你好,我是愛(ài)吃魚香ROS的小魚。上一節(jié)我們安裝好了MPU6050的三方庫(kù),這一節(jié)我們嘗試使用該庫(kù)將我們板子上的IMU模塊驅(qū)動(dòng)起來(lái)。
本教程所使用硬件平臺(tái)為MicroROS學(xué)習(xí)板V1.0.0,可點(diǎn)擊閱讀原文購(gòu)買及查看詳情
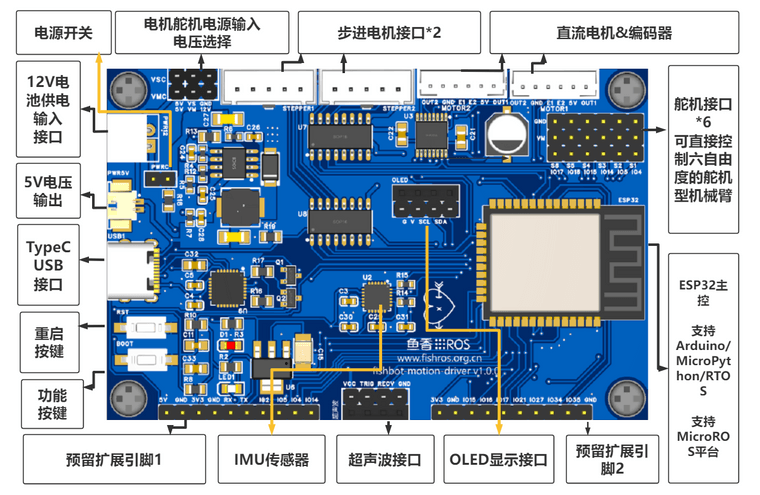
一、MPU6050介紹
首先我們了解下MPU6050模塊,從外觀看,長(zhǎng)這個(gè)樣子

MPU6050 為全球首例集成六軸傳感器的運(yùn)動(dòng)處理組件,內(nèi)置了運(yùn)動(dòng)融合引擎,用于手持和桌面的應(yīng)用程序、游戲控制器、體感遙控以及其他消費(fèi)電子設(shè)備。它內(nèi)置一個(gè)三軸 MEMS 陀螺儀、一個(gè)三軸 MEMS 加速度計(jì)、一個(gè)數(shù)字運(yùn)動(dòng)處理引擎(DMP)以及用于第三方的數(shù)字傳感器接口的輔助 I2C 端口(常用于擴(kuò)展磁力計(jì))。當(dāng)輔助 I2C 端口連接到一個(gè)三軸磁力計(jì),MPU6050 能提供一個(gè)完整的九軸融合輸出到其主 I2C 端口。
在我們板子上的位置是這里
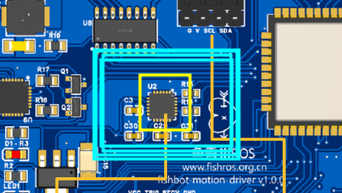
二、調(diào)用開(kāi)源庫(kù)驅(qū)動(dòng)
新建工程example06_mpu6050
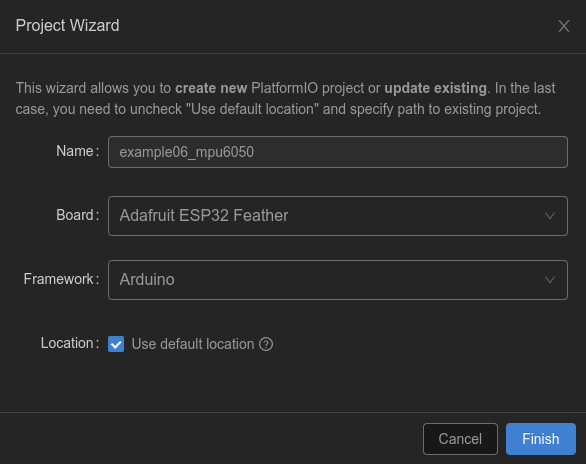
2.1 添加依賴
修改platformio.ini
[env:featheresp32]
platform = espressif32
board = featheresp32
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
https://ghproxy.com/https://github.com/rfetick/MPU6050_light.git
2.2 復(fù)制樣例程序
該開(kāi)源庫(kù)作者提供了開(kāi)源庫(kù)的使用方式,將.pio/libdeps/featheresp32/MPU6050_light/examples/GetAllData/GetAllData.ino復(fù)制到main.cpp中。
/* Get all possible data from MPU6050
* Accelerometer values are given as multiple of the gravity [1g = 9.81 m/s2]
* Gyro values are given in deg/s
* Angles are given in degrees
* Note that X and Y are tilt angles and not pitch/roll.
*
* License: MIT
*/
#include "Wire.h"
#include < MPU6050_light.h >
MPU6050 mpu(Wire);
unsigned long timer = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
byte status = mpu.begin();
Serial.print(F("MPU6050 status: "));
Serial.println(status);
while(status!=0){ } // stop everything if could not connect to MPU6050
Serial.println(F("Calculating offsets, do not move MPU6050"));
delay(1000);
mpu.calcOffsets(true,true); // gyro and accelero
Serial.println("Done!n");
}
void loop() {
mpu.update();
if(millis() - timer > 1000){ // print data every second
Serial.print(F("TEMPERATURE: "));Serial.println(mpu.getTemp());
Serial.print(F("ACCELERO X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getAccX());
Serial.print("tY: ");Serial.print(mpu.getAccY());
Serial.print("tZ: ");Serial.println(mpu.getAccZ());
Serial.print(F("GYRO X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getGyroX());
Serial.print("tY: ");Serial.print(mpu.getGyroY());
Serial.print("tZ: ");Serial.println(mpu.getGyroZ());
Serial.print(F("ACC ANGLE X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getAccAngleX());
Serial.print("tY: ");Serial.println(mpu.getAccAngleY());
Serial.print(F("ANGLE X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getAngleX());
Serial.print("tY: ");Serial.print(mpu.getAngleY());
Serial.print("tZ: ");Serial.println(mpu.getAngleZ());
Serial.println(F("=====================================================n"));
timer = millis();
}
}
2.3 修改代碼
1.修改波特率 9600->115200
2.修改IO地址 Wire.begin();->Wire.begin(18, 19);
修改完后代碼,并附上小魚對(duì)代碼的注釋講解
#include "Wire.h" // 導(dǎo)入I2C相關(guān)頭文件
#include < MPU6050_light.h > // 導(dǎo)入MPU6050庫(kù)
MPU6050 mpu(Wire); // 新建MPU6050對(duì)象mpu
unsigned long timer = 0;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin(18, 19); // 初始化I2C,設(shè)置sda引腳為GPIO18,SCL引腳為GPIO19
byte status = mpu.begin(); // 檢測(cè)IMU模塊狀態(tài)
Serial.print(F("MPU6050 status: "));
Serial.println(status);
while (status != 0)
{
} // stop everything if could not connect to MPU6050
Serial.println(F("Calculating offsets, do not move MPU6050"));
delay(1000);
mpu.calcOffsets(true, true); // gyro and accelero 校準(zhǔn)
Serial.println("Done!n");
}
void loop()
{
mpu.update();
if (millis() - timer > 1000)
{ // print data every second
Serial.print(F("TEMPERATURE: "));
Serial.println(mpu.getTemp()); // 溫度
Serial.print(F("ACCELERO X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getAccX()); // X軸加速度
Serial.print("tY: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getAccY()); // Y軸加速度
Serial.print("tZ: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAccZ()); // Z軸加速度
Serial.print(F("GYRO X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getGyroX()); // X軸 角速度
Serial.print("tY: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getGyroY()); // Y軸 角速度
Serial.print("tZ: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getGyroZ()); // Z軸 角速度
Serial.print(F("ACC ANGLE X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getAccAngleX()); // X軸角加速度
Serial.print("tY: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAccAngleY()); // Y軸角加速度
Serial.print(F("ANGLE X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getAngleX()); // X角度
Serial.print("tY: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getAngleY()); // Y角度
Serial.print("tZ: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAngleZ()); // Z角度
Serial.println(F("=====================================================n"));
timer = millis();
}
}
三、編譯測(cè)試
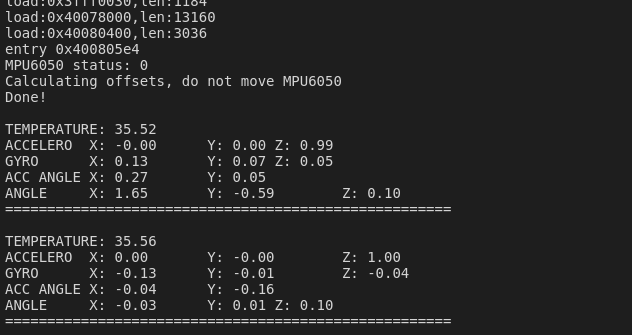
保存代碼,編譯下載到開(kāi)發(fā)板。打開(kāi)串口監(jiān)視器,查看結(jié)果。
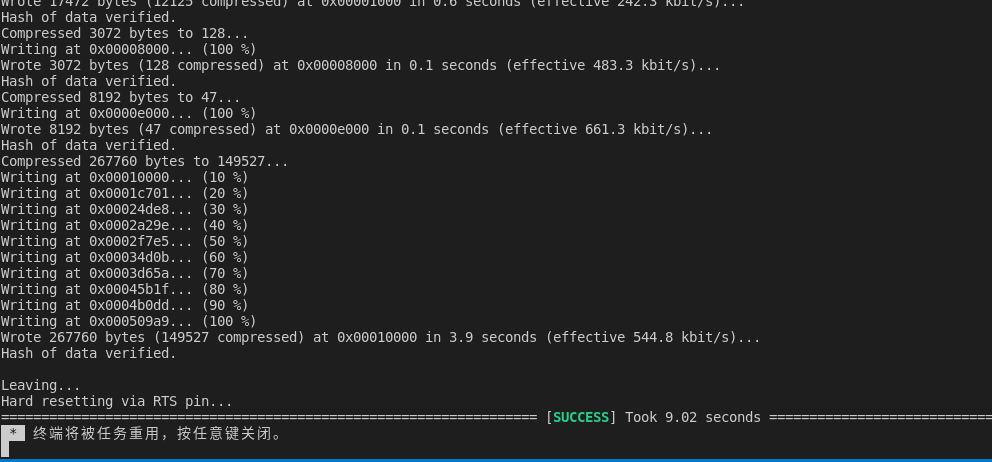
結(jié)果
四、總結(jié)
本節(jié)我們通過(guò)調(diào)用開(kāi)源庫(kù)實(shí)現(xiàn)了對(duì)IMU傳感器的的調(diào)用,如果你對(duì)該庫(kù)感興趣,可以隨時(shí)到.pio/libdeps/featheresp32/MPU6050_light/src/MPU6050_light.h查看源碼
class MPU6050{
public:
// INIT and BASIC FUNCTIONS
MPU6050(TwoWire &w);
byte begin(int gyro_config_num=1, int acc_config_num=0);
...
private:
...
};
可以看到,這里是通過(guò)面向?qū)ο蟮姆绞綄PU6050封裝成了一個(gè)類,我們使用的時(shí)候也是通過(guò)實(shí)例化后使用的,所以下一節(jié)我們將學(xué)習(xí)如何在我們的工程里使用面向?qū)ο蟮姆绞竭M(jìn)行封裝。
-
傳感器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
2554文章
51632瀏覽量
758044 -
I2C
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
28文章
1499瀏覽量
125109 -
學(xué)習(xí)板
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
46瀏覽量
12226 -
MPU6050
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
39文章
308瀏覽量
71831 -
ROS
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
281瀏覽量
17197
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
proteus第三方元器件庫(kù)
如何把第三方庫(kù)加到PROTEUS中?
第三方dll調(diào)用問(wèn)題!!!
怎樣去調(diào)用一個(gè)第三方的驅(qū)動(dòng)庫(kù)呢
鴻蒙開(kāi)源第三方組件資料合集
使用MPU6050開(kāi)源庫(kù)將板子上的IMU模塊驅(qū)動(dòng)起來(lái)
Arduino與MPU6050的通信
移動(dòng)應(yīng)用第三方庫(kù)自動(dòng)檢測(cè)和分類
MPU6050簡(jiǎn)介

MPU6050教程開(kāi)源分享

MPU6050運(yùn)動(dòng)跟蹤設(shè)備開(kāi)源分享

學(xué)會(huì)安裝第三方開(kāi)源庫(kù)





 使用第三方開(kāi)源庫(kù)驅(qū)動(dòng)MPU6050模塊
使用第三方開(kāi)源庫(kù)驅(qū)動(dòng)MPU6050模塊










評(píng)論