RAKE簡(jiǎn)介
RAKE英文全稱為Rapid Automatic keyword extraction,中文稱為快速自動(dòng)關(guān)鍵字提取,是一種非常高效的關(guān)鍵字提取算法,可對(duì)單個(gè)文檔進(jìn)行操作,以實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)動(dòng)態(tài)集合的應(yīng)用,也可非常輕松地應(yīng)用于新域,并且在處理多種類型的文檔時(shí)也非常有效。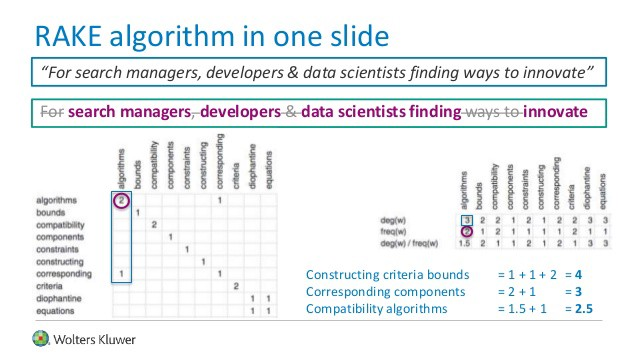
2
算法思想
RAKE算法用來做關(guān)鍵詞(keyword)的提取,實(shí)際上提取的是關(guān)鍵的短語(phrase),并且傾向于較長(zhǎng)的短語,在英文中,關(guān)鍵詞通常包括多個(gè)單詞,但很少包含標(biāo)點(diǎn)符號(hào)和停用詞,例如and,the,of等,以及其他不包含語義信息的單詞。
RAKE算法首先使用標(biāo)點(diǎn)符號(hào)(如半角的句號(hào)、問號(hào)、感嘆號(hào)、逗號(hào)等)將一篇文檔分成若干分句,然后對(duì)于每一個(gè)分句,使用停用詞作為分隔符將分句分為若干短語,這些短語作為最終提取出的關(guān)鍵詞的候選詞。
最后,每個(gè)短語可以再通過空格分為若干個(gè)單詞,可以通過給每個(gè)單詞賦予一個(gè)得分,通過累加得到每個(gè)短語的得分。一個(gè)關(guān)鍵點(diǎn)在于將這個(gè)短語中每個(gè)單詞的共現(xiàn)關(guān)系考慮進(jìn)去。最終定義的公式是:
3
算法步驟
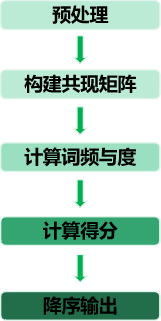
(1)算法首先對(duì)句子進(jìn)行分詞,分詞后去除停用詞,根據(jù)停 用詞劃分短語;
(2)之后計(jì)算每一個(gè)詞在短語的共現(xiàn)詞數(shù),并構(gòu)建 詞共現(xiàn)矩陣;
(3)共現(xiàn)矩陣的每一列的值即為該詞的度deg(是一個(gè)網(wǎng)絡(luò)中的概念,每與一個(gè)單詞共現(xiàn)在一個(gè)短語中,度就加1,考慮該單詞本身),每個(gè)詞在文本中出現(xiàn)的次數(shù)即為頻率freq;
(4)得分score為度deg與頻率 freq的商,score越大則該詞更重 ;
(5)最后按照得分的大小值降序 輸出該詞所在的短語。
下面我們以一個(gè)中文例子具體解釋RAKE算法原理,例如“系統(tǒng)有聲音,但系統(tǒng)托盤的音量小喇叭圖標(biāo)不見了”,經(jīng)過分詞、去除停用詞處理 后得到的詞集W = {系統(tǒng),聲音,托盤,音量,小喇叭,圖標(biāo),不見},短語集D={系統(tǒng),聲音,系統(tǒng)托盤,音量小喇叭圖標(biāo)不見},詞共現(xiàn)矩陣如表: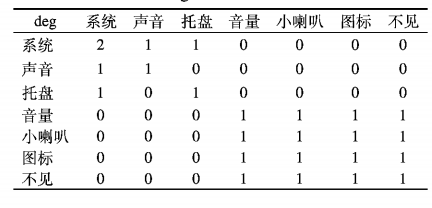
每一個(gè)詞的度為deg={"系統(tǒng)”:2,“聲音”:1,“托盤”:1; “音量” :3; “小喇叭” :3,“圖標(biāo)” :3,“不見” :3},頻率freq = { “系統(tǒng)” :2, “聲音” :1, “托盤” :1 ;“音量” :1;“小喇叭” :1, “圖標(biāo)”丄“不見” :1}, score ={“系統(tǒng)”:1,“聲音”:1,“托 盤” :1 ;“音量” :1小喇叭” :3, “圖標(biāo)” :3, “不見” :3 },輸出結(jié)果為{音量小喇叭圖標(biāo)不見 ,系統(tǒng)托盤,系統(tǒng),聲音}
4
代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)
importstring fromtypingimportDict,List,Set,Tuple PUNCTUATION=string.punctuation.replace(''','')#Donotuseapostropheasadelimiter ENGLISH_WORDS_STOPLIST:List[str]=[ '(',')','and','of','the','amongst','with','from','after','its','it','at','is', 'this',',','.','be','in','that','an','other','than','also','are','may','suggests', 'all','where','most','against','more','have','been','several','as','before', 'although','yet','likely','rather','over','a','for','can','these','considered', 'used','types','given','precedes', ] defsplit_to_tokens(text:str)->List[str]: ''' Splittextstringtotokens. Behaviorissimilartostr.split(), butemptylinesareomittedandpunctuationmarksareseparatedfromword. Example: split_to_tokens('Johnsaid'Hey!'(andsomeotherwords.)')-> ->['John','said',''','Hey','!',''','(','and','some','other','words','.',')'] ''' result=[] foritemintext.split(): whileitem[0]inPUNCTUATION: result.append(item[0]) item=item[1:] foriinrange(len(item)): ifitem[-i-1]notinPUNCTUATION: break ifi==0: result.append(item) else: result.append(item[:-i]) result.extend(item[-i:]) return[itemforiteminresultifitem] defsplit_tokens_to_phrases(tokens:List[str],stoplist:List[str]=None)->List[str]: """ Mergetokensintophrases,delimitedbyitemsfromstoplist. Phraseisasequenceoftokenthathasthefollowingproperties: -phrasecontains1ormoretokens -tokensfromphrasegoinarow -phrasedoesnotcontaindelimitersfromstoplist -eithertheprevious(notinaphrase)tokenbelongstostoplistoritisthebeginningoftokenslist -eitherthenext(notinaphrase)tokenbelongstostoplistoritistheendoftokenslist Example: split_tokens_to_phrases( tokens=['Mary','and','John',',','some','words','(','and','other','words',')'], stoplist=['and',',','.','(',')'])-> ->['Mary','John','somewords','otherwords'] """ ifstoplistisNone: stoplist=ENGLISH_WORDS_STOPLIST stoplist+=list(PUNCTUATION) current_phrase:List[str]=[] all_phrases:List[str]=[] stoplist_set:Set[str]={stopword.lower()forstopwordinstoplist} fortokenintokens: iftoken.lower()instoplist_set: ifcurrent_phrase: all_phrases.append(''.join(current_phrase)) current_phrase=[] else: current_phrase.append(token) ifcurrent_phrase: all_phrases.append(''.join(current_phrase)) returnall_phrases defget_cooccurrence_graph(phrases:List[str])->Dict[str,Dict[str,int]]: """ Getgraphthatstorescooccurenceoftokensinphrases. Matrixisstoredasdict, wherekeyistoken,valueisdict(keyissecondtoken,valueisnumberofcooccurrence). Example: get_occurrence_graph(['Mary','John','somewords','otherwords'])->{ 'mary':{'mary':1}, 'john':{'john':1}, 'some':{'some':1,'words':1}, 'words':{'some':1,'words':2,'other':1}, 'other':{'other':1,'words':1} } """ graph:Dict[str,Dict[str,int]]={} forphraseinphrases: forfirst_tokeninphrase.lower().split(): forsecond_tokeninphrase.lower().split(): iffirst_tokennotingraph: graph[first_token]={} graph[first_token][second_token]=graph[first_token].get(second_token,0)+1 returngraph defget_degrees(cooccurrence_graph:Dict[str,Dict[str,int]])->Dict[str,int]: """ Getdegreesforalltokensbycooccurrencegraph. Resultisstoredasdict, wherekeyistoken,valueisdegree(sumoflengthsofphrasesthatcontainthetoken). Example: get_degrees( { 'mary':{'mary':1}, 'john':{'john':1}, 'some':{'some':1,'words':1}, 'words':{'some':1,'words':2,'other':1}, 'other':{'other':1,'words':1} } )->{'mary':1,'john':1,'some':2,'words':4,'other':2} """ return{token:sum(cooccurrence_graph[token].values())fortokenincooccurrence_graph} defget_frequencies(cooccurrence_graph:Dict[str,Dict[str,int]])->Dict[str,int]: """ Getfrequenciesforalltokensbycooccurrencegraph. Resultisstoredasdict, wherekeyistoken,valueisfrequency(numberoftimesthetokenoccurs). Example: get_frequencies( { 'mary':{'mary':1}, 'john':{'john':1}, 'some':{'some':1,'words':1}, 'words':{'some':1,'words':2,'other':1}, 'other':{'other':1,'words':1} } )->{'mary':1,'john':1,'some':1,'words':2,'other':1} """ return{token:cooccurrence_graph[token][token]fortokenincooccurrence_graph} defget_ranked_phrases(phrases:List[str],*, degrees:Dict[str,int], frequencies:Dict[str,int])->List[Tuple[str,float]]: """ GetRAKEmeasureforeveryphrase. Resultisstoredaslistoftuples,everytuplecontainsofphraseanditsRAKEmeasure. Itemsaresortednon-ascendingbyRAKEmeasure,thanalphabeticallybyphrase. """ processed_phrases:Set[str]=set() ranked_phrases:List[Tuple[str,float]]=[] forphraseinphrases: lowered_phrase=phrase.lower() iflowered_phraseinprocessed_phrases: continue score:float=sum(degrees[token]/frequencies[token]fortokeninlowered_phrase.split()) ranked_phrases.append((lowered_phrase,round(score,2))) processed_phrases.add(lowered_phrase) #Sortbyscorethanbyphrasealphabetically. ranked_phrases.sort(key=lambdaitem:(-item[1],item[0])) returnranked_phrases defrake_text(text:str)->List[Tuple[str,float]]: """ GetRAKEmeasureforeveryphraseintextstring. Resultisstoredaslistoftuples,everytuplecontainsofphraseanditsRAKEmeasure. Itemsaresortednon-ascendingbyRAKEmeasure,thanalphabeticallybyphrase. """ tokens:List[str]=split_to_tokens(text) phrases:List[str]=split_tokens_to_phrases(tokens) cooccurrence:Dict[str,Dict[str,int]]=get_cooccurrence_graph(phrases) degrees:Dict[str,int]=get_degrees(cooccurrence) frequencies:Dict[str,int]=get_frequencies(cooccurrence) ranked_result:List[Tuple[str,float]]=get_ranked_phrases(phrases,degrees=degrees,frequencies=frequencies) returnranked_result
執(zhí)行效果:
if__name__=='__main__': text='Mercy-classincludesUSNSMercyandUSNSComforthospitalships.Credit:USNavyphotoMassCommunicationSpecialist1stClassJasonPastrick.TheUSNavalAirWarfareCenterAircraftDivision(NAWCAD)LakehurstinNewJerseyisusinganadditivemanufacturingprocesstomakefaceshields.........' ranked_result=rake_text(text) print(ranked_result)
關(guān)鍵短語抽取效果如下:
[
('additivemanufacturingprocesstomakefaceshields.the3dprintingfaceshields',100.4),
('usnavyphotomasscommunicationspecialist1stclassjasonpastrick',98.33),
('usnavy’smercy-classhospitalshipusnscomfort.currentlystationed',53.33),
...
]
-
算法
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
23文章
4713瀏覽量
95532 -
網(wǎng)絡(luò)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
14文章
7823瀏覽量
91045 -
Rake
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
2瀏覽量
7436
原文標(biāo)題:【NLP基礎(chǔ)】英文關(guān)鍵詞抽取RAKE算法
文章出處:【微信號(hào):zenRRan,微信公眾號(hào):深度學(xué)習(xí)自然語言處理】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
指紋識(shí)別算法流程介紹
數(shù)學(xué)建模十大算法介紹
SVPWM算法架構(gòu)介紹
SVPWM的原理及法則推導(dǎo)和控制算法介紹
在ADSP2181上實(shí)現(xiàn)Rake接收機(jī)路徑搜索
用于TD-SCDMA通信終端的RAKE接收機(jī)
自適應(yīng)RAKE接收技術(shù)
RAKE接收機(jī)與分集接收
擴(kuò)頻通信系統(tǒng)中Rake接收性能仿真研究
rake接收機(jī)的工作原理
RAKE接收機(jī)的合并方式
RAKE接收機(jī)的分集接收原理
RAKE接收機(jī)的作用及優(yōu)缺點(diǎn)
RAKE接收機(jī)的原理介紹和使用MATLAB以及RAKE接收機(jī)的性能說明等介紹



















評(píng)論