大家應該都在用U盤,而U盤中的存儲芯片就是NandFlash,你買的64G的U盤,實際并沒有64G,其中一個原因就是存在壞塊。
因為工藝和其他方面的原因,不能保證NandFlash不存在壞塊,因此就需要“挑選出壞塊”。
本文就為大家講述一下用于NandFlash的ECC校驗原理與實現。
ECC簡介
由于NAND Flash的工藝不能保證NAND的Memory Array在其生命周期中保持性能的可靠,因此,在NAND的生產中及使用過程中會產生壞塊。為了檢測數據的可靠性,在應用NAND Flash的系統中一般都會采用一定的壞區管理策略,而管理壞區的前提是能比較可靠的進行壞區檢測。
如果操作時序和電路穩定性不存在問題的話,NAND Flash出錯的時候一般不會造成整個Block或是Page不能讀取或是全部出錯,而是整個Page(例如512Bytes)中只有一個或幾個bit出錯。
對數據的校驗常用的有奇偶校驗、CRC校驗等,而在NAND Flash處理中,一般使用一種比較專用的校驗——ECC。ECC能糾正單比特錯誤和檢測雙比特錯誤,而且計算速度很快,但對1比特以上的錯誤無法糾正,對2比特以上的錯誤不保證能檢測。
ECC原理
ECC一般每256字節原始數據生成3字節ECC校驗數據,這三字節共24比特分成兩部分:6比特的列校驗和16比特的行校驗,多余的兩個比特置1,如下圖所示:
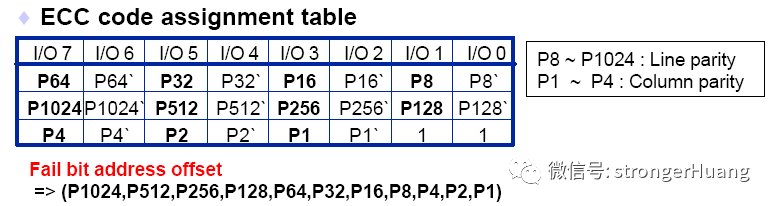
ECC的列校驗和生成規則如下圖所示:
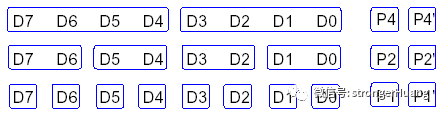
用數學表達式表示為:
P4=D7(+)D6(+)D5(+)D4P4`=D3(+)D2(+)D1(+)D0P2=D7(+)D6(+)D3(+)D2P2`=D5(+)D4(+)D1(+)D0P1=D7(+)D5(+)D3(+)D1P1`=D6(+)D4(+)D2(+)D0
備注:這里(+)表示“位異或”操作
ECC的行校驗和生成規則如下圖所示:
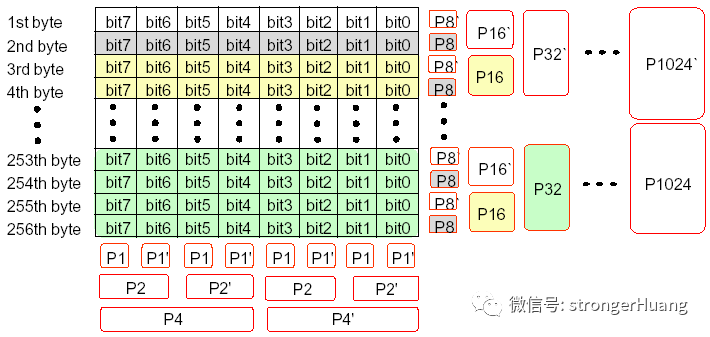
用數學表達式表示為:
P8 = bit7(+)bit6(+)bit5(+)bit4(+)bit3(+)bit2(+)bit1(+)bit0(+)P8
備注:這里(+)表示“位異或”操作
當往NAND Flash的page中寫入數據的時候,每256字節我們生成一個ECC校驗和,稱之為原ECC校驗和,保存到PAGE的OOB(out-of-band)數據區中。
當從NAND Flash中讀取數據的時候,每256字節我們生成一個ECC校驗和,稱之為新ECC校驗和。
校驗的時候,根據上述ECC生成原理不難推斷:將從OOB區中讀出的原ECC校驗和新ECC校驗和按位異或,若結果為0,則表示不存在錯(或是出現了ECC無法檢測的錯誤);若3個字節異或結果中存在11個比特位為1,表示存在一個比特錯誤,且可糾正;若3個字節異或結果中只存在1個比特位為1,表示OOB區出錯;其他情況均表示出現了無法糾正的錯誤。
ECC算法的實現
這里附上算法代碼:
static const u_char nand_ecc_precalc_table[] ={0x00, 0x55, 0x56, 0x03, 0x59, 0x0c, 0x0f, 0x5a, 0x5a, 0x0f, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x03, 0x56, 0x55, 0x00,0x65, 0x30, 0x33, 0x66, 0x3c, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x6a, 0x69, 0x3c, 0x66, 0x33, 0x30, 0x65,0x66, 0x33, 0x30, 0x65, 0x3f, 0x6a, 0x69, 0x3c, 0x3c, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x3f, 0x65, 0x30, 0x33, 0x66,0x03, 0x56, 0x55, 0x00, 0x5a, 0x0f, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x59, 0x0c, 0x0f, 0x5a, 0x00, 0x55, 0x56, 0x03,0x69, 0x3c, 0x3f, 0x6a, 0x30, 0x65, 0x66, 0x33, 0x33, 0x66, 0x65, 0x30, 0x6a, 0x3f, 0x3c, 0x69,0x0c, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x0f, 0x55, 0x00, 0x03, 0x56, 0x56, 0x03, 0x00, 0x55, 0x0f, 0x5a, 0x59, 0x0c,0x0f, 0x5a, 0x59, 0x0c, 0x56, 0x03, 0x00, 0x55, 0x55, 0x00, 0x03, 0x56, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x0f,0x6a, 0x3f, 0x3c, 0x69, 0x33, 0x66, 0x65, 0x30, 0x30, 0x65, 0x66, 0x33, 0x69, 0x3c, 0x3f, 0x6a,0x6a, 0x3f, 0x3c, 0x69, 0x33, 0x66, 0x65, 0x30, 0x30, 0x65, 0x66, 0x33, 0x69, 0x3c, 0x3f, 0x6a,0x0f, 0x5a, 0x59, 0x0c, 0x56, 0x03, 0x00, 0x55, 0x55, 0x00, 0x03, 0x56, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x0f,0x0c, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x0f, 0x55, 0x00, 0x03, 0x56, 0x56, 0x03, 0x00, 0x55, 0x0f, 0x5a, 0x59, 0x0c,0x69, 0x3c, 0x3f, 0x6a, 0x30, 0x65, 0x66, 0x33, 0x33, 0x66, 0x65, 0x30, 0x6a, 0x3f, 0x3c, 0x69,0x03, 0x56, 0x55, 0x00, 0x5a, 0x0f, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x59, 0x0c, 0x0f, 0x5a, 0x00, 0x55, 0x56, 0x03,0x66, 0x33, 0x30, 0x65, 0x3f, 0x6a, 0x69, 0x3c, 0x3c, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x3f, 0x65, 0x30, 0x33, 0x66,0x65, 0x30, 0x33, 0x66, 0x3c, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x6a, 0x69, 0x3c, 0x66, 0x33, 0x30, 0x65,0x00, 0x55, 0x56, 0x03, 0x59, 0x0c, 0x0f, 0x5a, 0x5a, 0x0f, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x03, 0x56, 0x55, 0x00};
//Creates non-inverted ECC code from line paritystatic void nand_trans_result(u_char reg2, u_char reg3,u_char *ecc_code){u_char a, b, i, tmp1, tmp2;
/* Initialize variables */a = b = 0x80;tmp1 = tmp2 = 0;
/* Calculate first ECC byte */for (i = 0; i 《 4; i++){if (reg3 & a) /* LP15,13,11,9 --》 ecc_code[0] */tmp1 |= b;b 》》= 1;if (reg2 & a) /* LP14,12,10,8 --》 ecc_code[0] */tmp1 |= b;b 》》= 1;a 》》= 1;}
/* Calculate second ECC byte */b = 0x80;for (i = 0; i 《 4; i++){if (reg3 & a) /* LP7,5,3,1 --》 ecc_code[1] */tmp2 |= b;b 》》= 1;if (reg2 & a) /* LP6,4,2,0 --》 ecc_code[1] */tmp2 |= b;b 》》= 1;a 》》= 1;}
/* Store two of the ECC bytes */ecc_code[0] = tmp1;ecc_code[1] = tmp2;}
//Calculate 3 byte ECC code for 256 byte blockvoid nand_calculate_ecc (const u_char *dat, u_char *ecc_code){u_char idx, reg1, reg2, reg3;int j;
/* Initialize variables */reg1 = reg2 = reg3 = 0;ecc_code[0] = ecc_code[1] = ecc_code[2] = 0;
/* Build up column parity */for(j = 0; j 《 256; j++){/* Get CP0 - CP5 from table */idx = nand_ecc_precalc_table[dat[j]];reg1 ^= (idx & 0x3f);
/* All bit XOR = 1 ? */if (idx & 0x40) {reg3 ^= (u_char) j;reg2 ^= ~((u_char) j);}}
/* Create non-inverted ECC code from line parity */nand_trans_result(reg2, reg3, ecc_code);
/* Calculate final ECC code */ecc_code[0] = ~ecc_code[0];ecc_code[1] = ~ecc_code[1];ecc_code[2] = ((~reg1) 《《 2) | 0x03;}
//Detect and correct a 1 bit error for 256 byte blockint nand_correct_data (u_char *dat, u_char *read_ecc, u_char *calc_ecc){u_char a, b, c, d1, d2, d3, add, bit, i;
/* Do error detection */d1 = calc_ecc[0] ^ read_ecc[0];d2 = calc_ecc[1] ^ read_ecc[1];d3 = calc_ecc[2] ^ read_ecc[2];
if ((d1 | d2 | d3) == 0){/* No errors */return 0;}else{a = (d1 ^ (d1 》》 1)) & 0x55;b = (d2 ^ (d2 》》 1)) & 0x55;c = (d3 ^ (d3 》》 1)) & 0x54;
/* Found and will correct single bit error in the data */if ((a == 0x55) && (b == 0x55) && (c == 0x54)){c = 0x80;add = 0;a = 0x80;for (i=0; i《4; i++){if (d1 & c)add |= a;c 》》= 2;a 》》= 1;}c = 0x80;for (i=0; i《4; i++){if (d2 & c)add |= a;c 》》= 2;a 》》= 1;}bit = 0;b = 0x04;c = 0x80;for (i=0; i《3; i++){if (d3 & c)bit |= b;c 》》= 2;b 》》= 1;}b = 0x01;a = dat[add];a ^= (b 《《 bit);dat[add] = a;return 1;}else{i = 0;while (d1){if (d1 & 0x01)++i;d1 》》= 1;}while (d2){if (d2 & 0x01)++i;d2 》》= 1;}while (d3){if (d3 & 0x01)++i;d3 》》= 1;}if (i == 1){/* ECC Code Error Correction */read_ecc[0] = calc_ecc[0];read_ecc[1] = calc_ecc[1];read_ecc[2] = calc_ecc[2];return 2;}else{/* Uncorrectable Error */return -1;}}}
/* Should never happen */return -1;}
參考文檔:
http://blogimg.chinaunix.net/blog/upfile2/080702112233.pdf
免責聲明:本文素材來源網絡,版權歸原作者所有。如涉及作品版權問題,請與我聯系刪除。
編輯:jq
-
ECC
+關注
關注
0文章
97瀏覽量
20560
原文標題:NandFlash ECC校驗原理與實現
文章出處:【微信號:strongerHuang,微信公眾號:strongerHuang】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
DDR Inline ECC在Jacinto7 SoC中的應用





 一文詮釋NandFlash ECC校驗原理與實現
一文詮釋NandFlash ECC校驗原理與實現










評論