Linux驅動等待隊列與poll機制
? 當我們在操作設備時,我們經常遇到當設備獲取不到資源時就會掛起進程,當設備資源滿足要求時再喚醒進程(如read函數,當讀不到數據時就會掛起,讀到了數據則可立刻返回)。這種通過阻塞方式訪問設備,可以極大的減輕CPU負荷,在進程掛起是可以讓CPU去執行其它資源。而通過等待隊列的方式就可實現進程阻塞,滿足要求時再喚醒進程。
因為阻塞的進程會進入休眠狀態, 因此, 必須確保有一個地方能夠喚醒休眠的進程。 喚醒進程的地方最大可能發生在中斷里面, 因為硬件資源獲得的同時往往伴隨著一個中斷。
在內核中,等待隊列的合理應用可以極大的提供CPU執行效率,尤其是在中斷處理、進程同步、定時等場合。可以使用等待隊列實現阻塞進程的喚醒。它以隊列為基礎數據結構,與進程調度機制緊密結合,能夠用于實現內核中的異步事件通知機制,同步對系統資源的訪問等。
等待隊列是一種基于資源狀態的線程管理的機制,它可以使線程在資源不滿足的情況下處于休眠狀態,讓出CPU資源,而資源狀態滿足時喚醒線程,使其繼續進行業務的處理。
等待隊列(wait queue)用于使線程等待某一特定的事件發生而無需頻繁的輪詢,進程在等待期間睡眠,在某件事發生時由內核自動喚醒。它是以雙循環鏈表為基礎數據結構,與進程的休眠喚醒機制緊密相聯,是實現異步事件通知、跨進程通信、同步資源訪問等技術的底層技術支撐。
1.等待隊列相關接口函數
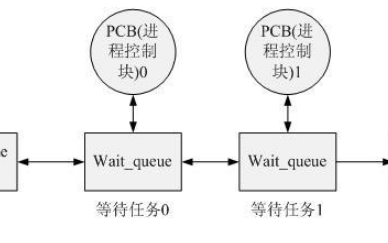
??在Linux中,等待隊列是由等待隊列頭wait_queue_head_t *q進行管理,結構體信息如下:
struct __wait_queue_head {
spinlock_t lock;
struct list_head task_list;
};
1.1 等待隊列頭初始化
??初始化等待隊列頭可以靜態初始化或者動態初始化
#define DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(name)
功能: 靜態初始化等待隊列頭
參數: name --等待隊列頭結構體變量名
#define init_waitqueue_head(q)
功能: 靜態初始化等待隊列頭
參數: q–等待隊列頭結構體指針變量
??注意:動態初始化時需要手動創建一個等待隊列頭結構體變量,而靜態初始化只需要填入等待隊列頭變量名即可。即:
??DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(q)等價于下面兩行代碼:
wait_queue_head_t q;
init_waitqueue_head(&q);//動態初始化等待隊列頭
1.2 休眠進程
??休眠進程由兩類函數:可中斷休眠 和 不可中斷休眠。可中斷休眠可中斷休眠是可以通過信號方式喚醒;不可中斷休眠則在休眠期間無法收到信號(如CTRL+C、CTRL+),信號將會被阻塞,必須等待進程喚醒后才能響應信號。
- 可中斷休眠函數
#define wait_event_interruptible(wq, condition)
({
int __ret = 0;
if (!(condition))
__wait_event_interruptible(wq, condition, __ret);
__ret;
})
//不可中斷休眠,但可以指定超時時間
#define __wait_event_timeout(wq, condition, ret)
do {
DEFINE_WAIT(__wait);
for (;;) {
prepare_to_wait(&wq, &__wait, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
if (condition)
break;
ret = schedule_timeout(ret);
if (!ret)
break;
}
finish_wait(&wq, &__wait);
} while (0)
??wq為等待隊列頭;
??condition為喚醒標志,condition為真喚醒進程,為假則為休眠狀態;
??ret為要指定的超時時間,單位為時鐘節拍jiffies
- 不可中斷休眠函數
#define wait_event(wq, condition)
do {
if (condition)
break;
__wait_event(wq, condition);
} while (0)
//可中斷休眠,但可以指定超時時間
#define __wait_event_interruptible_timeout(wq, condition, ret)
do {
DEFINE_WAIT(__wait);
for (;;) {
prepare_to_wait(&wq, &__wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (condition)
break;
if (!signal_pending(current)) {
ret = schedule_timeout(ret);
if (!ret)
break;
continue;
}
ret = -ERESTARTSYS;
break;
}
finish_wait(&wq, &__wait);
} while (0)
??wq為等待隊列頭;
??condition為喚醒標志,condition為真喚醒進程,為假則為休眠狀態。
??ret為要指定的超時時間,單位為時鐘節拍jiffies
1.3 喚醒進程
??喚醒休眠進程函數分為兩類:一是可喚醒可中斷和不可中斷休眠進程;二是只能喚醒可中斷休眠進程。
??喚醒進程函數一般是在設備獲取到資源時調用,調用位置常處于中斷處理函數中。
//可喚醒可中斷和不可中斷休眠進程
#define wake_up(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 1, NULL) //隨機喚醒一個休眠進程
#define wake_up_nr(x, nr) __wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, nr, NULL) //喚醒多個休眠進程
#define wake_up_all(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 0, NULL) //喚醒所有休眠進程
//只能喚醒可中斷休眠進程
#define wake_up_interruptible(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 1, NULL) //隨機喚醒一個休眠進程
#define wake_up_interruptible_nr(x, nr) __wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, nr, NULL) //喚醒多個休眠進程
#define wake_up_interruptible_all(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 0, NULL) //喚醒所有休眠進程
1.4 等待隊列應用示例
下面以按鍵為例,實現中斷方式按鍵檢測,通過工作隊列處理底半部分代碼,雜項設備框架實現設備注冊。在按鍵的工作函數中喚醒休眠進程。在位獲取到按鍵信息時將進程休眠。
Linux中斷編程參考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44453694/article/details/126812705
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define KEY_CNT sizeof(key_info)/sizeof(struct key_info) //按鍵個數
//static wait_queue_head_t key_q;/*等待隊列頭(動態初始化時需要定義)*/
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(key_q);//靜態初始化等待隊列頭
struct key_info
{
unsigned int gpio;//gpio口
int irq;//中斷號
char key_name[20];//注冊中斷名字
int key_num;//按鍵編號
};
//按鍵信息保存
static struct key_info key_info[]=
{
{EXYNOS4_GPX3(2),0,"key1",1},
{EXYNOS4_GPX3(3),0,"key2",2},
{EXYNOS4_GPX3(4),0,"key3",3},
{EXYNOS4_GPX3(5),0,"key4",4}
};
static struct key_info *key_p;
static struct work_struct key_work;/*工作結構體*/
static int key_val;
static int condition=0;/*喚醒標志*/
/*工作處理函數*/
void work_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
msleep(10);//按鍵消抖
if(gpio_get_value(key_p->gpio)==0)
{
//printk("KEY %d 按下n",key_p->key_num);
key_val=key_p->key_num;
}
condition=1;//將喚醒標志置位
wake_up(&key_q);
}
/*中斷服務函數*/
static irqreturn_t key_exit_work(int irq, void *dev)
{
key_p=(struct key_info *)dev;
schedule_work(&key_work);//工作調度
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int key_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("設備打開成功n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t key_read(struct file *file, char __user *data, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int ret;
int key;
//wait_event(key_q, condition);//休眠進程(不可中斷休眠)
wait_event_interruptible(key_q, condition);//休眠進程(可中斷休眠)
key=key_val;
condition=0;//清除喚醒標志
ret=copy_to_user(data,&key,sizeof(key));
return sizeof(key)-ret;
}
static int key_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("設備關閉成功n");
return 0;
}
/*文件操早集合*/
static struct file_operations key_fops=
{
.open= key_open,
.read= key_read,
.release= key_release
};
/*雜項設備結構體*/
static struct miscdevice key_misc=
{
.minor=MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,//次設備號,255,有內核分配
.name="key_exit",//在/dev下生成的設備節點名字
.fops=&key_fops
};
static int __init wbyq_key_exit_init(void)
{
int i=0;
int ret;
/*初始化等待隊列頭*/
//init_waitqueue_head(&key_q);
/*初始化工作*/
INIT_WORK(&key_work, work_func);
for(i=0;i;i++)>
-
執行效果

-
Linux
+關注
關注
87文章
11311瀏覽量
209689 -
接口函數
+關注
關注
0文章
11瀏覽量
8196
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
【AWorks280試用體驗】POLL機制、異步通知、互斥阻塞
【NanoPi M2試用體驗】一個逗逼的技術宅養成日記——POLL機制(一)
Linux 機制分析
Linux等待隊列如何實現
linux內核的異步機制
Linux內核的等待隊列是什么意思?如何實現呢
poll&&epoll之poll實現
詳細解讀Linux內核的poll機制





 Linux驅動等待隊列與poll機制
Linux驅動等待隊列與poll機制










評論