文章作者:李翊瑋 &Aidova, Ekaterina
前言
以下為當(dāng)前一代大型語言模型(LLM)的基石說明。
人類偏好強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí)Reinforcement learning with human preferences(RLHF)和 InstructGPT 等技術(shù)一直是 ChatGPT 和 GPT-4 等突破的核心基礎(chǔ)。
關(guān)于 RLHF:
關(guān)于 InstructGPT :
然而,這些強(qiáng)大的模型仍然隱藏在 API 后面,我們對它們的底層架構(gòu)知之甚少。指令遵循模型能夠生成文本以響應(yīng)提示(Prompt),通常用于協(xié)助編寫創(chuàng)作、聊天機(jī)器人和內(nèi)容生成等任務(wù)。許多用戶現(xiàn)在定期與這些模型交互,甚至將它們用于工作,但大多數(shù)此類模型仍然是閉源的,需要大量的計(jì)算資源進(jìn)行實(shí)驗(yàn)。
Dolly 2.0 是第一個(gè)開源的,遵循指令的 LLM,由 Databricks 在一個(gè)透明且免費(fèi)提供的數(shù)據(jù)集上進(jìn)行微調(diào),該數(shù)據(jù)集也是開源的,可用于商業(yè)目的。這意味著 Dolly 2.0 可用于商業(yè)應(yīng)用程序,而無需支付 API 訪問費(fèi)用或與第三方共享數(shù)據(jù)。盡管比 ChatGPT 要小得多 Dolly 2.0 也可表現(xiàn)出類似的特征。
接下來讓我們用來自原基科技帶有英特爾銳炫顯卡的 B18盒子配上OpenVINO Notebooks 開源代碼示例在本地端體驗(yàn)大語言模型的魅力吧!

安裝OpenVINO Notebooks
運(yùn)行相關(guān)工具及必要項(xiàng)
安裝 Git, Anaconda,Python,C++ Redistributable (For Python 3.8) 及 Anaconda
Git:
https://git-scm.com/
Python:
https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.8.8/python-3.8.8-amd64.exe
C++ Redistributable (For Python 3.8):
https://aka.ms/vs/16/release/vc_redist.x64.exe
Anaconda:
https://www.anaconda.com/
創(chuàng)建環(huán)境
conda create -n openvino_env python=3.9
運(yùn)行結(jié)果如下:
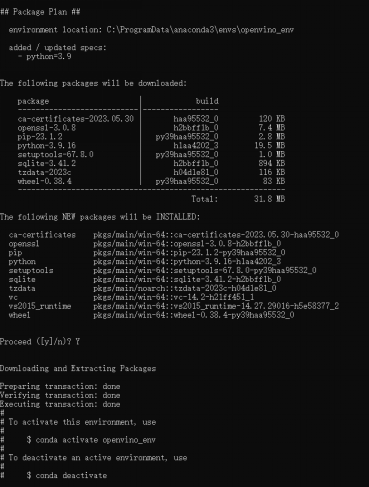
啟用環(huán)境 openvino_env
conda activate openvino_env
命令行開頭有“(openvino_env)”即為啟用成功。
用 Git 下載OpenVINO Notebooks 庫并進(jìn)入資料夾。
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git cd openvino_notebooks
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
安裝運(yùn)行相關(guān)包及必須項(xiàng),pip 使用清華鏡像:https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package
安裝約5-10分鐘。
python -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel setuptools pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
啟用OpenVINO Notebooks
jupyter lab notebooks
運(yùn)行成功會(huì)跳出網(wǎng)頁,挑選 Notebooks 里 240-dolly-2-instruction-following, 開始體驗(yàn)大模型的魅力及了解其機(jī)理。
LLM 大模型 Databricks Dolly 2.0和
OpenVINO 的使用說明
在本教程中,我們將研究如何使用Dolly 2.0 和OpenVINO運(yùn)行遵循指令的文本生成管道。我們將使用來自擁抱面變壓器庫中的預(yù)訓(xùn)練模型。為了簡化用戶體驗(yàn),擁抱面最佳英特爾庫用于將模型轉(zhuǎn)換為 OpenVINO IR 格式。
本 Notebooks 包括以下步驟:
安裝包及必要項(xiàng)
下載公開的模型并利用以下工具轉(zhuǎn)換OpenVINO Notebooks integration with Hugging Face Optimum:
https://huggingface.co/blog/openvino
建立指令推理管道(build Pipeline)
運(yùn)行指令推理管道(run Pipeline)
關(guān)于Dolly 2.0
Dolly 2.0 是在 Databricks 機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)平臺(tái)上訓(xùn)練的指令遵循大型語言模型,已獲得商業(yè)用途許可。它基于 Pythia,并接受 Databricks 員工在各種能力領(lǐng)域生成的~15k 指令/響應(yīng)微調(diào)記錄的培訓(xùn),包括頭腦風(fēng)暴、分類、封閉 QA、生成、信息提取、開放 QA 和總結(jié)。Dolly 2.0 的工作原理是處理自然語言指令并生成遵循給定指令的響應(yīng)。它可用于廣泛的應(yīng)用,包括封閉式問答、總結(jié)和生成。
模型訓(xùn)練過程的靈感來自 InstructGPT。為了訓(xùn)練 InstructGPT 模型,核心技術(shù)是從人類反饋(RLHF)中強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí),這種技術(shù)使用人類偏好作為獎(jiǎng)勵(lì)信號來微調(diào)模型,這很重要,因?yàn)樾枰鉀Q的安全和對齊問題是復(fù)雜和主觀的,并且不能完全被簡單的自動(dòng)指標(biāo)捕獲。有關(guān) InstructGPT 方法的更多詳細(xì)信息,請參閱 OpenAI 博客文章。
InstructGPT 發(fā)現(xiàn)的突破是語言模型不需要越來越大的訓(xùn)練集。通過使用人工評估的問答訓(xùn)練,作者能夠使用比以前的模型少一百倍的參數(shù)來訓(xùn)練更好的語言模型。Databricks 使用類似的方法來創(chuàng)建一個(gè)提示和響應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)集,稱為 databricks-dolly-15k。
這是一個(gè)由數(shù)千名 Databricks 員工生成的超過15,000條記錄的語料庫,使大型語言模型能夠展示 InstructGPT 的神奇交互性。有關(guān)模型和數(shù)據(jù)集的更多詳細(xì)信息,請參閱 Databricks 博客文章和存儲(chǔ)庫。
存儲(chǔ)庫:
https://github.com/databrickslabs/dolly
Hugging Face Optimum Intel API
首先,我們用以下代碼安裝由OpenVINO 集成 Hugging Face Optimum 庫。Hugging Face Optimum英特爾 API 是一個(gè) high-level API,使我們能夠?qū)?Hugging Face Transformers library 中的模型轉(zhuǎn)換和量化為OpenVINO IR 格式。有關(guān)更多詳細(xì)信息,請參閱 Hugging Face Optimum 英特爾 documentation 文檔。
!pip install -q "diffusers>=0.16.1" "transformers>=4.28.0" !pip install -q "git+https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel.git" datasets onnx onnxruntime gradio
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
下載及轉(zhuǎn)換模型
(注意:此模型大小約10GB)
Optimal 英特爾可從 Hugging Face Hub 加載優(yōu)化模型,并可創(chuàng)建 Pipeline 用OpenVINOrun time 并調(diào)用 Hugging Face APIs 運(yùn)行推理。Optimum 推理模型與 Hugging Face Transformers 模型的 API 是兼容。這意味著我們只需要將 AutoModelForXxx 類替換為相應(yīng)的 OVModelForXxx 類即可。
下面是 Dolly model 的示例:
-from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM +from optimum.intel.openvino import OVModelForCausalLM from transformers import AutoTokenizer, pipeline model_id = "databricks/dolly-v2-3b" -model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id) +model = OVModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, from_transformers=True)
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
模型類初始化從調(diào)用from_pretrained 開始。當(dāng)下載及轉(zhuǎn)換模型, 需添加此參數(shù) from_transformers=True。我們用 save_pretrained 儲(chǔ)存轉(zhuǎn)換模型。Tokenizer class and pipelines API 是與 Optimus 模型兼容的。
from pathlib import Path
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVModelForCausalLM
model_id = "databricks/dolly-v2-3b"
model_path = Path("dolly-v2-3b")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
current_device = "CPU"
if model_path.exists():
ov_model = OVModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, device=current_device)
else:
ov_model = OVModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device=current_device, from_transformers=True)
ov_model.save_pretrained(model_path)
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
運(yùn)行結(jié)果

創(chuàng)建遵循指令的推理管道
(Inference Pipeline)
run_generation函數(shù)接受用戶提供的文本輸入,對其進(jìn)行令牌(Token)化,然后運(yùn)行生成過程。文本生成是一個(gè)迭代過程,其中每個(gè)下一個(gè)標(biāo)記都依賴于先前生成的令牌,直到達(dá)到最大令牌數(shù)或停止生成條件。為了獲得中間生成結(jié)果而不需等到生成完成,我們將使用 TextIteratorStreamer,作為 HuggingFace Streaming API 的一部分提供。
TextIteratorStreamer
HuggingFace Streaming API
下圖說明了指令遵循管道的工作原理:
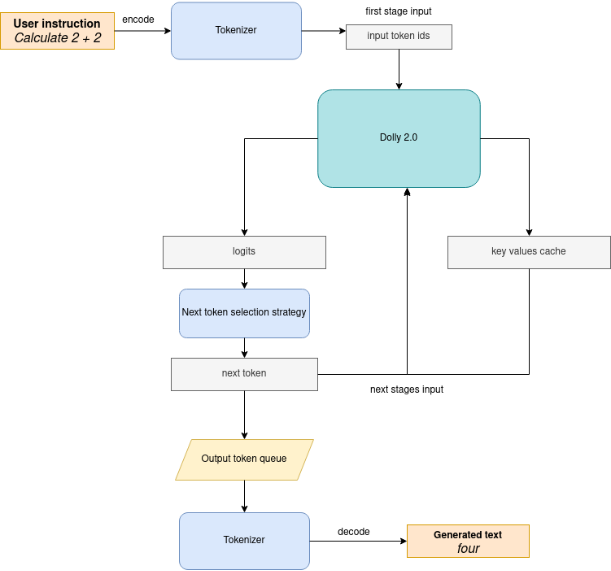
可以看出,在第一次迭代中,用戶提供的指令使用分詞器轉(zhuǎn)換為令牌 ID,然后準(zhǔn)備的輸入提供給模型。該模型以 logits 格式為所有令牌生成概率在預(yù)測概率上選擇下一個(gè)令牌的方式由所選解碼方法驅(qū)動(dòng)。您可以在此博客中找到有關(guān)最流行的解碼方法的更多信息。
有幾個(gè)參數(shù)可以控制文本生成質(zhì)量:
#·1
Temperature是用于控制 AI 生成文本中創(chuàng)造力水平的參數(shù)。通過調(diào)整 Temperature,您可以影響 AI 模型的概率分布,使文本更加集中或多樣化。考慮以下示例:AI 模型必須使用以下令牌概率完成句子“The cat is ____.”:
playing: 0.5
sleeping: 0.25
eating: 0.15
driving: 0.05
flying: 0.05
Low temperature(e.g., 0.2): AI 模型變得更加集中和確定性,選擇概率最高的令牌,例如"playing."
Medium temperature(e.g., 1.0): AI 模型在創(chuàng)造力和專注力之間保持平衡,根據(jù)其概率選擇令牌,沒有明顯的偏見,例如"playing," "sleeping," or "eating."
High temperature(e.g., 2.0): AI 模型變得更加冒險(xiǎn),增加了選擇不太可能的令牌的機(jī)會(huì),例如"driving" and "flying."
#·2
Top-p 也稱為核心采樣(nucleus sampling),用于根據(jù)累積概率控制 AI 模型考慮的令牌范圍的參數(shù)。通過調(diào)整 Top-p值,您可以影響 AI 模型的令牌選擇,使其更加集中或多樣化。對相同的示例 cat ,請考慮以下 top_p 設(shè)置:
Low top_p(e.g., 0.5): AI 模型僅考慮累積概率最高的令牌,例如"playing."
Medium top_p(e.g., 0.8): AI 模型考慮具有較高累積概率的令牌,例如"playing," "sleeping," and "eating."
High top_p(e.g., 1.0): AI 模型考慮所有令牌,包括概率較低的令牌,例如"driving" and "flying."
#·3
Top-k是另一種流行的采樣策略。與 Top-P 進(jìn)行比較,Top-P 從累積概率超過概率 P 的最小可能單詞組進(jìn)行選擇,在 Top-K 抽樣中,K 最有可能被過濾掉下一個(gè)單詞,并且概率質(zhì)量僅在下一個(gè) K 個(gè)單詞之間重新分配。在我們的 cat 示例中,如果 k=3,則只有“playing”、“sleeping”和“eathing”將被考慮為下一個(gè)單詞。
為了優(yōu)化生成過程并更有效地使用內(nèi)存,請啟用use_cache=True選項(xiàng)。由于輸出端是自動(dòng)回歸的,因此輸出令牌隱藏狀態(tài)在計(jì)算后每進(jìn)一步生成步驟后保持不變。因此,每次想要生成新令牌時(shí)重新計(jì)算它似乎很浪費(fèi)。使用緩存,模型會(huì)在計(jì)算后保存成隱藏狀態(tài)。該模型僅在每個(gè)時(shí)長計(jì)算最近要生成的輸出令牌的令牌,將保存的令牌重用于隱藏令牌。這將transformer模型的生成復(fù)雜度從 O(n^3) 降低到 O(n^2)。有關(guān)其工作原理的更多詳細(xì)信息,請參閱文章。
使用此選項(xiàng),模型獲取上一步的隱藏狀態(tài)(緩存的attention keys和values)作為輸入,此外還提供當(dāng)前步驟的隱藏狀態(tài)作為輸出。這意味著對于所有后續(xù)迭代,只需提供從上一步獲得的新令牌和緩存的鍵值即可獲得下一個(gè)令牌預(yù)測。
生成周期重復(fù),直到到達(dá)序列令牌的末尾,或者在生成最大令牌時(shí)中斷。如前所述,我們可以啟用打印當(dāng)前生成的令牌,而無需等到整個(gè)生成完成使用 Streaming API 時(shí),它會(huì)將新令牌添加到輸出隊(duì)列,然后在它們準(zhǔn)備就緒時(shí)打印(print)它們。
運(yùn)行指令推理管道(run Pipeline)
輸入設(shè)定
from threading import Thread from time import perf_counter from typing import List import gradio as gr from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TextIteratorStreamer import numpy as np
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
為 user prompt 準(zhǔn)備模板
為了有效生成,模型期望具有特定格式的輸入。下面的代碼準(zhǔn)備了將用戶指令傳遞到模型中的模板,并提供額外的上下文。
INSTRUCTION_KEY = "### Instruction:"
RESPONSE_KEY = "### Response:"
END_KEY = "### End"
INTRO_BLURB = (
"Below is an instruction that describes a task. Write a response that appropriately completes the request."
)
# This is the prompt that is used for generating responses using an already trained model. It ends with the response
# key, where the job of the model is to provide the completion that follows it (i.e. the response itself).
PROMPT_FOR_GENERATION_FORMAT = """{intro}
{instruction_key}
{instruction}
{response_key}
""".format(
intro=INTRO_BLURB,
instruction_key=INSTRUCTION_KEY,
instruction="{instruction}",
response_key=RESPONSE_KEY,
)
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
輸出分析的幫助程序
模型被重新訓(xùn)練以使用特殊令牌### End 完成生成,下面的代碼找到它的 id 并用它當(dāng)作停止標(biāo)準(zhǔn)(stop-criteria)。
def get_special_token_id(tokenizer: AutoTokenizer, key: str) -> int:
"""
Gets the token ID for a given string that has been added to the tokenizer as a special token.
When training, we configure the tokenizer so that the sequences like "### Instruction:" and "### End" are
treated specially and converted to a single, new token. This retrieves the token ID each of these keys map to.
Args:
tokenizer (PreTrainedTokenizer): the tokenizer
key (str): the key to convert to a single token
Raises:
RuntimeError: if more than one ID was generated
Returns:
int: the token ID for the given key
"""
token_ids = tokenizer.encode(key)
if len(token_ids) > 1:
raise ValueError(f"Expected only a single token for '{key}' but found {token_ids}")
return token_ids[0]
tokenizer_response_key = next((token for token in tokenizer.additional_special_tokens if token.startswith(RESPONSE_KEY)), None)
end_key_token_id = None
if tokenizer_response_key:
try:
end_key_token_id = get_special_token_id(tokenizer, END_KEY)
# Ensure generation stops once it generates "### End"
except ValueError:
pass
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
主要生成功能代碼
如上所述,run_generation 函數(shù)是開始生成的開始點(diǎn)。它獲得提供的輸入指令作為參數(shù)并返回模型響應(yīng)。
ef run_generation(user_text:str, top_p:float, temperature:float, top_k:int, max_new_tokens:int, perf_text:str): """ Text generation function Parameters: user_text (str): User-provided instruction for a generation. top_p (float): Nucleus sampling. If set to < 1, only the smallest set of most probable tokens with probabilities that add up to top_p or higher are kept for a generation. ? ? ?temperature (float): The value used to module the logits distribution. ? ? ?top_k (int): The number of highest probability vocabulary tokens to keep for top-k-filtering. ? ? ?max_new_tokens (int): Maximum length of generated sequence. ? ? ?perf_text (str): Content of text field for printing performance results. ? ?Returns: ? ? ?model_output (str) - model-generated text ? ? ?perf_text (str) - updated perf text filed content ? ?""" ? ? ? ?# Prepare input prompt according to model expected template ? ?prompt_text = PROMPT_FOR_GENERATION_FORMAT.format(instruction=user_text) ? ? ? ?# Tokenize the user text. ? ?model_inputs = tokenizer(prompt_text, return_tensors="pt") ? ?# Start generation on a separate thread, so that we don't block the UI. The text is pulled from the streamer ? ?# in the main thread. Adds timeout to the streamer to handle exceptions in the generation thread. ? ?streamer = TextIteratorStreamer(tokenizer, skip_prompt=True, skip_special_tokens=True) ? ?generate_kwargs = dict( ? ? ? ?model_inputs, ? ? ? ?streamer=streamer, ? ? ? ?max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens, ? ? ? ?do_sample=True, ? ? ? ?top_p=top_p, ? ? ? ?temperature=float(temperature), ? ? ? ?top_k=top_k, ? ? ? ?eos_token_id=end_key_token_id ? ?) ? ?t = Thread(target=ov_model.generate, kwargs=generate_kwargs) ? ?t.start() ? ?# Pull the generated text from the streamer, and update the model output. ? ?model_output = "" ? ?per_token_time = [] ? ?num_tokens = 0 ? ?start = perf_counter() ? ?for new_text in streamer: ? ? ? ?current_time = perf_counter() - start ? ? ? ?model_output += new_text ? ? ? ?perf_text, num_tokens = estimate_latency(current_time, perf_text, new_text, per_token_time, num_tokens) ? ? ? ?yield model_output, perf_text ? ? ? ?start = perf_counter() ? ?return model_output, perf_text
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
應(yīng)用 UI 助手
為了制作交互式用戶界面,我們將使用 Gradio 庫。下面的代碼提供了用于與 UI 元素通信的有用函數(shù)。
def estimate_latency(current_time:float, current_perf_text:str, new_gen_text:str, per_token_time:List[float], num_tokens:int):
"""
Helper function for performance estimation
Parameters:
current_time (float): This step time in seconds.
current_perf_text (str): Current content of performance UI field.
new_gen_text (str): New generated text.
per_token_time (List[float]): history of performance from previous steps.
num_tokens (int): Total number of generated tokens.
Returns:
update for performance text field
update for a total number of tokens
"""
num_current_toks = len(tokenizer.encode(new_gen_text))
num_tokens += num_current_toks
per_token_time.append(num_current_toks / current_time)
if len(per_token_time) > 10 and len(per_token_time) % 4 == 0:
current_bucket = per_token_time[:-10]
return f"Average generaton speed: {np.mean(current_bucket):.2f} tokens/s. Total generated tokens: {num_tokens}", num_tokens
return current_perf_text, num_tokens
def reset_textbox(instruction:str, response:str, perf:str):
"""
Helper function for resetting content of all text fields
Parameters:
instruction (str): Content of user instruction field.
response (str): Content of model response field.
perf (str): Content of performance info filed
Returns:
empty string for each placeholder
"""
return "", "", ""
def select_device(device_str:str, current_text:str = "", progress:gr.Progress = gr.Progress()):
"""
Helper function for uploading model on the device.
Parameters:
device_str (str): Device name.
current_text (str): Current content of user instruction field (used only for backup purposes, temporally replacing it on the progress bar during model loading).
progress (gr.Progress): gradio progress tracker
Returns:
current_text
"""
if device_str != ov_model._device:
ov_model.request = None
ov_model._device = device_str
for i in progress.tqdm(range(1), desc=f"Model loading on {device_str}"):
ov_model.compile()
return current_text
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
運(yùn)行指令遵循管道
(instruction-following pipeline)
現(xiàn)在,我們已準(zhǔn)備好探索模型功能。請運(yùn)行以下代碼:
from openvino.runtime import Core core = Core() available_devices = core.available_devices examples = [ "Give me recipe for pizza with pineapple", "Write me a tweet about new OpenVINO release", "Explain difference between CPU and GPU", "Give five ideas for great weekend with family", "Do Androids dream of Electric sheep?", "Who is Dolly?", "Please give me advice how to write resume?", "Name 3 advantages to be a cat", "Write instructions on how to become a good AI engineer", "Write a love letter to my best friend", ] with gr.Blocks() as demo: gr.Markdown( "# Instruction following using Databricks Dolly 2.0 and OpenVINO. " "Provide insturction which describes a task below or select among predefined examples and model writes response that performs requested task." ) with gr.Row(): with gr.Column(scale=4): user_text = gr.Textbox( placeholder="Write an email about an alpaca that likes flan", label="User instruction" ) model_output = gr.Textbox(label="Model response", interactive=False) performance = gr.Textbox(label="Performance", lines=1, interactive=False) with gr.Column(scale=1): button_clear = gr.Button(value="Clear") button_submit = gr.Button(value="Submit") gr.Examples(examples, user_text) with gr.Column(scale=1): device = gr.Dropdown(choices=available_devices, value=current_device, label="Device") max_new_tokens = gr.Slider( minimum=1, maximum=1000, value=256, step=1, interactive=True, label="Max New Tokens", ) top_p = gr.Slider( minimum=0.05, maximum=1.0, value=0.92, step=0.05, interactive=True, label="Top-p (nucleus sampling)", ) top_k = gr.Slider( minimum=0, maximum=50, value=0, step=1, interactive=True, label="Top-k", ) temperature = gr.Slider( minimum=0.1, maximum=5.0, value=0.8, step=0.1, interactive=True, label="Temperature", ) user_text.submit(run_generation, [user_text, top_p, temperature, top_k, max_new_tokens, performance], [model_output, performance]) button_submit.click(select_device, [device, user_text], [user_text]) button_submit.click(run_generation, [user_text, top_p, temperature, top_k, max_new_tokens, performance], [model_output, performance]) button_clear.click(reset_textbox, [user_text, model_output, performance], [user_text, model_output, performance]) device.change(select_device, [device, user_text], [user_text]) if __name__ == "__main__": try: demo.launch(enable_queue=True, share=False, height=800) except Exception: demo.launch(enable_queue=True, share=True, height=800)
向右滑動(dòng)查看完整代碼
運(yùn)行結(jié)果
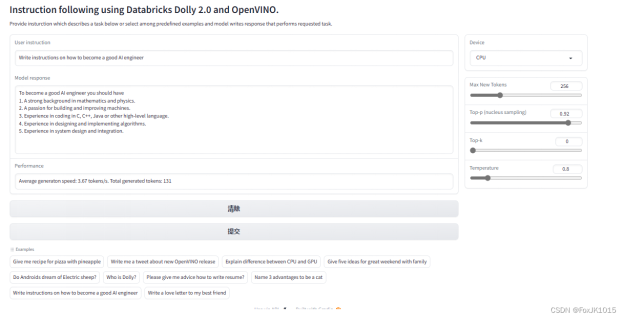
此演示提供了一個(gè)簡單的界面,允許使用文本指令與模型進(jìn)行通信。在“User instruction”字段中鍵入您的指令,或從預(yù)定義的示例中選擇一個(gè)指令,然后單擊“Submit”按鈕開始生成。此外,您還可以修改高級生成參數(shù):
Device- 允許切換推理設(shè)備。請注意,每次選擇新設(shè)備時(shí),都會(huì)重新編譯模型,這需要一些時(shí)間。
Max New Tokens- 生成文本的最大尺寸。.
Top-p (nucleus sampling)- 如果設(shè)置為< 1,則只有概率加起來為 top_p 或更高的最小概率的最小標(biāo)記集一代保留。
Top-k- 保留用于 top-k-filtering 的最高概率詞匯令牌的數(shù)量。
Temperature- 用于對數(shù)分布(logits distribution)進(jìn)行模塊化的值。
以下運(yùn)行結(jié)果約2分鐘。
范例1:
Write instruction on how to become a good AI engineer
范例2:
Who is Dolly?
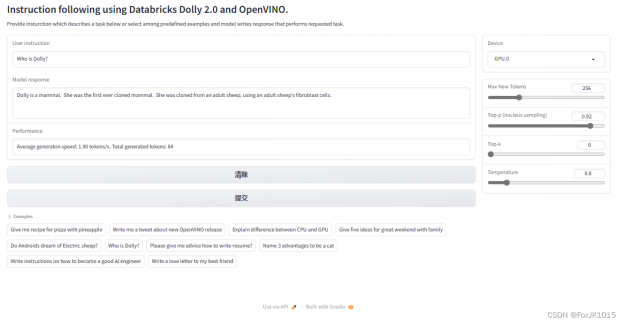
范例3:
Explain difference between CPU and GPU?
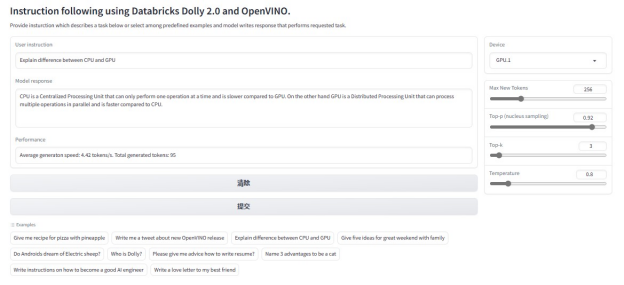
以下是右側(cè)設(shè)備選擇
(GPU.0 為 iGPU;GPU.1 為英特爾銳炫及各參數(shù)調(diào)控局部放大圖)
結(jié)語
Dolly 2.0 是第一個(gè)開源的,遵循指令的 LLM,由 Databricks 在一個(gè)透明且免費(fèi)提供的數(shù)據(jù)集上進(jìn)行微調(diào),該數(shù)據(jù)集也是開源的,可用于商業(yè)目的。這意味著 Dolly 2.0 可用于商業(yè)應(yīng)用程序,而無需支付 API 訪問費(fèi)用或與第三方共享數(shù)據(jù)。
英特爾 OpenVINO Notebooks 展示了此 LLM 開源代碼及原理注釋,配合英特爾銳炫顯卡在基于 Gradio 庫做了一個(gè)用戶界面讓開發(fā)者可親自體驗(yàn)單機(jī)版的 GPT 示例, 感受大語言模型的魅力。
關(guān)于原基科技(easy-base.com.cn)
深圳市原基科技有限公司,坐落于深圳科技新區(qū)的光明新區(qū),專注于嵌入式主板和工控電腦、AI盒子、邊緣計(jì)算服務(wù)器的研發(fā)、定制以及解決方案,是一家集研發(fā)、生產(chǎn)、銷售、服務(wù)為一體的國家高新技術(shù)型企業(yè),致力于為大數(shù)據(jù)、物聯(lián)網(wǎng)、人工智能的發(fā)展提供解決方案。
主要核心骨干均為從事本行業(yè)10年以上的資深人員,依據(jù)豐富的經(jīng)驗(yàn)和ISO9001體系的指導(dǎo),設(shè)立了運(yùn)營部、產(chǎn)品部、研發(fā)部、供應(yīng)鏈、品質(zhì)部等,具備了主板的研發(fā)設(shè)計(jì)、生產(chǎn)線的DIP、SMT以及整機(jī)的組裝測試的能力。目前擁有20多項(xiàng)自主知識(shí)產(chǎn)權(quán), 獲評為國家高新技術(shù)企業(yè)且通ISO9001認(rèn)證。
主要業(yè)務(wù)涉及智慧社區(qū)、智慧園區(qū)、智慧零售、智慧教育、智慧辦公、智慧安防、智慧工業(yè)等領(lǐng)域;憑借靈活、快速響應(yīng)的特點(diǎn),得到了客戶的大量認(rèn)可。
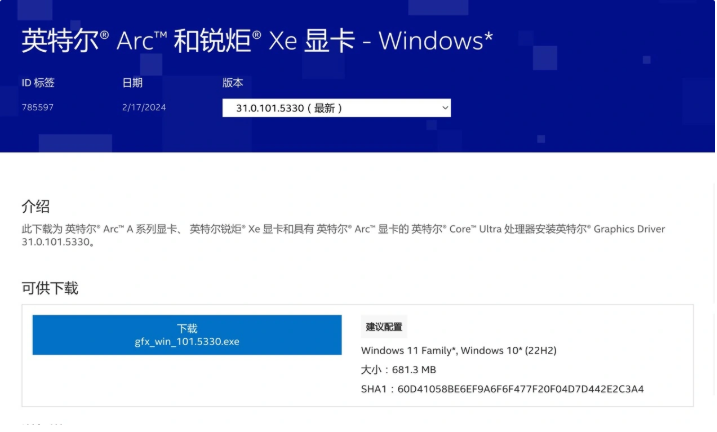
英特爾銳炫 顯卡驅(qū)動(dòng)安裝
英特爾銳炫與Iris Xe 顯示芯片- WHQL - Windows* 下載并安裝英特爾銳炫 驅(qū)動(dòng)
安裝完畢確認(rèn)版本如下圖為31.0.101.4369, 并在左側(cè)性能確認(rèn)顯卡設(shè)備已有A380選項(xiàng)。

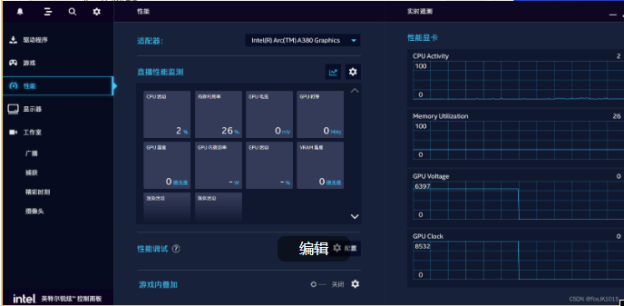 ? ??
? ??
審核編輯:湯梓紅
-
英特爾
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
61文章
9949瀏覽量
171692 -
顯卡
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
16文章
2431瀏覽量
67573 -
開源
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
3309瀏覽量
42471 -
語言模型
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
520瀏覽量
10268 -
ChatGPT
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
29文章
1558瀏覽量
7595 -
LLM
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
286瀏覽量
327
原文標(biāo)題:英特爾銳炫? 顯卡運(yùn)行類 ChatGPT 的開源大語言模型(LLM) Dolly 2.0 | 開發(fā)者實(shí)戰(zhàn)
文章出處:【微信號:英特爾物聯(lián)網(wǎng),微信公眾號:英特爾物聯(lián)網(wǎng)】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處。
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
英特爾推出了英特爾銳炬Xe MAX獨(dú)立顯卡
英特爾發(fā)布銳炫A系列獨(dú)顯
英特爾推出銳炫A系列獨(dú)立顯卡 微星推出GeForce RTX 3090 Ti系列顯卡
英特爾推出面向移動(dòng)設(shè)備和臺(tái)式機(jī)的銳炫Pro圖形顯卡
銳意進(jìn)取,炫力出彩!英特爾持續(xù)耕耘銳炫顯卡

英特爾銳炫顯卡DX11性能更新,并推出全新英特爾PresentMon?Beta

英特爾銳炫A580顯卡發(fā)布,全面媒體功能助力創(chuàng)作者盡情揮灑創(chuàng)意

英特爾銳炫A750顯卡新驅(qū)動(dòng)測評:新老游戲雨露均沾




 英特爾銳炫顯卡運(yùn)行類ChatGPT的開源大語言模型(LLM)Dolly 2.0解讀
英特爾銳炫顯卡運(yùn)行類ChatGPT的開源大語言模型(LLM)Dolly 2.0解讀












評論