GSM模塊使用起來非常吸引人,尤其是當我們的項目需要遠程訪問時。這些模塊可以執(zhí)行我們普通手機可以執(zhí)行的所有操作,例如撥打/接聽電話,發(fā)送/接收短信,使用GPRS連接到互聯(lián)網(wǎng)等。您還可以將普通麥克風和揚聲器連接到此模塊,并在移動通話中交談。如果它可以與微控制器連接,這將為許多創(chuàng)意項目打開大門。因此,在本教程中,我們將學習如何將GSM模塊(SIM900A)與我們的PIC微控制器連接,并通過使用GSM模塊撥打和接聽電話來演示它。
所需材料:
- PIC 微控制器 (PIC16F877A)
- GSM 模塊(SIM900 或任何其他)
- 連接線
- 12V 適配器
- 圖片套件 3
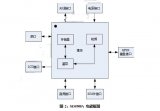
GSM模塊:
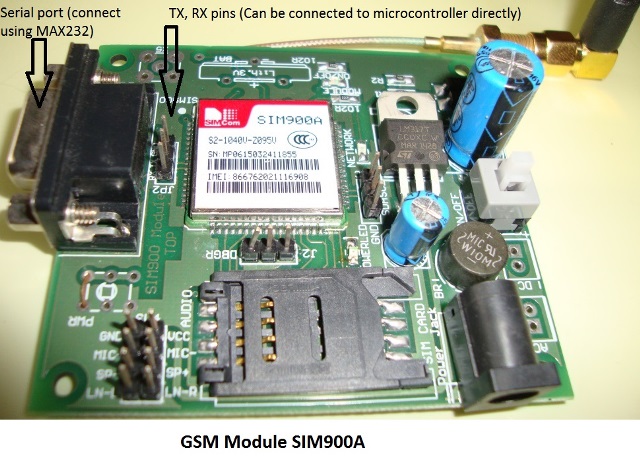
即使沒有任何微控制器,也可以通過使用AT命令模式使用GSM模塊。如上所示,GSM模塊帶有USART適配器,可以使用MAX232模塊直接連接到計算機,或者Tx和Rx引腳可用于將其連接到微控制器。您還可以注意到可以連接麥克風或揚聲器的其他引腳,如MIC +,MIC-,SP+,SP-等。該模塊可以通過普通的直流桶形插孔由 12V 適配器供電。
將SIM卡插入模塊插槽并打開電源,您應該注意到電源指示燈亮起。現(xiàn)在等待一分鐘左右,您應該會看到紅色(或任何其他顏色)LED 每 3 秒閃爍一次。這意味著您的模塊能夠與您的SIM卡建立連接。現(xiàn)在,您可以繼續(xù)將模塊與手機或任何微控制器連接。
使用 AT 命令與 GSM 模塊通信:
正如您可能已經(jīng)猜到的那樣,GSM模塊可以通過串行通信進行通信,并且只能理解一種語言,即“ AT命令 ”。無論您想告訴或詢問GSM模塊什么,都只能通過AT命令進行。例如,如果您想知道模塊是否處于活動狀態(tài)。您應該詢問(發(fā)送)像“AT”這樣的命令,您的模塊將回答“確定”。
這些AT命令在其數(shù)據(jù)手冊中有很好的解釋,可以在其官方數(shù)據(jù)手冊中找到。好!好!這是一份 271 頁的數(shù)據(jù)表,您可能需要幾天時間才能通讀它們。因此,我在下面給出了一些最重要的AT命令,以便您盡快啟動并運行它。
| 在 | 回復“確定”進行確認 |
|---|---|
| AT+CPIN? | 檢查信號質(zhì)量 |
| AT+COPS? | 查找服務提供商名稱 |
| ATD96XXXXXXXX; | 撥打特定號碼,以分號結(jié)尾 |
| AT+CNUM | 查找SIM卡的數(shù)量(可能不適用于某些SIM卡) |
| ATA | 接聽來電 |
| 阿特 | 掛斷當前來電 |
| AT+COLP | 顯示來電號碼 |
| AT+VTS=(數(shù)字) | 發(fā)送 DTMF 編號。您可以使用移動鍵盤上的任意數(shù)字(數(shù)字) |
| AT+CMGR | AT+CMGR=1 在第一個位置讀取消息 |
| AT+CMGD=1 | 刪除第一個位置的消息 |
| AT+CMGDA=“DEL ALL” | 從SIM卡中刪除所有郵件 |
| AT+CMGL=“ALL” | 讀取來自 SIM 卡的所有消息 |
| AT+CMGF=1 | 設置短信配置。“1”表示純文本模式 |
| AT+CMGS = “+91 968837XXXX”>電路摘要文本 | 在此處向特定號碼發(fā)送短信 968837XXXX。當您看到“>”時,請開始輸入文本。按 Ctrl+Z 發(fā)送文本。 |
| AT+CGATT? | 檢查SIM卡上的互聯(lián)網(wǎng)連接 |
| AT+CIPSHUT | 關閉TCP連接,意味著斷開互聯(lián)網(wǎng) |
| AT+CSTT = “APN”,“用戶名”,“通行證” | 使用您的 APN 和通行密鑰連接到 GPRS。可以從網(wǎng)絡提供商處獲得。 |
| AT+CIICR | 檢查SIM卡是否有數(shù)據(jù)包 |
| AT+CIFSR | 獲取 SIM 卡網(wǎng)絡的 IP |
| AT+CIPSTART = “TCP”,“服務器 IP”,“端口” | 用于設置 TCP IP 連接 |
| AT+CIPSEND | 此命令用于將數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送到服務器 |
電路圖:
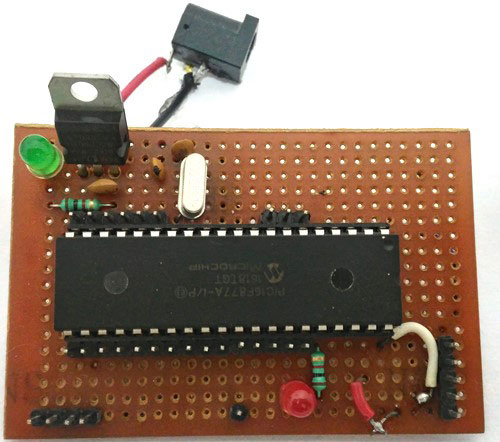
我們只是簡單地將GSM模塊的Tx和Rx引腳分別與PIC MCU PIC16F877A的Rx和Tx引腳連接。這將在兩者之間建立串行連接。另外,不要忘記將GSM和PIC模塊共同接地。我們還使用LCD顯示屏來了解GSM模塊的狀態(tài)。連接完成后,您的硬件將如下所示。

PIC微控制器編程:
可以在本教程的底部找到此項目的完整程序。在這里,我將解釋一些重要的函數(shù)和代碼片段。該程序還具有LCD代碼,該代碼來自與PIC微控制器的接口LCD,如果您想知道如何將LCD與PIC微控制器一起使用,可以訪問該教程。
如前所述,我們將通過串行通信模式使用 AT 命令在 PIC 和 GSM 之間進行通信。因此,首先我們必須使用 Initialize***_SIM900()* **初始化 PIC 微控制器中的 USART 通信模塊;功能。在此函數(shù)中,我們聲明 Tx 和 RX 引腳,并以 9600 波特率和 8 位模式初始化異步接收和傳輸。
//***Initialize UART for SIM900**//
void Initialize_SIM900(void)
{
//****Setting I/O pins for UART****//
TRISC6 = 0; // TX Pin set as output
TRISC7 = 1; // RX Pin set as input
//________I/O pins set __________//
/**Initialize SPBRG register for required
baud rate and set BRGH for fast baud_rate**/
SPBRG = 129; //SIM900 operates at 9600 Baud rate so 129
BRGH = 1; // for high baud_rate
//_________End of baud_rate setting_________//
//****Enable Asynchronous serial port*******//
SYNC = 0; // Asynchronous
SPEN = 1; // Enable serial port pins
//_____Asynchronous serial port enabled_______//
//**Lets prepare for transmission & reception**//
TXEN = 1; // enable transmission
CREN = 1; // enable reception
//__UART module up and ready for transmission and reception__//
//**Select 8-bit mode**//
TX9 = 0; // 8-bit reception selected
RX9 = 0; // 8-bit reception mode selected
//__8-bit mode selected__//
}
//________UART module Initialized__________//
現(xiàn)在我們需要從/向我們的 GSM 模塊讀取和寫入信息。為此,我們使用函數(shù) **_SIM900_putch)、_SIM900_getch()、_SIM900_send_string()、_SIM900_print()。 **這些函數(shù)使用發(fā)送和接收緩沖區(qū)寄存器(如 TXREG 和 RCREG)串行讀取或?qū)懭霐?shù)據(jù)。
//**Function to send one byte of date to UART**//
void _SIM900_putch(char bt)
{
while(!TXIF); // hold the program till TX buffer is free
TXREG = bt; //Load the transmitter buffer with the received value
}
//_____________End of function________________//
//**Function to get one byte of date from UART**//
char _SIM900_getch()
{
if(OERR) // check for Error
{
CREN = 0; //If error -> Reset
CREN = 1; //If error -> Reset
}
while(!RCIF); // hold the program till RX buffer is free
return RCREG; //receive the value and send it to main function
}
//_____________End of function________________//
//**Function to convert string to byte**//
void SIM900_send_string(char* st_pt)
{
while(*st_pt) //if there is a char
_SIM900_putch(*st_pt++); //process it as a byte data
}
//___________End of function______________//
//**End of modified Codes**//
void _SIM900_print(unsigned const char *ptr) {
while (*ptr != 0) {
_SIM900_putch(*ptr++);
}
上述功能是通用的,無需為任何應用程序進行更改。對它們的解釋只是為了給出一個粗略的介紹。如果你愿意,你可以通過理解深入了解它們。
現(xiàn)在在我們的主函數(shù)中,我們初始化 USART 連接,并使用以下代碼行檢查我們在發(fā)送“AT”時是否能夠收到“OK”
do
{
Lcd_Set_Cursor(2,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Module not found");
}while (!SIM900_isStarted()); //wait till the GSM to send back "OK"
Lcd_Set_Cursor(2,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Module Detected ");
__delay_ms(1500);
函數(shù) SIM900_isStarted(); 將向 GSM 發(fā)送“AT”并等待其響應“OK”。如果是,它將返回 1 其他 0;
如果未檢測到模塊或存在任何連接問題,則LCD將顯示“未找到模塊”,否則將顯示“檢測到模塊”并繼續(xù)下一步,我們檢查是否可以通過以下代碼行檢測到SIM卡。
/*Check if the SIM card is detected*/
do
{
Lcd_Set_Cursor(2,1);
Lcd_Print_String("SIM not found ");
}while (!SIM900_isReady()); //wait till the GSM to send back "+CPIN: READY"
Lcd_Set_Cursor(2,1);
Lcd_Print_String("SIM Detected ");
__delay_ms(1500);
函數(shù) SIM900_isReady() 將向 GSM 發(fā)送“AT+CPIN?”,并等待來自它的響應“+CPIN:READY”。如果是,它將返回 1 其他 0;
如果找到SIM卡,我們將在LCD上顯示檢測到SIM卡。然后,我們可以嘗試使用命令“ ATD手機號碼 ;”撥打電話。作為一個例子,我使用我的號碼作為ATD93643159XX;。您必須在那里替換各自的手機號碼。
/*Place a Phone Call*/
do
{
_SIM900_print("ATD93643XXXXX;\\r\\n"); //Here we are placing a call to number 93643XXXXX
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Placing Call....");
}while (_SIM900_waitResponse() != SIM900_OK); //wait till the ESP send back "OK"
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Call Placed....");
__delay_ms(1500);
發(fā)出呼叫后,液晶屏將顯示“呼叫已發(fā)出”,您應該會收到該指定號碼的來電。
您還可以撥打連接到GSM模塊的手機號碼,并使用以下代碼在LCD屏幕上獲得通知
while(1)
{
if (_SIM900_waitResponse() == SIM900_RING) //Check if there is an incoming call
{
Lcd_Set_Cursor(2,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Incoming Call!!.");
}
}
當GSM模塊檢測到來電時,它將在LCD模塊的第二行上顯示來電。函數(shù) *_SIM900_waitResponse() *將檢查來自 GSM 模塊的傳入數(shù)據(jù)。當它收到SIM900_RING時,由于 waitResponce() 而相當于“RING”,我們將顯示狀態(tài)“來電”。
您可以像這樣創(chuàng)建自己的函數(shù),以使用 GSM 模塊執(zhí)行幾乎所有類型的激活。如果你想對東西進行硬編碼,你可以簡單地使用 __SIM900_print() 函數(shù)發(fā)送任何 AT 命令,如下所示。
_SIM900_print("AT+CPIN?\\r\\n");
請記住,所有命令后面都應跟有“\\r\\n”,以指示命令正在終止。
模擬:
了解程序的工作原理后,您可以嘗試模擬并進行更改以滿足您的需求。模擬將為您節(jié)省大量時間。模擬是使用 Proteus 完成的,如下所示。

如您所見,我們在Proteus中使用了虛擬終端選項來檢查程序是否按預期響應。我們可以通過彈出對話框輸入值。例如,一旦我們點擊運行,就會出現(xiàn)一個像上面這樣的黑色對話框并顯示 AT,這意味著它已將 GSM 模塊發(fā)送到 AT,現(xiàn)在我們可以通過在框中輸入“確定”并按回車鍵來回復 PIC,PIC 將響應它。同樣,我們可以嘗試所有 AT 命令。
使用 GSM 和 PIC 撥打和接聽電話:
了解代碼和硬件的工作原理后,只需將以下程序上傳到 PIC 并打開模塊電源即可。如果一切正常,您的液晶屏應顯示“檢測到模塊”,“檢測到SIM卡”和“呼叫已放置”。一旦您看到“已撥打電話”,您將接到程序中指定的號碼的來電。
您也可以嘗試撥打GSM模塊中的號碼,LCD將顯示“來電”以指示正在呼叫SIM卡。

// CONFIG
#pragma config FOSC = HS // Oscillator Selection bits (HS oscillator)
#pragma config WDTE = OFF // Watchdog Timer Enable bit (WDT disabled)
#pragma config PWRTE = OFF // Power-up Timer Enable bit (PWRT enabled)
#pragma config BOREN = OFF // Brown-out Reset Enable bit (BOR enabled)
#pragma config LVP = OFF // Low-Voltage (Single-Supply) In-Circuit Serial Programming Enable bit (RB3 is digital I/O, HV on MCLR must be used for programming)
#pragma config CPD = OFF // Data EEPROM Memory Code Protection bit (Data EEPROM code protection off)
#pragma config WRT = OFF // Flash Program Memory Write Enable bits (Write protection off; all program memory may be written to by EECON control)
#pragma config CP = OFF // Flash Program Memory Code Protection bit (Code protection off)
//End of CONFIG registers
#define _XTAL_FREQ 20000000
#define RS RD2
#define EN RD3
#define D4 RD4
#define D5 RD5
#define D6 RD6
#define D7 RD7
#define SIM900_OK 1
#define SIM900_READY 2
#define SIM900_FAIL 3
#define SIM900_RING 4
#define SIM900_NC 5
#define SIM900_UNLINK 6
#include-
微控制器
+關注
關注
48文章
7922瀏覽量
153790 -
PIC
+關注
關注
8文章
507瀏覽量
88783 -
GSM模塊
+關注
關注
6文章
48瀏覽量
23436
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
STM32 GSM打電話和SIM900A模塊命令手冊
基于SIM900A的應用與實現(xiàn)
怎么才能使Atmel Studio 7.0將伺服電機與Atmega16 AVR微控制器連接起來?
GSM和GPRS的原理與應用詳解及SIM900A使設計一個雙頻GSM和GPRS模塊
使用Arduino實現(xiàn)GSM模塊SIM900A發(fā)短信的實驗免費下載
使用Arduino實現(xiàn)GSM模塊SIM900A打電話的實驗免費下載
單片機控制SIM900A型GSM模塊發(fā)送數(shù)字短信(附源碼)

將HC-05和MSP430連接起來控制LED的方式
將微型伺服電機與Atmega16連接起來的方法

AN4309_將STM32L1xx微控制器與外部I2S音頻編解碼器連接起來播放音頻文件

將RF 433MHz發(fā)射器/接收器模塊與MCU連接起來




















評論