial.println(“+- 8G”);
break;
case LSM303_RANGE_16G:
Serial.println(“+- 16G”);
break;
}
accel.setMode(LSM303_MODE_NORMAL);
Serial.print(“Mode set to: ”);
lsm303_accel_mode_t new_mode = accel.getMode();
switch (new_mode) {
case LSM303_MODE_NORMAL:
Serial.println(“Normal”);
break;
case LSM303_MODE_LOW_POWER:
Serial.println(“Low Power”);
break;
case LSM303_MODE_HIGH_RESOLUTION:
Serial.println(“High Resolution”);
break;
}
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
accel.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (acceleration is measured in m/s^2) */
Serial.print(“X: ”);
Serial.print(event.acceleration.x);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Y: ”);
Serial.print(event.acceleration.y);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Z: ”);
Serial.print(event.acceleration.z);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.println(“m/s^2”);
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
}
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified accel = Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified(54321);
void displaySensorDetails(void) {
sensor_t sensor;
accel.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.print(“Sensor: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print(“Driver Ver: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print(“Unique ID: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print(“Max Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(“ m/s^2”);
Serial.print(“Min Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(“ m/s^2”);
Serial.print(“Resolution: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(“ m/s^2”);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
delay(500);
}
void setup(void) {
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial)
; // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(“Accelerometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!accel.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the ADXL345 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
accel.setRange(LSM303_RANGE_4G);
Serial.print(“Range set to: ”);
lsm303_accel_range_t new_range = accel.getRange();
switch (new_range) {
case LSM303_RANGE_2G:
Serial.println(“+- 2G”);
break;
case LSM303_RANGE_4G:
Serial.println(“+- 4G”);
break;
case LSM303_RANGE_8G:
Serial.println(“+- 8G”);
break;
case LSM303_RANGE_16G:
Serial.println(“+- 16G”);
break;
}
accel.setMode(LSM303_MODE_NORMAL);
Serial.print(“Mode set to: ”);
lsm303_accel_mode_t new_mode = accel.getMode();
switch (new_mode) {
case LSM303_MODE_NORMAL:
Serial.println(“Normal”);
break;
case LSM303_MODE_LOW_POWER:
Serial.println(“Low Power”);
break;
case LSM303_MODE_HIGH_RESOLUTION:
Serial.println(“High Resolution”);
break;
}
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
accel.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (acceleration is measured in m/s^2) */
Serial.print(“X: ”);
Serial.print(event.acceleration.x);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Y: ”);
Serial.print(event.acceleration.y);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Z: ”);
Serial.print(event.acceleration.z);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.println(“m/s^2”);
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
}
LSM303AGR磁力計(jì)和指南針代碼
下載:Project Zip 或 magsensor.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified(12345);
void displaySensorDetails(void) {
sensor_t sensor;
mag.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.print(“Sensor: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print(“Driver Ver: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print(“Unique ID: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print(“Max Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Min Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Resolution: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
delay(500);
}
void setup(void) {
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial)
; // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Enable auto-gain */
mag.enableAutoRange(true);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303AGR detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT)) */
Serial.print(“X: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.x);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Y: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.y);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Z: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.z);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.println(“uT”);
/* Note: You can also get the raw (non unified values) for */
/* the last data sample as follows. The .getEvent call populates */
/* the raw values used below. */
// Serial.print(“X Raw: ”); Serial.print(mag.raw.x); Serial.print(“ ”);
// Serial.print(“Y Raw: ”); Serial.print(mag.raw.y); Serial.print(“ ”);
// Serial.print(“Z Raw: ”); Serial.print(mag.raw.z); Serial.println(“”);
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
}
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified(12345);
void displaySensorDetails(void) {
sensor_t sensor;
mag.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.print(“Sensor: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print(“Driver Ver: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print(“Unique ID: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print(“Max Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Min Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Resolution: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
delay(500);
}
void setup(void) {
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial)
; // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Enable auto-gain */
mag.enableAutoRange(true);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303AGR detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT)) */
Serial.print(“X: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.x);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Y: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.y);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Z: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.z);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.println(“uT”);
/* Note: You can also get the raw (non unified values) for */
/* the last data sample as follows. The .getEvent call populates */
/* the raw values used below. */
// Serial.print(“X Raw: ”); Serial.print(mag.raw.x); Serial.print(“ ”);
// Serial.print(“Y Raw: ”); Serial.print(mag.raw.y); Serial.print(“ ”);
// Serial.print(“Z Raw: ”); Serial.print(mag.raw.z); Serial.println(“”);
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
}
下載:Project Zip 或 compass.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified(12345);
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”); Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if(!mag.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while(1);
}
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
float Pi = 3.14159;
// Calculate the angle of the vector y,x
float heading = (atan2(event.magnetic.y,event.magnetic.x) * 180) / Pi;
// Normalize to 0-360
if (heading 《 0)
{
heading = 360 + heading;
}
Serial.print(“Compass Heading: ”);
Serial.println(heading);
delay(500);
}
#include
#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified(12345);
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”); Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if(!mag.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while(1);
}
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
float Pi = 3.14159;
// Calculate the angle of the vector y,x
float heading = (atan2(event.magnetic.y,event.magnetic.x) * 180) / Pi;
// Normalize to 0-360
if (heading 《 0)
{
heading = 360 + heading;
}
Serial.print(“Compass Heading: ”);
Serial.println(heading);
delay(500);
}
LSM303/LSM303DLH磁力計(jì)和指南針代碼
下載:Project Zip 或 magsensor.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified(12345);
void displaySensorDetails(void) {
sensor_t sensor;
mag.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.print(“Sensor: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print(“Driver Ver: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print(“Unique ID: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print(“Max Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Min Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Resolution: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
delay(500);
}
void setup(void) {
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial)
; // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Enable auto-gain */
mag.enableAutoRange(true);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT)) */
Serial.print(“X: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.x);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Y: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.y);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Z: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.z);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.println(“uT”);
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
} #include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified(12345);
void displaySensorDetails(void) {
sensor_t sensor;
mag.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.print(“Sensor: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print(“Driver Ver: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print(“Unique ID: ”);
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print(“Max Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Min Value: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.print(“Resolution: ”);
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(“ uT”);
Serial.println(“------------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
delay(500);
}
void setup(void) {
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial)
; // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Enable auto-gain */
mag.enableAutoRange(true);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT)) */
Serial.print(“X: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.x);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Y: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.y);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(“Z: ”);
Serial.print(event.magnetic.z);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.println(“uT”);
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
}
下載:Project Zip 或 compass.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified(12345);
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
float Pi = 3.14159;
// Calculate the angle of the vector y,x
float heading = (atan2(event.magnetic.y, event.magnetic.x) * 180) / Pi;
// Normalize to 0-360
if (heading 《 0) {
heading = 360 + heading;
}
Serial.print(“Compass Heading: ”);
Serial.println(heading);
delay(500);
} #include
#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified(12345);
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
float Pi = 3.14159;
// Calculate the angle of the vector y,x
float heading = (atan2(event.magnetic.y, event.magnetic.x) * 180) / Pi;
// Normalize to 0-360
if (heading 《 0) {
heading = 360 + heading;
}
Serial.print(“Compass Heading: ”);
Serial.println(heading);
delay(500);
}
Adafruit_LSM303DLHC庫已存檔
較早的LSM303DLH分支的Adafruit_LSM303DLHC庫已歸檔,并已由上面使用的Adafruit_LSM303_Accel和Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag庫替換。我們建議您切換到較新的庫,因?yàn)椴恢С峙f的庫或添加了功能。
如果您仍然希望使用舊的庫,則可以單擊下面的按鈕轉(zhuǎn)到存儲(chǔ)庫或以ZIP格式下載。
存檔的Adafruit_LSMDLHC存儲(chǔ)庫
下載Adafruit_LSM303DLHC
Python和CircuitPython
很容易將LSM303傳感器與CircuitPython和Adafruit CircuitPython LSM303加速度計(jì)以及Adafruit CircuitPython LSM303DLH磁力計(jì)庫一起使用。這些庫可讓您輕松編寫可從傳感器讀取加速度和磁力計(jì)值的Python代碼。
由于Adafruit_Blinka,您可以將此傳感器與任何CircuitPython微控制器板或具有GPIO和Python的計(jì)算機(jī)一起使用,我們的CircuitPython-for-Python兼容性庫。
在繼續(xù)之前,請確保您知道傳感器的版本
CircuitPython微控制器布線
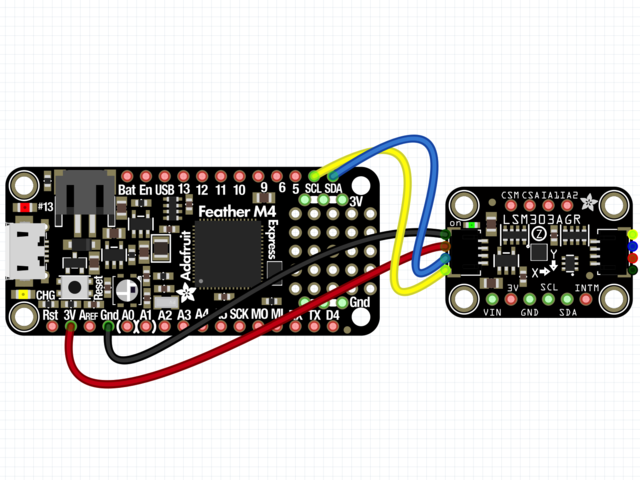
首先連接LSM303使用I2C連接完全按照Arduino的前幾頁中的說明連接到板上。以下是使用I2C將Feather M0連接到傳感器的示例:
 li》
li》
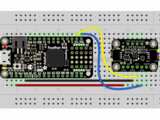
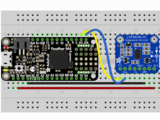
板3V 到傳感器VIN(紅線)
板GND 到傳感器GND (黑線)
板SCL 到傳感器SCL(黃線)
板SDA 到傳感器SDA(藍(lán)線)
Python計(jì)算機(jī)接線
因?yàn)橛袔资畟€(gè) 您可以使用的Linux計(jì)算機(jī)/主板,我們將顯示Raspberry Pi的接線。對于其他平臺(tái),請?jiān)L問Linux上的CircuitPython指南,以了解您的平臺(tái)是否受支持。
以下是與I2C相連的Raspberry Pi:
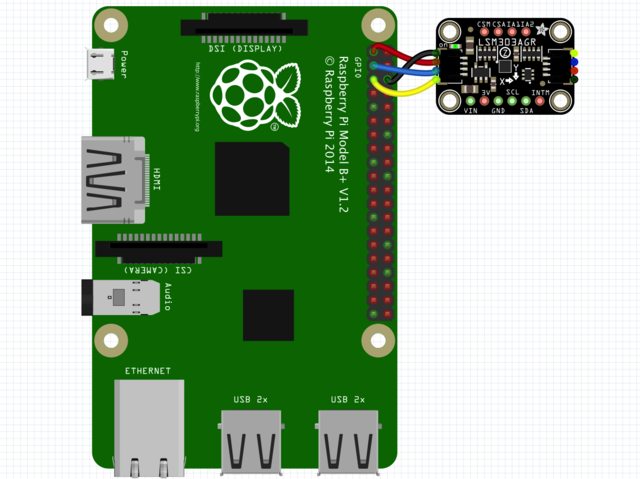



Pi 3V 到傳感器VIN(紅線)
Pi GND 到傳感器GND(黑線)
Pi SCL 到傳感器SCL(黃線)
Pi SDA 到傳感器SDA(藍(lán)線)
》
CircuitPython安裝LSM303庫
接下來,您需要安裝Adafruit CircuitPython LSM303加速度計(jì)和Adafruit CircuitPython LSM303AGR或Adafruit CircuitPython LSM303DLH magn etometer(取決于您擁有的LSM303)庫。
首先請確保您正在為板運(yùn)行最新版本的Adafruit CircuitPython。
下一步,您需要安裝使用硬件所需的庫-請仔細(xì)按照以下步驟從Adafruit的CircuitPython庫捆綁包中查找和安裝這些庫。我們的簡介指南上有一個(gè)很棒的頁面,介紹如何為快速和非表達(dá)板安裝庫包。
請記住非表達(dá)板,例如,您需要從束中手動(dòng)安裝必要的庫:
adafruit_lsm303agr_mag.mpy或adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag.mpy
adafruit_lsm303_accel.mpy
adafruit_bus_device
adafruit_register
在繼續(xù)之前,請確保您董事會(huì)的lib文件夾或根文件系統(tǒng)具有 adafruit_lsm303agr_mag .mpy或adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag.mpy, adafruit_lsm303_accel.mpy,adafruit_register,和 adafruit_bus_device 文件和文件夾
下一步連接到開發(fā)板的串行REPL,因此您位于CircuitPython的》》》 提示符下。
LSM303 Li的Python安裝braries
您需要安裝 Adafruit_Blinka 庫,該庫在Python中提供了CircuitPython支持。這可能還需要在您的平臺(tái)上啟用I2C并驗(yàn)證您正在運(yùn)行Python3。由于每個(gè)平臺(tái)都有所不同,并且Linux經(jīng)常更改,請?jiān)L問Linux上的CircuitPython指南以準(zhǔn)備好您的計(jì)算機(jī)!
完成后,從命令行運(yùn)行以下命令:
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-lsm303-accel
然后為您的LSM303版本安裝磁力計(jì)庫。 :
LSM303AGR:
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-lsm303agr-mag
LSM303DLH:
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-lsm303dlh-mag
如果您的默認(rèn)Python是版本3,則可能需要運(yùn)行“ pip”。只要確保您不嘗試在Python 2.x上使用CircuitPython,就不支持它!
CircuitPython和Python用法
這些示例使用adafruit_lsm303agr_mag庫。如果您擁有l(wèi)sm303dlh,則必須更改代碼以使用adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag庫
為演示傳感器的用法,我們將對其進(jìn)行初始化并讀取
運(yùn)行以下代碼以導(dǎo)入必要的模塊,并初始化與傳感器的I2C連接:
》 LSM303AGR
下載:文件
復(fù)制代碼
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303agr_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303agr_mag.LSM303AGR_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c) import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303agr_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303agr_mag.LSM303AGR_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)

LSM303DLH
下載:文件
復(fù)制代碼
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag.LSM303DLH_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c) import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag.LSM303DLH_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)

現(xiàn)在,您可以使用以下屬性之一從傳感器讀取值:
加速度計(jì)
加速度-X,Y, Z加速度值,單位為米每秒每秒(m/s ^ 2)。
磁力計(jì)
磁性-微型特斯拉中X,Y,Z磁力計(jì)讀數(shù)的三元組。
下載:文件
復(fù)制代碼
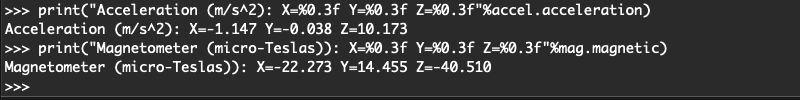
print(“Acceleration (m/s^2): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%accel.acceleration)
print(“Magnetometer (micro-Teslas)): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%mag.magnetic) print(“Acceleration (m/s^2): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%accel.acceleration)
print(“Magnetometer (micro-Teslas)): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%mag.magnetic)
點(diǎn)擊檢測
LSM303的加速度計(jì)還可以檢測單次或兩次點(diǎn)擊!
set_tap 方法可用于設(shè)置要檢測的抽頭數(shù)(1或2),以及設(shè)置抽頭閾值。閾值越低,加速度計(jì)對檢測抽頭越敏感。您可能必須使用這個(gè)數(shù)字來找到適合您需求的值
在這里,我們還將使用 range 屬性將加速度計(jì)的測量范圍更改為 +/- 8G
下載:文件
復(fù)制代碼
accel.range = adafruit_lsm303_accel.Range.RANGE_8G
accel.set_tap(1, 30)
while True:
if accel.tapped:
print(“Tapped! ”) accel.range = adafruit_lsm303_accel.Range.RANGE_8G
accel.set_tap(1, 30)
while True:
if accel.tapped:
print(“Tapped! ”)
當(dāng)您在REPL中鍵入上面的代碼并給傳感器一個(gè)良好的固定點(diǎn)擊時(shí),您應(yīng)該會(huì)看到類似于輸出如下。如果看不到“已點(diǎn)擊!” 消息,則可能需要調(diào)整閾值。

As您可以從上面看到,tapped屬性將在一個(gè)單擊事件的多個(gè)周期內(nèi)返回True。您必須在代碼中對此進(jìn)行說明。不幸的是,這似乎只是傳感器的一個(gè)怪癖
這是將LSM303與CircuitPython一起使用的全部內(nèi)容。
下面是一個(gè)每秒讀取傳感器并打印其值的完整示例。將其另存為板上的 code.py 并打開REPL以查看輸出。
點(diǎn)擊檢測代碼
下載:Project Zip 或 tap_detection.py | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)
accel.range = adafruit_lsm303_accel.Range.RANGE_8G
accel.set_tap(1, 30)
while True:
if accel.tapped:
print(“Tapped! ”)
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)
accel.range = adafruit_lsm303_accel.Range.RANGE_8G
accel.set_tap(1, 30)
while True:
if accel.tapped:
print(“Tapped! ”)
LSM303AGR示例代碼
下載:Project Zip 或 lsm303agr_combined .py | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
from time import sleep
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303agr_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303agr_mag.LSM303AGR_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)
while True:
print(“Acceleration (m/s^2): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%accel.acceleration)
print(“Magnetometer (micro-Teslas)): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%mag.magnetic)
print(“”)
sleep(0.5)
from time import sleep
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303agr_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303agr_mag.LSM303AGR_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)
while True:
print(“Acceleration (m/s^2): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%accel.acceleration)
print(“Magnetometer (micro-Teslas)): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%mag.magnetic)
print(“”)
sleep(0.5)
LSM303DLH示例代碼
下載:Project Zip 或 lsm303dlh_combined.py | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
from time import sleep
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag.LSM303DLH_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)
while True:
print(“Acceleration (m/s^2): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%accel.acceleration)
print(“Magnetometer (micro-Teslas)): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%mag.magnetic)
print(“”)
sleep(0.5)
from time import sleep
import board
import busio
import adafruit_lsm303_accel
import adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
mag = adafruit_lsm303dlh_mag.LSM303DLH_Mag(i2c)
accel = adafruit_lsm303_accel.LSM303_Accel(i2c)
while True:
print(“Acceleration (m/s^2): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%accel.acceleration)
print(“Magnetometer (micro-Teslas)): X=%0.3f Y=%0.3f Z=%0.3f”%mag.magnetic)
print(“”)
sleep(0.5)
Adafruit_CircuitPython_LSM303庫已存檔
用于較早的LSM303DLH突破的Adafruit_CircuitPython_LSM303庫已存檔,并已由上面使用的Adafruit_CircuitPython_LSM303_Accel和Adafruit_CircuitPython_LSM303DLH_Mag庫替換。我們建議您切換到較新的庫,因?yàn)椴恢С峙f的庫或添加了功能。
如果您仍然希望使用舊的庫,則可以單擊下面的按鈕轉(zhuǎn)到存儲(chǔ)庫或以ZIP格式下載。
已存檔的Adafruit_CircuitPython_LSM303存儲(chǔ)庫
下載Adafruit_CircuitPython_LSM303
校準(zhǔn)
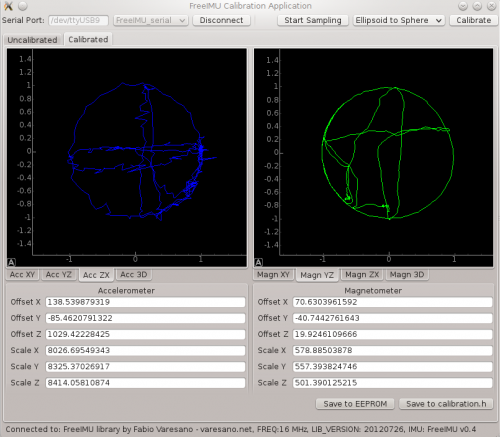
(Fabio Varesano的校準(zhǔn)GUI圖像)
LSM303芯片在出廠時(shí)已校準(zhǔn)到足以滿足多種目的的精確度。但是對于IMU等超臨界應(yīng)用程序,您可能需要進(jìn)一步校準(zhǔn)設(shè)備。
最終校準(zhǔn):
要進(jìn)行超高精度加速度計(jì)校準(zhǔn),您將需要查看已故的Fabio Varesano提供的FreeIMU磁力計(jì)和加速度計(jì)GUI。上面的圖像(來自Fabio網(wǎng)站)顯示了傳感器讀數(shù)的圖形表示以及根據(jù)原始數(shù)據(jù)計(jì)算出的校準(zhǔn)偏差。
此全面的校準(zhǔn)套件旨在在PC上運(yùn)行。它太大了,無法在像Arduino這樣的微控制器上運(yùn)行,但是它產(chǎn)生的校準(zhǔn)偏差可以并入您的Arduino草圖中,以提高準(zhǔn)確性。
簡化的校準(zhǔn):
可以在Arduino上完成仍然產(chǎn)生良好結(jié)果的更簡單方法。該方法使用一個(gè)簡單的草圖記錄所有3軸上的最小和最大讀數(shù)。運(yùn)行草圖時(shí),在所有三個(gè)軸上緩慢旋轉(zhuǎn)LSM303模塊多次。目的是記錄每個(gè)軸的絕對最小值和最大值,因此旋轉(zhuǎn)得越多,捕獲絕對峰值的可能性就越大。
請確保將傳感器緩慢繞其中心旋轉(zhuǎn),以使加速度計(jì)讀數(shù)將僅表示由于重力引起的加速度,而不表示由于運(yùn)動(dòng)引起的傳感器線性加速度。稍后,草圖輸出將穩(wěn)定。顯示的值將是每個(gè)軸的最小和最大范圍,可用于重新縮放傳感器的輸出。
通過校準(zhǔn)草圖獲得的值可用于執(zhí)行在三個(gè)軸上分別進(jìn)行兩點(diǎn)校準(zhǔn):兩點(diǎn)校準(zhǔn)
校準(zhǔn)草圖:
LSM303AGR
下載:Project Zip 或 calibration.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified(12345);
float MagMinX, MagMaxX;
float MagMinY, MagMaxY;
float MagMinZ, MagMaxZ;
long lastDisplayTime;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“LSM303 Calibration”); Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the magnetometer */
if(!mag.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while(1);
}
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t magEvent;
mag.getEvent(&magEvent);
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 《 MagMinX) MagMinX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 》 MagMaxX) MagMaxX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 《 MagMinY) MagMinY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 》 MagMaxY) MagMaxY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 《 MagMinZ) MagMinZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 》 MagMaxZ) MagMaxZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if ((millis() - lastDisplayTime) 》 1000) // display once/second
{
Serial.print(“Mag Minimums: ”); Serial.print(MagMinX); Serial.print(“ ”);Serial.print(MagMinY); Serial.print(“ ”); Serial.print(MagMinZ); Serial.println();
Serial.print(“Mag Maximums: ”); Serial.print(MagMaxX); Serial.print(“ ”);Serial.print(MagMaxY); Serial.print(“ ”); Serial.print(MagMaxZ); Serial.println(); Serial.println();
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
}
#include
#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303AGR_Mag_Unified(12345);
float MagMinX, MagMaxX;
float MagMinY, MagMaxY;
float MagMinZ, MagMaxZ;
long lastDisplayTime;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“LSM303 Calibration”); Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the magnetometer */
if(!mag.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while(1);
}
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t magEvent;
mag.getEvent(&magEvent);
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 《 MagMinX) MagMinX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 》 MagMaxX) MagMaxX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 《 MagMinY) MagMinY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 》 MagMaxY) MagMaxY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 《 MagMinZ) MagMinZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 》 MagMaxZ) MagMaxZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if ((millis() - lastDisplayTime) 》 1000) // display once/second
{
Serial.print(“Mag Minimums: ”); Serial.print(MagMinX); Serial.print(“ ”);Serial.print(MagMinY); Serial.print(“ ”); Serial.print(MagMinZ); Serial.println();
Serial.print(“Mag Maximums: ”); Serial.print(MagMaxX); Serial.print(“ ”);Serial.print(MagMaxY); Serial.print(“ ”); Serial.print(MagMaxZ); Serial.println(); Serial.println();
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
}
LSM303/LSM303DLH
下載:項(xiàng)目Zip 或 calibration.ino | 在Github上查看
復(fù)制代碼
#include
#include
//#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified(12345);
float MagMinX, MagMaxX;
float MagMinY, MagMaxY;
float MagMinZ, MagMaxZ;
long lastDisplayTime;
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“LSM303 Calibration”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the magnetometer */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t magEvent;
mag.getEvent(&magEvent);
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 《 MagMinX)
MagMinX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 》 MagMaxX)
MagMaxX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 《 MagMinY)
MagMinY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 》 MagMaxY)
MagMaxY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 《 MagMinZ)
MagMinZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 》 MagMaxZ)
MagMaxZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if ((millis() - lastDisplayTime) 》 1000) // display once/second
{
Serial.print(“Mag Minimums: ”);
Serial.print(MagMinX);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMinY);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMinZ);
Serial.println();
Serial.print(“Mag Maximums: ”);
Serial.print(MagMaxX);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMaxY);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMaxZ);
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
} #include
#include
//#include
#include
Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303DLH_Mag_Unified(12345);
float MagMinX, MagMaxX;
float MagMinY, MagMaxY;
float MagMinZ, MagMaxZ;
long lastDisplayTime;
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(“LSM303 Calibration”);
Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the magnetometer */
if (!mag.begin()) {
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while (1)
;
}
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
void loop(void) {
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t magEvent;
mag.getEvent(&magEvent);
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 《 MagMinX)
MagMinX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.x 》 MagMaxX)
MagMaxX = magEvent.magnetic.x;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 《 MagMinY)
MagMinY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.y 》 MagMaxY)
MagMaxY = magEvent.magnetic.y;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 《 MagMinZ)
MagMinZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if (magEvent.magnetic.z 》 MagMaxZ)
MagMaxZ = magEvent.magnetic.z;
if ((millis() - lastDisplayTime) 》 1000) // display once/second
{
Serial.print(“Mag Minimums: ”);
Serial.print(MagMinX);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMinY);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMinZ);
Serial.println();
Serial.print(“Mag Maximums: ”);
Serial.print(MagMaxX);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMaxY);
Serial.print(“ ”);
Serial.print(MagMaxZ);
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
lastDisplayTime = millis();
}
}
制作曲目!
現(xiàn)在讓我們使用LSM303模塊進(jìn)行一些簡單的導(dǎo)航!
此頁面上的圖像顯示較舊的LSM303DLH。您也可以使用更新的LSM303AGR,但需要參考“引腳分配”頁面來確定要使用的引腳
一天,制作曲目
在Prax草原上,
來一個(gè)北向Zax
和一個(gè)南向Zax。
此Zax-O-Meter是北部或南部Zax的理想導(dǎo)航工具。該項(xiàng)目演示了如何使用LSM303磁力計(jì)輸出來實(shí)現(xiàn)簡單的導(dǎo)航系統(tǒng)。無論您以哪種方式旋轉(zhuǎn),指針都將始終旋轉(zhuǎn)到所需的行進(jìn)方向。
永不退縮!這是我的規(guī)則。
從不退縮!
向西不遠(yuǎn)一英寸!
向東不一英寸!
Zax-O-Meter使用計(jì)算出的指南針航向作為連續(xù)旋轉(zhuǎn)的反饋伺服。當(dāng)指南針航向?yàn)榱愣龋ㄕ保r(shí),伺服器停止旋轉(zhuǎn)。與該值的任何偏差都會(huì)導(dǎo)致伺服器朝相反的方向旋轉(zhuǎn)以進(jìn)行補(bǔ)償。負(fù)反饋的基本原理可用于構(gòu)建自主機(jī)器人的導(dǎo)航系統(tǒng)。
材料:要構(gòu)建Zax-O-Meter,您將需要:
Adafruit LSM303接線板
Arduino Uno
Arduino機(jī)箱
連續(xù)旋轉(zhuǎn)伺服系統(tǒng)
跳線
卡片紙
紙板或泡沫芯
校準(zhǔn)伺服器:為使Zax-O-Meter準(zhǔn)確運(yùn)行,您首先需要找到連續(xù)旋轉(zhuǎn)伺服器的“中性”點(diǎn)。這是導(dǎo)致最小旋轉(zhuǎn)的伺服輸出值。該值通常約為90,但在伺服之間有所不同。運(yùn)行此草圖并修改值,直到獲得最小旋轉(zhuǎn)。那就是您應(yīng)該在Zax-O-Meter草圖中為ServoNeutral使用的值。
下載:文件
復(fù)制代碼
#include
Servo servo;
void setup()
{
servo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
servo.write(90); // change this value to achieve minimum rotation!
}
void loop()
{
} #include
Servo servo;
void setup()
{
servo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
servo.write(90); // change this value to achieve minimum rotation!
}
void loop()
{
}
安裝伺服器,標(biāo)記并加寬外殼中的開口以適合伺服器。將伺服器的轉(zhuǎn)子對準(zhǔn)外殼的中心。向下按直到法蘭與表面齊平,舵機(jī)應(yīng)卡入到位并牢固固定。
安裝Uno并將其連接使用隨附的螺釘將Uno安裝在機(jī)箱中。如下連接伺服和傳感器:
伺服:
黑色-》 Gnd
紅色-》 5v
白色-》數(shù)字引腳9
LSM303:
Gnd-》 Gnd
Vin-》 3.3v
SDA-》模擬4
SCL-》模擬5
然后將傳感器導(dǎo)線穿過伺服器旁邊的開口并關(guān)閉外殼。
添加指針從一些堅(jiān)硬的硬紙板或泡沫芯,并用一些雙面泡沫膠帶將其粘貼到伺服喇叭上。
用一些雙面泡沫膠帶將傳感器固定在箭頭的下方。將傳感器放置在盡可能遠(yuǎn)離伺服主體的位置,以避免電動(dòng)機(jī)產(chǎn)生電磁干擾。
添加Zaxen!查找您最喜歡的Zax的圖片。使用“畫圖”或其他圖像編輯工具制作一對鏡像圖像。
將圖像打印在一些較重的卡片紙上,然后將其折疊以制作雙面圖像。
將其切出并安裝在其頂部。帶有雙面膠帶的指示箭頭。
代碼:加載以下代碼。不要忘記在“伺服校準(zhǔn)”步驟中將“ ServoNeutral”更改為中性值。
示例代碼適用于北向Zax,目標(biāo)標(biāo)題為0。如果您是南向說服的Zax ,targetHeading為180將使您一直處在向南的位置。對于那些背叛的人,請?jiān)?-360度之間選擇任何targetHeading設(shè)置,然后開始在您選擇的標(biāo)題中進(jìn)行跟蹤!
下載:文件
復(fù)制代碼
// **********************************************
// Zax-O-Meter Sketch
// for the Adafruit LSM303 Magnetometer Breakout
//
// Written by Bill Earl for Adafruit Industries
//
// **********************************************
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303_Mag_Unified(12345);
// This is our continuous rotation servo
Servo servo;
// Pi for calculations - not the raspberry type
const float Pi = 3.14159;
// This is the value that gives you minimal rotation on
// a continuous rotation servo. It is usually about 90.
// adjust this value to give minimal rotation for your servo
const float ServoNeutral = 97;
// This is the desired direction of travel
// expressed as a 0-360 degree compass heading
// 0.0 = North
// 90.0 = East
// 180.0 = South
// 270 = West
const float targetHeading = 0.0;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”); Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if(!mag.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while(1);
}
servo.attach(9); // Attach servo to pin 9
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
// Calculate the angle of the vector y,x
float heading = (atan2(event.magnetic.y,event.magnetic.x) * 180) / Pi;
// Normalize to 0-360
if (heading 《 0)
{
heading = 360 + heading;
}
// Calculate the error between tha measured heading and the target heading.
float error = heading - targetHeading;
if (error 》 180)
{
error = error - 360; // for angles 》 180, correct in the opposite direction.
}
// A non-zero difference between the heading and the
// targetHeading will bias the servoNeutral value and
// cause the servo to rotate back toward the targetHeading.
// The divisor is to reduce the reaction speed and avoid oscillations
servo.write(ServoNeutral + error / 4 );
delay(40);
} // **********************************************
// Zax-O-Meter Sketch
// for the Adafruit LSM303 Magnetometer Breakout
//
// Written by Bill Earl for Adafruit Industries
//
// **********************************************
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303_Mag_Unified mag = Adafruit_LSM303_Mag_Unified(12345);
// This is our continuous rotation servo
Servo servo;
// Pi for calculations - not the raspberry type
const float Pi = 3.14159;
// This is the value that gives you minimal rotation on
// a continuous rotation servo. It is usually about 90.
// adjust this value to give minimal rotation for your servo
const float ServoNeutral = 97;
// This is the desired direction of travel
// expressed as a 0-360 degree compass heading
// 0.0 = North
// 90.0 = East
// 180.0 = South
// 270 = West
const float targetHeading = 0.0;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(“Magnetometer Test”); Serial.println(“”);
/* Initialise the sensor */
if(!mag.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the LSM303 。.. check your connections */
Serial.println(“Ooops, no LSM303 detected 。.. Check your wiring!”);
while(1);
}
servo.attach(9); // Attach servo to pin 9
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
// Calculate the angle of the vector y,x
float heading = (atan2(event.magnetic.y,event.magnetic.x) * 180) / Pi;
// Normalize to 0-360
if (heading 《 0)
{
heading = 360 + heading;
}
// Calculate the error between tha measured heading and the target heading.
float error = heading - targetHeading;
if (error 》 180)
{
error = error - 360; // for angles 》 180, correct in the opposite direction.
}
// A non-zero difference between the heading and the
// targetHeading will bias the servoNeutral value and
// cause the servo to rotate back toward the targetHeading.
// The divisor is to reduce the reaction speed and avoid oscillations
servo.write(ServoNeutral + error / 4 );
delay(40);
}
下載和鏈接
文件 strong》
LSM303AGR
LSM303AGR數(shù)據(jù)表
PCB文件(Eagle格式)
Adafruit Fritzing庫中的裝飾對象
LSM303DLHC
LSM303DLHC數(shù)據(jù)表
PCB文件(鷹格式)
Adafruit中的Fritzing對象Fritzing庫
LSM0303AGR示意圖&Fab Print

LSM303DLHC示意圖和構(gòu)造打印


責(zé)任編輯:wv
-
Arduino
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
188文章
6471瀏覽量
187244 -
LSM303D
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
2瀏覽量
9826
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
將ADS8402/ADS8412連接到TMS320C6713 DSP

將ADS8320/ADS8325連接到TMS320C6711 DSP

將ADS8401/ADS8411連接到TMS320C6713 DSP

將ADS8383連接到TMS320C6711 DSP

將ADS7881連接到TMS320C6713 DSP

如何將LVDS/OLDI橋接到HDMI/DVI

將C2000連接到AFE03x:B-FSK示例

使用ESP8266將arduino連接到thinkspeak云,無法將其連接到任何網(wǎng)頁,為什么?
能將ESP8266連接到arduino UNO上,使用mesh組網(wǎng)嗎?
如何將KY-008連接到Arduino
如何將按鈕連接到Arduino板
如何將光敏電阻連接到Arduino板并讀取電壓
如何將HC-SR04連接到Arduino并編寫一個(gè)簡單的程序來測量距離
如何將增量旋轉(zhuǎn)編碼器與Arduino連接




 如何將LSM303連接到Arduino
如何將LSM303連接到Arduino










評論