SVA in Formal
FPV對不同的SVA Property,調用合適的算法engine進行建模,依據算法模型從初始狀態Reset state對DUT所有的input自動施加激勵,隨著cycle的depth增加,逐漸窮盡狀態空間。
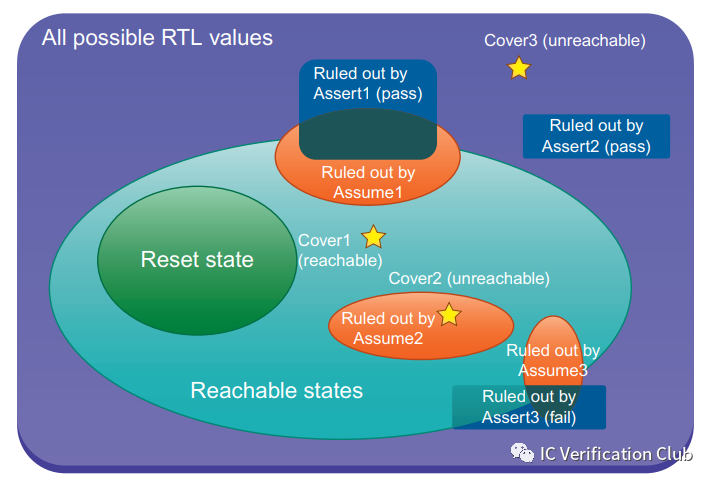
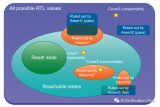
The full space of all possible RTL state values: 最外層的紫方框為RTL的所有可能存在的狀態空間(input + state element(dff,latch))。
The reset states:初始狀態,一般從reset復位開始。
The reachable states:從reset state可以,自動對input施加激勵,可以達到的狀態。(所以紫方框以內綠橢圓以外的空間,是無法達到的空間,例如RTL中的dead code)Assumptions:使用SVA的assume對DUT進行約束;橙色橢圓型,約束縮小了狀態空間。
Assertion: 使用SVA的assert對property進行斷言;斷言屬性定義了模型的行為,例如assert property: ( @(posedge clk) clr |=> ((overfloat==0)&&(cnt==0)));斷言了在clk上升沿采樣時,若clr為高(先行算子anteceden成功),下一個clk上升沿采樣到的overfloat和cnt都為0(后續算子consequent);而Formal工具要做的就是窮盡狀態空間找出一個counter-exampleCEX反例,進行falsified證偽,例如overfloat和cnt都不為0或者只有一個為0;如果CEX出現,而assertion為golden,則就說明DUT不滿足spec。
Asser1: pass,因為這個CEX不滿足assumptions的約束,不是一個有效狀態。
Assert2: pass,因為這個CEX本身不是可以達到的狀態。
Assert3: fail,有效狀態和約束內,出現了一個CEX。
Cover Points: 使用SVA的cover對property設置覆蓋點;相當于設置一個觀察點,Formal工具會窮盡狀態空間,找到一個滿足要求的狀態;
Cover1: 該覆蓋點被cover
Cover2: 該覆蓋點在約束之外,unreachable
Cover3: 該覆蓋點在有效空間之外,unreachable
VC Formal定義了Assertion和Cover Points的結果如下:
Assertion:proven: assertion pass,窮盡狀態空間也找不到一個CEXfalsified:assertion fail,出現不滿足斷言的CEXinconclusive: Formal在N個cycle depth內,沒有找到CEX,屬于Bounded Proof,有界證明,這個"界“bounded (safe) depth就是N個cycle depth。vacuous:對于包含蘊含操作符|->|=>的property,如果antecedent一直未被觸發,也一定不會出現CEX,此時為空成功vacuous success。vacuous在Simulation中經常出現,因為施加的有限激勵,沒有觸發antecedent成功。但是在Formal中,需要引起注意。
Cover Points:Covered: 覆蓋Uncovered: 未覆蓋
the SVA differences
在Simaltion和Formal中,SVA的使用略有不同:
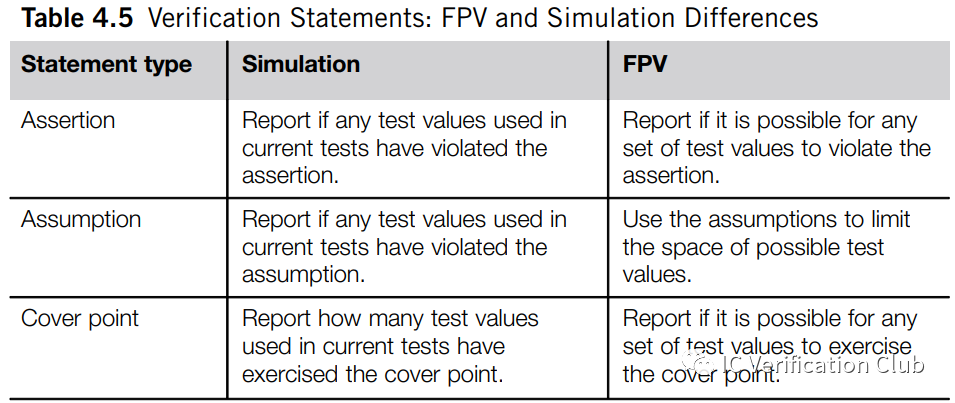
Simulation中的assume和assertion作用相同,不起到約束的作用;而Formal中,assume實現約束的作用;對于Simulation的vacuous success,并不會報錯引起用戶注意,一般建議對property同時做assert和cover處理。
Sequential depth
Sequential depth:也就是上文提及到的Cycle depth;較大的Sequential depth,容易產生inconclusive的結果。
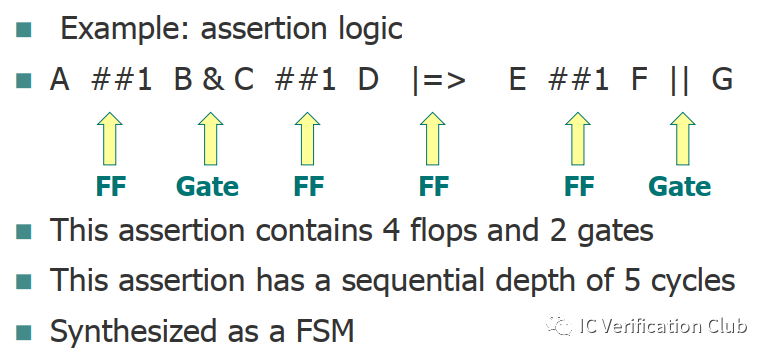
Assertion Logic Contributes to State Space
COI
COI(CONES OF INFLUENCE):COI是Formal工具對property的邏輯電路映射,也被稱作Logic Cones邏輯錐。COI包含property的所有input和state element,這些決定了不同的輸出結果。
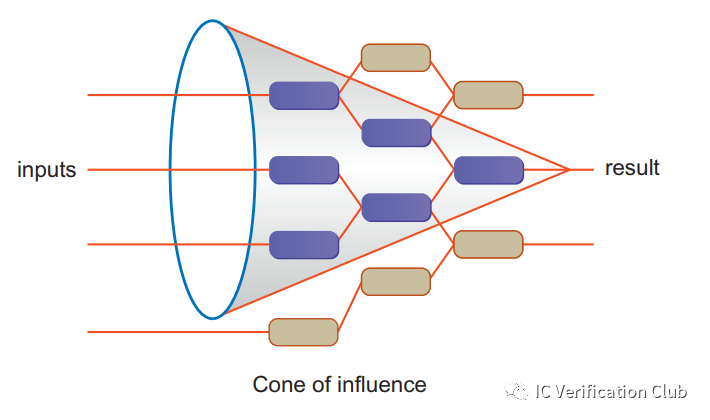
Formal工具對一個property解析生成的COI Schematic:
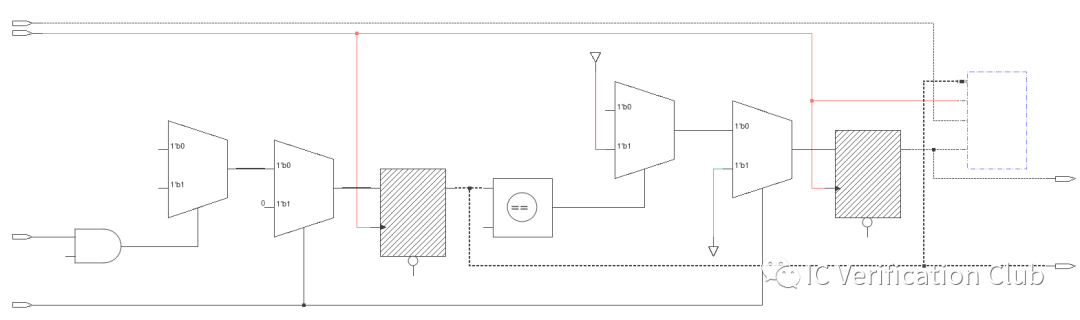
從用戶角度,我們不必關心一個property的COI具體是什么樣子;用戶創建的所有property的COI集合對DUT RTL的覆蓋情況,類似于Simulation中的Code coverage,稱為Property Density。
The suggestion of SVA for Formal
formal model從SVA中提取,所以SVA的書寫方式,也會影響Formal的效率,推薦的SVA Coding Guidelines可以參考《VC_Formal_UG》Appendix B。下面介紹一些常見的assertion”技巧“:
uniform format
assertion的書寫,需要遵循同一的格式,每條assertion有相應的文檔記錄;每條property都有可讀性的lable標注;可以采用一些宏定義,簡化assertion的書寫,參考:prim_assert.sv[4]當assertion的clock,reset都是同一個時,可以聲明default clocking和default disable iff,簡化書寫。
Immediate VS Concurrent
雖然立即斷言在一些情況下等效于并發斷言,如下:
//ConcurrentAssertion assert_overfloat_func:assertproperty(`clk_rst$rose(overfloat)|->$past(cnt==4'hF)); //ImmediateAssertion always@(posedgeclk) if($rose(overfloat)&&(rstn==1)) assert_overfloat_func_2:assert($past(cnt==4'hF));
但是建議使用并發斷言,Formal工具對蘊含操作符的支持更好。
Try use implication
不建議直接對sequence進行斷言,sequence會在每個cycle都被檢查;推薦使用蘊含操作符的方式。
//BAD propertysend_header_payload; @(posedgeclk)disableiff(reset) (enable##1header##1payload[*16]); endproperty //GOOD propertysend_header_payload; @(posedgeclk)disableiff(reset) $rose(enable)|=>header##1payload[*16]; endproperty
SVA Modeling Layer Code
可以通過增加Auxiliary Code,簡化property的書寫難度;如下:
moduleassert_top(inputrstn,inputclk,inputA,
input,B,inputC,inputwr,inputrd);
//Requirement:inputsA,B,Caremutuallyexclusive
wire[2:0]my_bus={A,B,C};
a_abc_mutex:assertproperty(@(posedgeclk)$onehot0(my_bus));
//Requirement:Nomorethan5outstandingwr’s(withoutard)
//andnordbeforewr
reg[2:0]my_cnt;
always@(posedgeclkornegedgerstn)
if(!rstn)my_cnt<=?3’b000;
????????else
????????????if?(?wr?&&?!rd)?my_cnt?<=?my_cnt?+?1;
????????????else?if?(!wr?&&?rd)?my_cnt?<=?my_cnt?–?1;
????????????else?my_cnt?<=?my_cnt;
a_wr_outstand_le5:?assert?property?(@(posedge?clk)?my_cnt?<=?3’d5?);
a_no_rd_wo_wr:?assert?property?(@(posedge?clk)?!((my_cnt?==?3’d0)?&&?rd));
endmodule
use function
assertion中可以調用funciton。
//Computenextgrantforround-robinscheme functionlogic[3:0]fv_rr_next(logic[3:0]req,logic[3:0]gnt); fv_rr_next=0; for(inti=1;(i<4);?i++)?begin ????????if?(req[(fv_which_bit(gnt)+i)%4])?begin ??????????fv_rr_next[(fv_which_bit(gnt)+i)%4]?=?1; ??????????break; ????????end ????end endfunction Page81_rr_next:??assert?property?(((opcode?==?NOP)?&&? ????(|gnt?==?1)?&&?(|req?==?1)?&&?(|(req&gnt)==4'b0))?|=>(gnt==fv_rr_next(req,gnt))) else$error("Violationofroundrobingrantpolicy.");
as SIMPLE as possible
將一個大的assertion才分為多個小的assertion
$rose(START)|=>(ENABLE&&~START&&~STOP)[*7] ##1(ENABLE&&~START&&STOP)|=> (~ENABLE&&~START&&~STOP); $rose(START)|->~ENABLE##1ENABLE; $rose(ENABLE)|->(~START&&~STOP)[*7]; $rose(STOP)|->ENABLE##1~ENABLE; $fell(START)|=>##5$rose(STOP);
as SHORT as possible
盡量縮短Cycle Depth,使用[0:$]或者太大的時間delay不利于formal分析。
a5:assertproperty@(posedgeclk)a|->(##[0:$]b); a6:assertproperty(@(posedgeclk)disableiff(~rst_n)A##1B|=>C##[1:100]D);
use Systemverilog
采用可綜合的systemvrilog語法,如interface,struct等,使用更便捷;像s_eventually, 在sv09才支持。
Formal Property Verification
以一個counter做簡單的演示:
modulecounter( inputclk, inputrstn, inputen, inputclr, outputcnt, outputoverfloat ); reg[3:0]cnt; regoverfloat; always@(posedgeclk,negedgerstn) begin if(!rstn) cnt<=?4'b0; ????else?if?(clr) ???????cnt?<=?0; ????else?if?(en?&?(cnt!=4'hF)) ???????cnt?<=?cnt?+?1; end always@(posedge?clk,negedge?rstn) begin ????if(!rstn) ???????overfloat?<=?1'b0; ????else?if?(clr) ???????overfloat?<=?1'b0; ????else?if?(cnt==15) ???????overfloat?<=?1'b1; end `ifdef?FPV `define?clk_rst?@(posedge?clk)?disable?iff?(!rstn) //ASSUME assume_en_clr_conflit:?assume?property?(`clk_rst?!(en?&&?clr)); //COVER cover_clr_overfloat:?cover?property?(`clk_rst?$fell(overfloat)); cover_cnt_value:?cover?property?(`clk_rst?(cnt==20)); //ASSERT assert_clr_func:?assert?property(`clk_rst?clr?|=>((overfloat==0)&&(cnt==0))); propertyp_en_func; inttmp; `clk_rst(en,tmp=cnt)|=>if(cnt!=4'hF)(tmp+1==cnt); endproperty assert_en_func:assertproperty(p_en_func); assert_clr_overfloat:assertproperty(`clk_rst$fell(overfloat)|->$past(clr)); //PASS assert_overfloat_func:assertproperty(`clk_rst$rose(overfloat)|->$past(cnt==4'hF)); //WRONGassertion assert_overfloat_func_fail:assertproperty(`clk_rst(cnt==4'hF)|=>overfloat); //ImmediateAssert always@(posedgeclk) if($rose(overfloat)&&(rstn==1)) assert_overfloat_func_2:assert($past(cnt==4'hF)); `endif endmodule
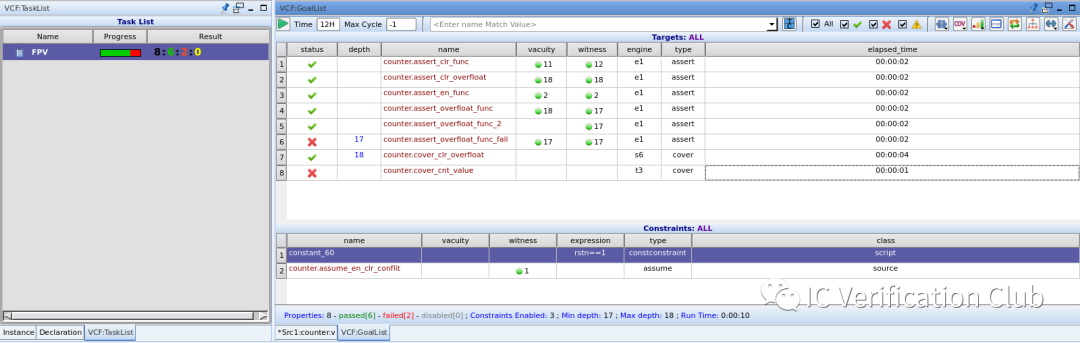
Result:vacuity欄為property的先行算子成立的cycle depth。witness欄為property的后續算子成立的cycle depth。對于assert_overfloat_func這個property,witness早于vacuity1個cycle,是因為$past()是對過去的判斷。
Initial State定義clk,rstn;從復位狀態開始,Formal工具自動對input信號灌入激勵。
#ClockDefinitions create_clockclk-period100 #ResetDefinitions create_resetrstn-senselow #InitialisationCommands sim_run-stable sim_save_reset
ASSUME
增加了en和clr不可能同時為高的約束。
COVER
增加一些關心的cover point,工具可以快速地跑出對應波形:例如$fell(overfloat)的cover:
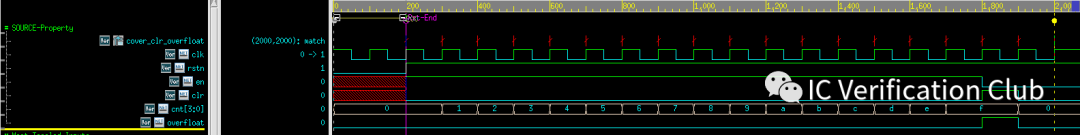
200ns:完成復位2000ns:cover point match(注意采樣的上升沿前的數據)
對于(cnt==20))則是uncover,cnt最大值為15。
ASSERT
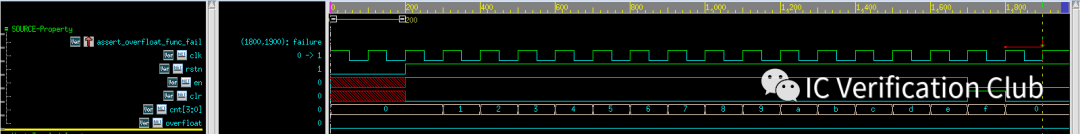
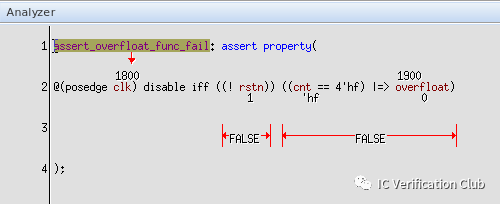
assert_overfloat_func_fail: assert property (`clk_rst (cnt==4'hF) |=> overfloat);這個propery斷言失敗,被工具找到了一個CEX: 當cnt==4'hF時,同時拉高clr,overfloat就不會為高了。
 在這里插入圖片描述
在這里插入圖片描述
assertion annotation:
**ENGINE** Type欄的e1,s6,t3為算法引擎的代號;工具會根據property的特性選擇合適的算法,調用相應的引擎處理;VC Formal中的engines:
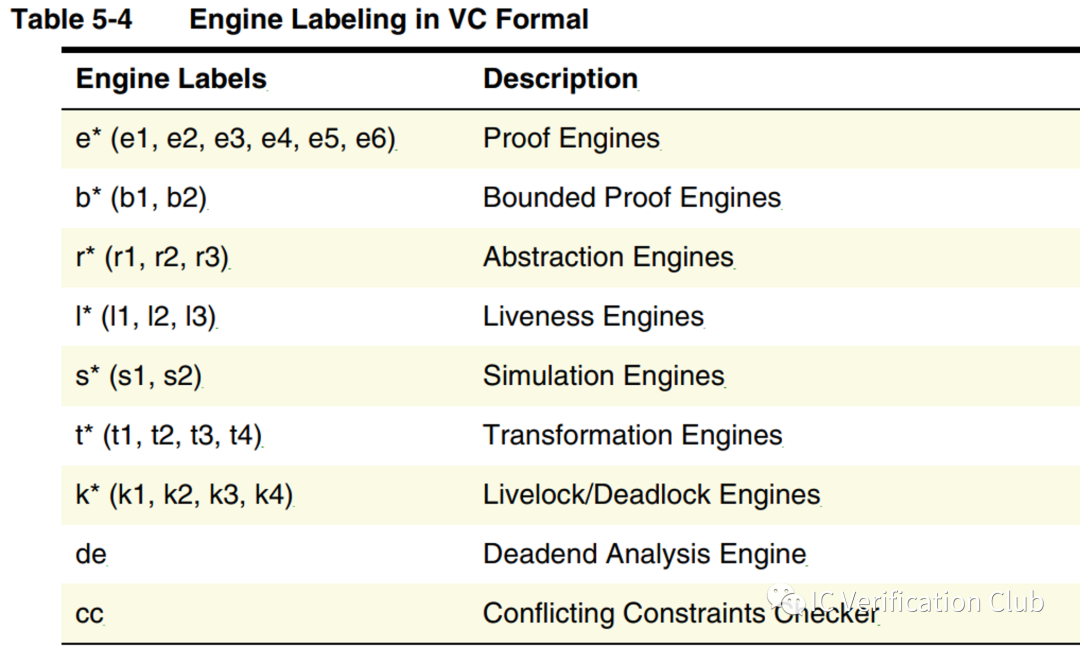
常見算法為:
?Binary Decision Diagrams orBDD
?"SATisfiability" Proofs orSAT
?Bounded Model Checking orBMC
?Craig Interpolation, usually shortened to "Craig"
?Property Directed Reachability orPDR
一般使用工具默認分配的engine,當然用戶也可以自己指定;VC Formal提供了多種引擎編排的recipes,適用FPV不同的使用場景。
JasperGold Result
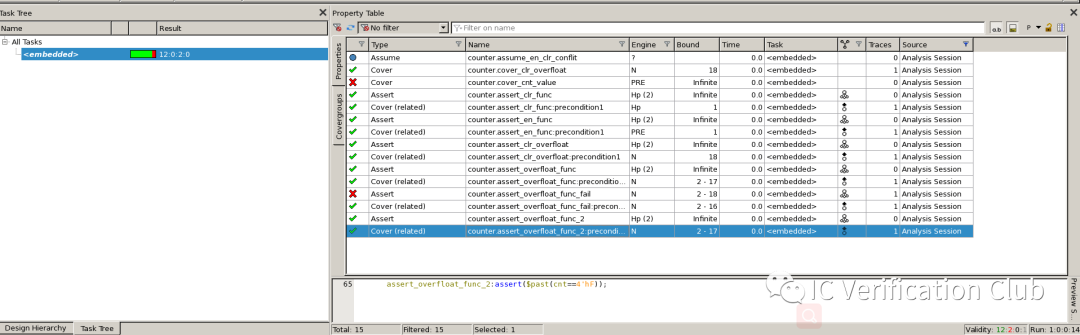
CEX wave:
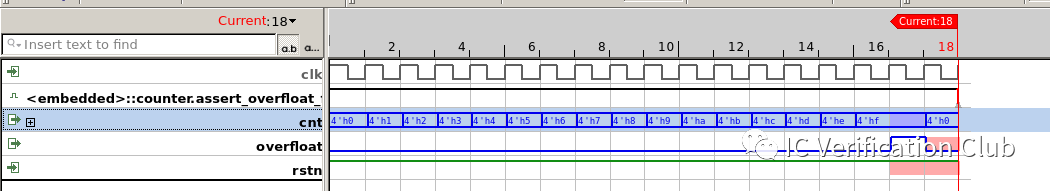
JasperGold中的engines:
FPV的使用場景
design exercise FPV
FPV不需要搭建平臺和手動施加激勵,適合快速的在一些新設計的RTL上跑一些基礎功能;例如上一節$fell(overfloat))這個cover point,如果通過Simulatin,需要搭建testbench并詳盡地施加每一拍的激勵;而使用Formal,設計人員不需要關注整個過程,只關注最終結果,工具會自動施加相應的激勵并達到你想要的結果。
所以當你有以下需求時,可以考慮使用design exercise FPV:
1.對于新設計的模塊,想要跑一些基礎功能進行確認
2.在驗證人員的驗證平臺還沒有準備好時,需要自己提前做一些簡略地驗證
3.接手遺留的RTL代碼,可以跑一下FPV,結合波形加深對特定功能的理解
設計人員自己跑FPV,對RTL內部細節很了解;思路一般是:首先增加感興趣的cover point;再添加一些assumption,可以過度約束;先跑出一些簡單功能的波形;增加一些assertion,做檢查;接著添加一些復雜功能的assertion和cover point,并逐漸放寬assumption;跑FPV并不是可以一次性把所有property都寫完備,需要"wiggle"幾輪,多次調試property;
有些公司對IP開發有額外的斷言標準要求,例如property應該占RTL總代碼行數的三分之一;這些property既可以用于formal,也可以用于simulation。《Assertion-Based Design》,《Creating Assertion-Based IP》書籍中介紹了相關經驗。
Bug hunting FPV
當你有以下需求時,可以考慮使用Bug hunting FPV:
1.你所驗證的模塊有很多corner cases,需要額外的FPV驗證保證完備性
2.Simulation回歸random case時,陸續發現新的error,需要額外的FPV驗證提高置信度
3.對于一個成熟的模塊,加了一個新的feature,需要額外的FPV驗證
Bug hunting FPV是Simulation的補充驗證手段,采用更高層級的assertion,加入過約束,將注意力集中于某一個功能點;
full proof FPV
對一個設計只采用FPV進行驗證,保證設計功能100%符合spec;這個從理論上是完全可行的,也是Formal Verification的初衷:只要property是完備的,正確的,相對于RTL,就可以建立一個golden model,遍歷RTL的所有狀態空間,保證100%正確。當你滿足以下條件時,可以采用full proof FPV:
1.待測設計有一個詳細的規格書或者一個包含所有功能點的表格
對于full proof FPV,每種Formal工具都有推薦的sign-off流程,來保證驗證的完備。
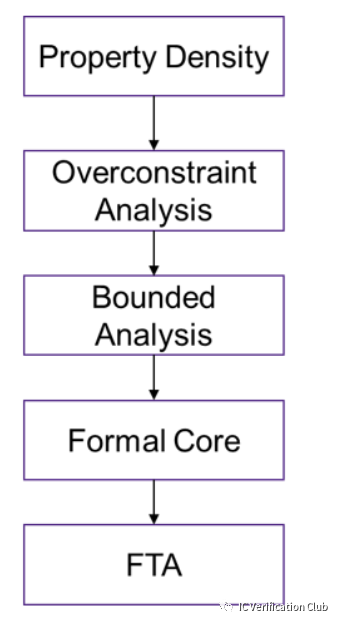
VC Formal的推薦流程如下:
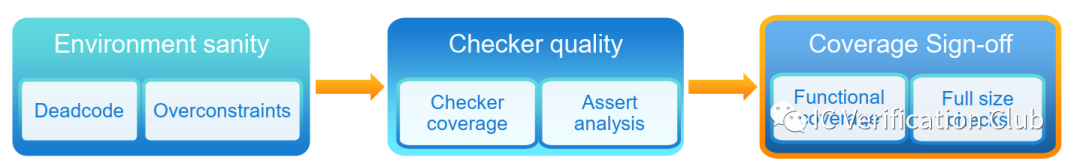
JasperGold的推薦流程如下:
通過收集覆蓋率,保證property的完備,完成sign-off工作。具體后文介紹。
APPs
formal tool除了FPV,還提供了其他適用不同場景的APPs,如對于pinmux可以采用connectivity連通性檢查,對于寄存器的訪問采用register檢查,對于一塊mem,是否存在其他非法訪問路勁,可以才用security檢查;這一類app都是FPV的衍生,通過提供一文件或約束,工具自動產生property,調用最佳engine處理。相較于FPV,學習成本低。對于汽車產品,有額外的Functional Safety要求,工具會自動對rtl注錯分析其影響結果。
VC Fomrla Apps:
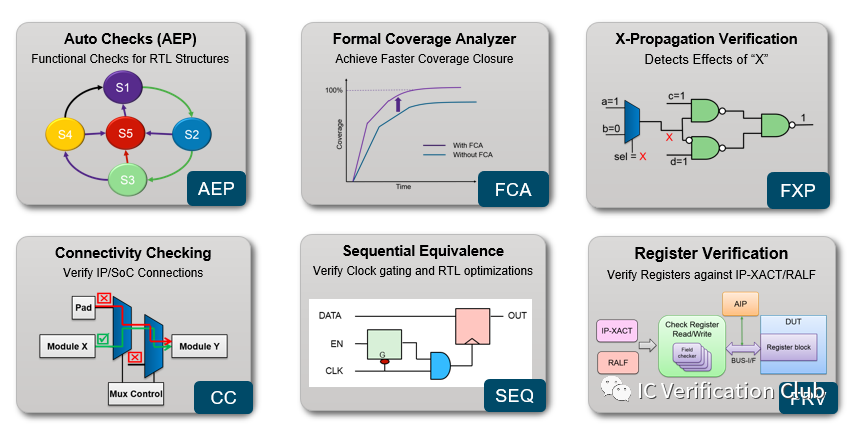
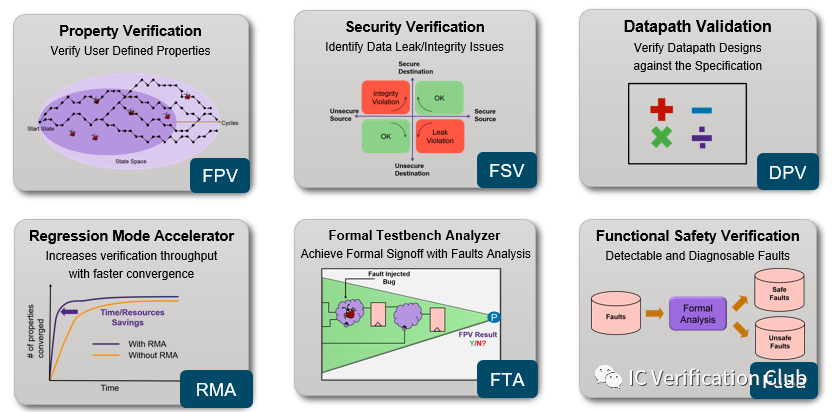
對于以上Apps, 可能除了DPV, JasperGold都有對應的Apps.
審核編輯:劉清
-
處理器
+關注
關注
68文章
19761瀏覽量
233018 -
邏輯電路
+關注
關注
13文章
502瀏覽量
43100 -
SVA
+關注
關注
1文章
19瀏覽量
10220 -
DUT
+關注
關注
0文章
190瀏覽量
12785 -
FPV
+關注
關注
0文章
20瀏覽量
4652
原文標題:Formal Verification (二) FPV、APPs
文章出處:【微信號:數字芯片設計工程師,微信公眾號:數字芯片設計工程師】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
什么是FPV?怎樣去搭建FPV驗證環境呢?
搭建FPV驗證環境之創建assert與執行FPV簡析
一、什么是FPV?
FPV設計的狀態空間主要由什么因素決定的
A Roadmap for Formal Property

路線圖正式產權核查

Advanced Formal Verification
Functional Verification Coverage Measurement and Analysis

功能驗證覆蓋測量與分析

AVM Based Unified Verification
新思科技升級Verification Continuum平臺繼續引領技術
Formal Verification的基礎知識



















評論