第一次接觸RTTI,是在<<深度探索c++對象模型>>這本書中,當時對這塊的理解比較淺,可能因為知識積累不足吧。后面在工作中用到的越來越多,也逐漸加深了對其認識,但一直沒有一個系統的認知,所以抽出一段時間,把這塊內容整理下。
背景
RTTI的英文全稱是"Runtime Type Identification",中文稱為"運行時類型識別",它指的是程序在運行的時候才確定需要用到的對象是什么類型的。用于在運行時(而不是編譯時)獲取有關對象的信息。
在C++中,由于存在多態行為,基類指針或者引用指向一個派生類,而其指向的真正類型,在編譯階段是無法知道的:
Base*b=newDerived;
Base&b1=*b;
在上述代碼中,如果想知道b的具體類型,只能通過其他方式,而RTTI正是為了解決此問題而誕生,也就是說在運行時,RTTI可以通過特有的方式來告訴調用方其所調用的對象具體信息,一般有如下幾種:
-
?
typeid操作符 -
?
type_info類 -
?
dynamic_cast操作符
typeid 和 type_info
typeid是C++的關鍵字之一,等同于sizeof這類的操作符。用來獲取類型、變量、表達式的類型信息,適用于C++基礎類型、內置類、用戶自定義類、模板類等。有如下兩種形式:
-
?
typeid(type) -
?
typeid(expr)
用法如下:
#include
返回值
在上面的例子中,用到了了typeid(xxx).name(),通過其名稱可以看出name()函數返回的是具體類型的變量名稱(以字符串的方式),那么typeid()的類型又是什么?
在翻閱了cppreference之后了解到,typeid操作符的結果是名為type_info的標準庫類型的對象的引用(在頭文件
ISO C++標準并沒有對type_info有明確的要求,僅僅要求必須有以下幾個行為接口:
-
? t1 == t2 // 如果兩個對象t1和t2類型相同,則返回true;否則返回false
-
? t1 != t2 // 如果兩個對象t1和t2類型不同,則返回true;否則返回false
-
?t.name() // 返回類型的C-style字符串
-
?t1.before(t2) // 抱歉,我沒用過
正是因為標準對type_info做了有限的規定,這就使得每個編譯器廠商對type_info類的實現均不相同,從而使得函數功能也不盡相同。以常用的函數typeid().name()舉例,int和Base(自定義類)在VS下輸出分別為int和Base,而在gcc編譯器下,其輸出為i和4Base,又比如typeid(std::vector).name()在gcc下輸出為St6vectorIiSaIiEE,這是因為編譯期對名稱進行了mangle,如果我們想得到跟VS下一樣結果的話,可以采用如下方式:
#include
輸出如下:
before:St6vectorIiSaIiEEafter:std::vector<int,std::allocator<int>>
下面是gcc編譯器對type_info類的定義(僅抽取了聲明部分),如果有興趣的讀者可以點擊鏈接自行閱讀:
classtype_info{
public:
virtual~type_info();
constchar*name()const;
boolbefore(consttype_info&__arg)const;
booloperator==(consttype_info&__arg)const;
boolbefore(consttype_info&__arg)const;
booloperator==(consttype_info&__arg)const;
boolbefore(consttype_info&__arg)const;
booloperator==(consttype_info&__arg)const;
booloperator!=(consttype_info&__arg)const;
size_thash_code()constthrow();
virtualbool__is_pointer_p()const;
virtualbool__is_function_p()const;
virtualbool__do_catch(consttype_info*__thr_type,void**__thr_obj,
unsigned__outer)const;
virtualbool__do_upcast(const__cxxabiv1::__class_type_info*__target,
void**__obj_ptr)const;
protected:
constchar*__name;
explicittype_info(constchar*__n):__name(__n){}
private:
type_info&operator=(consttype_info&);
type_info(consttype_info&);
};
從上述定義可以看出,其析構函數聲明為virtual,至少可以說明其存在子對象,那么子對象又是如何被使用的呢?
其實,type_info可以當做一個接口類(通過調用typeid()獲取type_info對象,實際上返回的是一個指向子類對象的type_info引用),其有多個子類,對于有虛函數的類來說,在虛函數表中有一個slot專門用來存儲該對象的信息,這塊內容在文章后面將有詳細說明。
實現
在前面有提到,typeid()會返回一個const std::type_info&對象,其中存儲這對象的基本信息,那么如果其類型對象為多態和非多態時候,其又有什么區別呢?
如果類型對象至少包含一個虛函數,那么typeid操作符的類型是運行時的事情,也就是說在運行時才能獲取到其真正的類型信息;否則,在編譯期就能獲取其具體類型,甚至在某些情況下,可以對typeid()的結果直接進行替換。
多態
多態,我們知道經常用于運行時,也就是說在運行時刻才會知道其指針或者引用指向的具體類型,如果要對一個包含虛函數的對象獲取其類型信息(typeid),那么也是在運行時才能具體知道,舉例如下:
#include
上述代碼匯編后(只取了部分關鍵代碼),如下所示:
fun(Base*):
pushrbp
movrbp,rsp
movQWORDPTR[rbp-24],rdi
movQWORDPTR[rbp-8],OFFSETFLAT:typeinfoforBase*
poprbp
ret
vtableforDerived:
.quad0
.quadtypeinfoforDerived
.quadDerived::fun()
vtableforBase:
.quad0
.quadtypeinfoforBase
.quadBase::fun()
typeinfonameforBase*:
.string"P4Base"
typeinfoforBase*:
.quadvtablefor__cxxabiv1::__pointer_type_info+16
.quadtypeinfonameforBase*
.long0
.zero4
.quadtypeinfoforBase
typeinfonameforDerived:
.string"7Derived"
typeinfoforDerived:
.quadvtablefor__cxxabiv1::__si_class_type_info+16
.quadtypeinfonameforDerived
.quadtypeinfoforBase
typeinfonameforBase:
.string"4Base"
typeinfoforBase:
.quadvtablefor__cxxabiv1::__class_type_info+16
.quadtypeinfonameforBase
首先,我們看fun()函數的匯編(fun(Base*):處),在其中有一行OFFSET FLAT:typeinfo for Base*代表獲取Base指針所指向對象的typeinfo。那么typeinfo又是如何獲取的呢?
我們以Base指針實際指向Derived對象為例,vtable for Derived:部分代表著Derived類的虛函數表內容,其中有一行typeinfo for Derived代表著Derived類的typeinfo信息,而在該段中有一句typeinfo name for Derived代表著該類的名稱(7Derived經過mangle之后,該句在上述代碼中可以找到)。
綜上內容,可以知道,對于存在虛函數的類來說,其對象的typeinfo信息存儲在該類的虛函數表中。在運行時刻,根據指針的實際指向,獲取其typeinfo()信息,從而進行相關操作。
其實,不難看出,上述匯編基本列出了類的對象布局,但仍然不是很清晰,gcc提供了一個參數-fdump-class-hierarchy,可以輸出類的布局信息,仍然以上述代碼為例,其布局信息如下:
VtableforBase
Base:3uentries
0(int(*)(...))0
8(int(*)(...))(&_ZTI4Base)
16(int(*)(...))Base::fun
ClassBase
size=8align=8
basesize=8basealign=8
Base(0x0x7f59773402a0)0nearly-empty
vptr=((&Base::_ZTV4Base)+16u)
VtableforDerived
Derived:3uentries
0(int(*)(...))0
8(int(*)(...))(&_ZTI7Derived)
16(int(*)(...))Derived::fun
ClassDerived
size=8align=8
basesize=8basealign=8
Derived(0x0x7f59773756e8)0nearly-empty
vptr=((&Derived::_ZTV7Derived)+16u)
Base(0x0x7f5977340300)0nearly-empty
primary-forDerived(0x0x7f59773756e8)
我們注意查看,以_ZTI開頭的代表類型信息,也就是Type Info的意思(至于以_Z的意思嘛,我理解的是編譯器的行為),那么_ZTI7Derived前面的_ZTI代表類型信息,而后面7代表類名(Derived)的長度,最后面的代表類名。通過上面內存布局信息可以看出,在虛函數表中存在一項_ZTI7Derived,其中存儲著該對類的類型信息。
如果想要知道其具體名稱,可以使用c++filt來查看,如下:
c++filt_ZTI7Derived
typeinfoforDerived
非多態
代碼如下:
#include
在上述代碼中,實現了一個空類MyClass,然后在main()中,獲取該類對象的typeinfo,上述代碼匯編如下:
main:
pushrbp
movrbp,rsp
movQWORDPTR[rbp-8],OFFSETFLAT:typeinfoforMyClss
moveax,0
poprbp
ret
typeinfonameforMyClss:
.string"6MyClss"
typeinfoforMyClss:
.quadvtablefor__cxxabiv1::__class_type_info+16
.quadtypeinfonameforMyClss
我們注意下在源碼中的第三行即const std::type_info &info = typeid(s);對應匯編的第三行即QWORD PTR [rbp-8], OFFSET FLAT:typeinfo for MyClss,從而可以看出,在編譯期,編譯器已經知道了對象的具體信息,進而可以在某些情況下,直接由編譯器進行替換(比如typeinf().name()操作等)。
dynamic_cast
記得在幾年前的一次面試中,面試官提了個問題,對于dynamic_cast,如果操作失敗了會有什么行為?當時對這塊理解的也不深,所以僅僅回答了:對于指針類型轉換,如果失敗,則返回NULL,而對于引用,轉換失敗就拋出bad_cast。
作為C++開發人員,基本都知道dynamic_cast是C++中幾個常用的類型轉換符之一,其通過類型信息(typeinfo)進行相對安全的類型轉換,在轉換時,會檢查轉換的src對象是否真的可以轉換成dst類型。dynamic_cast轉換符只能用于含有虛函數的類,因此其常常用于運行期,對于不包括虛函數的類,完全可以使用其它幾個轉換符在編譯期進行轉換。通常來說,其類型轉換分為向上轉換和向下轉換兩種,如下圖所示:
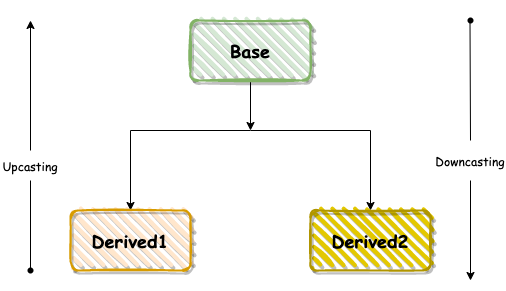
實例代碼如下:
#include(b1);//downcasting向下轉換
return0;
}
實現
通過查閱資料,發現dynamic_cast最終會調用libstdc++中的__dynamic_cast函數,所以曾經以為__dynamic_cast函數就是dynamic_cast的實現版本,但是通過對比參數,發現并非如此:
dynamic_cast(t);//只有一個參數
//__dynamic_cast聲明
__dynamic_cast(constvoid*src_ptr,//objectstartedfrom
const__class_type_info*src_type,//typeofthestartingobject
const__class_type_info*dst_type,//desiredtargettype
ptrdiff_tsrc2dst)//howsrcanddstarerelated
所以,有沒有可能__dynamic_cast只是dynamic_cast的一個分支實現?
為了驗證猜測,示例如下:
#include(t)){
n|=1;
}
if(dynamic_cast(t)){
n|=2;
}
if(dynamic_cast(t)){
n|=4;
}
returnn;
}
intmain(){
Derived*d=newDerived;
Base1*b1=newBase1;
Base2*b2=newBase2;
CheckType(d);
CheckType(b1);
CheckType(b2);
return0;
}
既然本節內容是dynamic_cast,而只在CheckType()函數中才有對dynamic_cast的調用,那么我們著重分析CheckType函數。
首先,我們通過g++的命令-fdump-class-hierarchy獲取其內存布局,Derived內存布局如下(需要注意32 (int (*)(...))-16和Base2 (0x0x7f7fbbe5b6c0) 16部分):
VtableforDerived
Derived:7uentries
0(int(*)(...))0
8(int(*)(...))(&_ZTI7Derived)
16(int(*)(...))Base1::f1
24(int(*)(...))Derived::f2
32(int(*)(...))-16
40(int(*)(...))(&_ZTI7Derived)
48(int(*)(...))Derived::_ZThn16_N7Derived2f2Ev
ClassDerived
size=32align=8
basesize=32basealign=8
Derived(0x0x7f7fbbf10c40)0
vptr=((&Derived::_ZTV7Derived)+16u)
Base1(0x0x7f7fbbe5b660)0
primary-forDerived(0x0x7f7fbbf10c40)
Base2(0x0x7f7fbbe5b6c0)16
vptr=((&Derived::_ZTV7Derived)+48u)
向上轉換
在CheckType(Derived*)處,通過gdb進行分析,如下:
(gdb)disas
Dumpofassemblercodeforfunction_Z9CheckTypeIP7DerivedEiT_:
0x00000000004009ce<+0>:push%rbp
0x00000000004009cf<+1>:mov%rsp,%rbp
0x00000000004009d2<+4>:mov%rdi,-0x18(%rbp)
=>0x00000000004009d6<+8>:movl$0x0,-0x4(%rbp)
0x00000000004009dd<+15>:cmpq$0x0,-0x18(%rbp)
0x00000000004009e2<+20>:je0x4009e8<_Z9CheckTypeIP7DerivedEiT_+26>
0x00000000004009e4<+22>:orl$0x1,-0x4(%rbp);ift!=nullptr
0x00000000004009e8<+26>:cmpq$0x0,-0x18(%rbp)
0x00000000004009ed<+31>:je0x4009f3<_Z9CheckTypeIP7DerivedEiT_+37>
0x00000000004009ef<+33>:orl$0x2,-0x4(%rbp);ift!=nullptr
0x00000000004009f3<+37>:cmpq$0x0,-0x18(%rbp)
0x00000000004009f8<+42>:je0x400a0b<_Z9CheckTypeIP7DerivedEiT_+61>
0x00000000004009fa<+44>:mov-0x18(%rbp),%rax
0x00000000004009fe<+48>:add$0x10,%rax
0x0000000000400a02<+52>:test%rax,%rax
0x0000000000400a05<+55>:je0x400a0b<_Z9CheckTypeIP7DerivedEiT_+61>
0x0000000000400a07<+57>:orl$0x4,-0x4(%rbp);ift!=nullptr&&t+0x10!=nullptr
0x0000000000400a0b<+61>:mov-0x4(%rbp),%eax
0x0000000000400a0e<+64>:pop%rbp
0x0000000000400a0f<+65>:retq
Endofassemblerdump.
為了便于理解,在上述代碼關鍵部分加上了注釋.
我們注意到,在上述匯編代碼中,沒有找到外部函數調用(__dynamic_cast),而僅僅是一些常用的跳轉和比較指令。其中,前兩條orl指令的執行條件為t不為0,而第三條orl指令的執行條件為t不為0且t+16不為0。這幾個行為是在編譯期完成的,也就是說在本例中,dynamic_cast由編譯器在編譯期實現了轉換,所以可以說其是靜態轉換。
在前面的內存布局中,Derived對象有3個偏移量,分別為(Derived/Base1 = 0, Base2 = +0x10),即相對于Derived和Base1其偏移量為0,而相對于Base2其偏移量為16。前兩個dynamic_cast是Derived* -> Derived* 和 Derived* -> Base1*,都不需要調整指針,所以在CheckType的if語句中使用t的值作為dynamic_cast的返回值。在第三次Derived* -> Base2*轉換中,編譯時知道地址是t+0x10,所以計算t+0x10的結果就是dynamic_cast的返回值。
至此,我們可以說,dynamic_cast操作中,向上轉換是靜態操作,在編譯階段完成。
向下轉換
在CheckType(Base1*)處,通過gdb進行分析,如下:
(gdb)disas
Dumpofassemblercodeforfunction_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_:
0x0000000000400a10<+0>:push%rbp
0x0000000000400a11<+1>:mov%rsp,%rbp
0x0000000000400a14<+4>:sub$0x20,%rsp
0x0000000000400a18<+8>:mov%rdi,-0x18(%rbp)
=>0x0000000000400a1c<+12>:movl$0x0,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000400a23<+19>:mov-0x18(%rbp),%rax
0x0000000000400a27<+23>:test%rax,%rax
0x0000000000400a2a<+26>:je0x400a4f<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+63>
0x0000000000400a2c<+28>:mov$0x0,%ecx;src2dst=0
0x0000000000400a31<+33>:mov$0x400c98,%edx;dst_type<_ZTV7Derived>
0x0000000000400a36<+38>:mov$0x400cf8,%esi;src_type<_ZTI5Base1>
0x0000000000400a3b<+43>:mov%rax,%rdi
0x0000000000400a3e<+46>:callq0x4006d0<__dynamic_cast@plt>
0x0000000000400a43<+51>:test%rax,%rax
0x0000000000400a46<+54>:je0x400a4f<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+63>
0x0000000000400a48<+56>:mov$0x1,%eax
0x0000000000400a4d<+61>:jmp0x400a54<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+68>
0x0000000000400a4f<+63>:mov$0x0,%eax
0x0000000000400a54<+68>:test%al,%al
0x0000000000400a56<+70>:je0x400a5c<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+76>
0x0000000000400a58<+72>:orl$0x1,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000400a5c<+76>:cmpq$0x0,-0x18(%rbp)
0x0000000000400a61<+81>:je0x400a67<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+87>
0x0000000000400a63<+83>:orl$0x2,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000400a67<+87>:mov-0x18(%rbp),%rax
0x0000000000400a6b<+91>:test%rax,%rax
0x0000000000400a6e<+94>:je0x400a95<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+133>
0x0000000000400a70<+96>:mov$0xfffffffffffffffe,%rcx;src2dst=-2
0x0000000000400a77<+103>:mov$0x400ce0,%edx;dst_type<_ZTI5Base2>
0x0000000000400a7c<+108>:mov$0x400cf8,%esi;src_type<_ZTI5Base1>
0x0000000000400a81<+113>:mov%rax,%rdi
0x0000000000400a84<+116>:callq0x4006d0<__dynamic_cast@plt>
0x0000000000400a89<+121>:test%rax,%rax
0x0000000000400a8c<+124>:je0x400a95<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+133>
0x0000000000400a8e<+126>:mov$0x1,%eax
0x0000000000400a93<+131>:jmp0x400a9a<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+138>
0x0000000000400a95<+133>:mov$0x0,%eax
0x0000000000400a9a<+138>:test%al,%al
0x0000000000400a9c<+140>:je0x400aa2<_Z9CheckTypeIP5Base1EiT_+146>
0x0000000000400a9e<+142>:orl$0x4,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000400aa2<+146>:mov-0x4(%rbp),%eax
0x0000000000400aa5<+149>:leaveq
---Typetocontinue,orqtoquit---
0x0000000000400aa6<+150>:retq
Endofassemblerdump.
通過上述匯編代碼,很明顯可以看出,Base1* -> Base1*不進行任何轉換(這不廢話嘛,類型是相同的)。而對于Base1* -> Derived* 以及 Base1* -> Base2* 則需要調用__dynamic_cast函數,而其所需要的參數,在匯編指令中也可以看出,下面將對該函數進行詳細分析。
__dynamic_cast參數語義
聲明如下:
__dynamic_cast(constvoid*src_ptr,//objectstartedfrom
const__class_type_info*src_type,//typeofthestartingobject
const__class_type_info*dst_type,//desiredtargettype
ptrdiff_tsrc2dst)//howsrcanddstarerelated
在上述聲明中:
-
?src_ptr代表需要轉換的指針
-
?src_type原始類型
-
?dst_type目標類型
-
?src2dst表示從dst到src的偏移量,當該值為如下3個之一時候,有特殊含義:
-
?-1: no hint
-
?-2: src is not a public base of dst
-
?-3: src is a multiple public base type but never a virtual base type
-
src2dst的值中,-2代表src 不是 dst 的公共基類,如上節中的Base1* -> Base2*;-3代表src是多個(dst的)公共基類并且不是虛基類,即沒有虛擬繼承的菱形繼承。如果不為-1 -2 -3三值之一,則src2dst代表src和dst的偏移,如上一節中從Base1* -> Base1*轉換的時候傳值為0,即偏移為0;Base1*->Base2*轉換的時候,傳的值為-2(0xfffffffffffffffe)。
__dynamic_cast實現
extern"C"void*
__dynamic_cast(constvoid*src_ptr,//objectstartedfrom
const__class_type_info*src_type,//typeofthestartingobject
const__class_type_info*dst_type,//desiredtargettype
ptrdiff_tsrc2dst)//howsrcanddstarerelated
{
constvoid*vtable=*static_cast<constvoid*const*>(src_ptr);
constvtable_prefix*prefix=
adjust_pointer(vtable,
-offsetof(vtable_prefix,origin));
constvoid*whole_ptr=
adjust_pointer<void>(src_ptr,prefix->whole_object);
const__class_type_info*whole_type=prefix->whole_type;
__class_type_info::__dyncast_resultresult;
//Ifthewholeobjectvptrdoesn'trefertothewholeobjecttype,we're
//inthemiddleofconstructingaprimarybase,andsrcisaseparate
//base.Thishasundefinedbehaviorandwecan'tfindanythingoutside
//ofthebasewe'reactuallyconstructing,sofailnowratherthan
//segfaultlatertryingtouseavbaseoffsetthatdoesn'texist.
constvoid*whole_vtable=*static_cast<constvoid*const*>(whole_ptr);
constvtable_prefix*whole_prefix=
adjust_pointer(whole_vtable,
-offsetof(vtable_prefix,origin));
constvoid*whole_vtable=*static_cast<constvoid*const*>(whole_ptr);
constvtable_prefix*whole_prefix=
(adjust_pointer
(whole_vtable,-ptrdiff_t(offsetof(vtable_prefix,origin))));
if(whole_prefix->whole_type!=whole_type)
returnNULL;
//Avoidvirtualfunctioncallinthesimplesuccesscase.
if(src2dst>=0
&&src2dst==-prefix->whole_object
&&*whole_type==*dst_type)
returnconst_cast<void*>(whole_ptr);
whole_type->__do_dyncast(src2dst,__class_type_info::__contained_public,
dst_type,whole_ptr,src_type,src_ptr,result);
...
這個函數先通過src_ptr來初始化部分局部變量:
-
?vtable通過對src_ptr解引用(deref)獲取
-
?vtable_prefix子對象虛函數表地址,通過vtable的類型信息和offset_to_top來獲取
-
?whole_ptrsrc_ptr最底層的派生類地址,一般為src_ptr的值加上offset_to_top
-
?whole_typesrc_ptr最底層的派生類的虛函數表中的類型信息(type info)
-
?whole_vtablewhole對象的虛函數表地址
然后調用whole_type->__do_dyncast,而這也是該函數的核心模塊。然后根據返回值的內容來判斷結果,并進行相應的操作。
其中,vtable_prefix的定義如下:
structvtable_prefix
{
//Offsettomostderivedobject.
ptrdiff_twhole_object;
//Pointertomostderivedtype_info.
const__class_type_info*whole_type;
//Whataclass'svptrpointsto.
constvoid*origin;
};
-
?whole_object 表示當前指針指向對象的偏移量
-
? whole_type 指向 C++ 對象的類型:class(基類)、si_class(單一繼承類型)、vmi_class(多重或虛擬繼承類型)
-
? origin 表示虛函數表的入口,等于實例的虛指針。origin在這里的作用是offsetof,反向獲取whole_object的指針。
__class_type_info::__dyncast_result 定義如下:
struct__class_type_info::__dyncast_result
{
constvoid*dst_ptr;//pointertotargetobjectorNULL
__sub_kindwhole2dst;//pathfrommostderivedobjecttotarget
__sub_kindwhole2src;//pathfrommostderivedobjecttosubobject
__sub_kinddst2src;//pathfromtargettosubobject
intwhole_details;//detailsofthewholeclasshierarchy
...
在前面提到,__do_dyncast被調用之后,后面就根據其出參result的返回值進行各種判斷,那么result到底什么意思呢?其實,從上述定義就能看出,whole2dst代表whole對象向dst的轉換結果,而whole2src代表whole對象向src的轉換結果等,通過下面的圖能更加清晰的理解轉換過程:
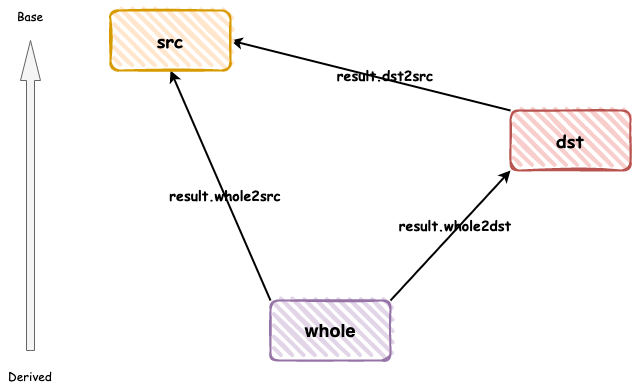
在上圖中,有3中類型,src、whole以及dst,__do_dyncast函數功能則是提供該3中類型的轉換結果,在只有滿足以下3中情況時候,__dynamic_cast才返回非空:
-
?src是dst的公共基類
-
?dst和src不是直接繼承的關系,但是whole2src和whole2dst都是public
-
?dst2src未知且whole2src是非public虛繼承關系,則不使用whole,重新獲取dst和src的關系
這塊邏輯比較繞,其實可以將關系理解為圖上的一條條連接線,節點理解為類型信息,dynamic_cast的過程,就是判斷有沒有從src到dst有沒有路徑的過程。
繼承關系
在前面的內容中,遇到過vtable for __cxxabiv1::__si_class_type_info+16這種,那么si_class_type_info又是什么呢?同樣,在翻閱了源碼之后,發現其是gcc中繼承關系的一種。
在gcc中,將繼承關系表示為圖結構,對于類,有以下三種類型(type info):
-
?class __class_type_info : public std::type_info
-
?class __si_class_type_info : public __class_type_info
-
?class __vmi_class_type_info : public __class_type_info
其中,__class_type_info 表示沒有繼承關系的類,__si_class_type_info 表示單繼承的類,__vmi_class_type_info 表示多繼承或虛擬繼承的類。類名開頭的si代表單繼承,vmi代表虛擬或多重繼承。
查看定義,__si_class_type_info 包含指向基類類型的單個指針,而 __vmi_class_type_info 包含指向基類類型的指針數組。基類類型存儲其子對象的位置和基類的類型(public、virtual)。
仍然以上一節中的代碼為例,使用gdb來分析__ZTI7Derived、__ZTI5Base1、__ZTI5Base2的關系
(gdb)x/2xg&_ZTI7Derived
0x555555755d80<_ZTI7Derived>:0x00007ffff7dca5d80x0000555555554d74
(gdb)x/2xg0x00007ffff7dca5d8
0x7ffff7dca5d8<_ZTVN10__cxxabiv121__vmi_class_type_infoE+16>:0x00007ffff7ae09200x00007ffff7ae0940
(gdb)p*(__cxxabiv1::__vmi_class_type_info*)0x555555755d80
$2={
<__cxxabiv1::__class_type_info>={
={
_vptr.type_info=0x7ffff7dca5d8,
__name=0x555555554d74"7Derived"
},},
membersof__cxxabiv1:
__flags=0,
__base_count=2,
__base_info={{
__base_type=0x555555755dc8,
__offset_flags=2
}}
(gdb)p(*(__cxxabiv1::__vmi_class_type_info*)0x555555755d80)->__base_info[0]
$4={
__base_type=0x555555755dc8,
__offset_flags=2<----?__public_mask(2)?|?offset:0x00
}
(gdb)?p?(*(__cxxabiv1::__vmi_class_type_info*)0x555555755d80)->__base_info[1]
$5={
__base_type=0x555555755db8,
__offset_flags=4098<----?__public_mask(2)?|?offset:0x10
}
(gdb)?x/2xg?0x555555755dc8
0x555555755dc8?<_ZTI5Base1>:0x00007ffff7dc98d80x0000555555554d7b
(gdb)x/2xg0x00007ffff7dc98d8
0x7ffff7dc98d8<_ZTVN10__cxxabiv117__class_type_infoE+16>:0x00007ffff7add9300x00007ffff7add950
(gdb)x/2xg0x555555755db8
0x555555755db8<_ZTI5Base2>:0x00007ffff7dc98d80x0000555555554d77
(gdb)x/2xg0x00007ffff7dc98d8
0x7ffff7dc98d8<_ZTVN10__cxxabiv117__class_type_infoE+16>:0x00007ffff7add9300x00007ffff7add950
(gdb)p*(__cxxabiv1::__class_type_info*)0x555555755dc8
$6={
={
_vptr.type_info=0x7ffff7dc98d8,
__name=0x555555554d7b"5Base1"
},}
(gdb)p*(__cxxabiv1::__class_type_info*)0x555555755db8
$7={
={
_vptr.type_info=0x7ffff7dc98d8,
__name=0x555555554d77"5Base2"
},}
通過上述代碼,可以看出_ZTI7Derived是__vmi_class_type_info的一個實例,其基類數組的類型分別是_ZTI5Base1和_ZTI5Base2,通過將這些類型展開,就能獲取一張圖結構,進而說明dynamic_cast的過程就是遍歷圖結構確定路徑關系的過程,采用的是深度優先搜索。
審核編輯 :李倩
-
C++
+關注
關注
22文章
2108瀏覽量
73623 -
代碼
+關注
關注
30文章
4779瀏覽量
68525 -
編譯
+關注
關注
0文章
657瀏覽量
32852
原文標題:C++:從技術實現角度聊聊RTTI
文章出處:【微信號:CPP開發者,微信公眾號:CPP開發者】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
ostream在c++中的用法
OpenVINO2024 C++推理使用技巧
C++中實現類似instanceof的方法
C/C++中兩種宏實現方式
使用 MISRA C++:2023? 避免基于范圍的 for 循環中的錯誤

c語言,c++,java,python區別
vb語言和c++語言的區別
C++簡史:C++是如何開始的





 C++:從技術實現角度聊聊RTTI
C++:從技術實現角度聊聊RTTI












評論