流程分析
kobject/kset的相關(guān)代碼比較簡單,畢竟它只是作為一個結(jié)構(gòu)體嵌入其他high-level的結(jié)構(gòu)中,充當紐帶的作用。不過,我還是簡單的上一張圖吧:
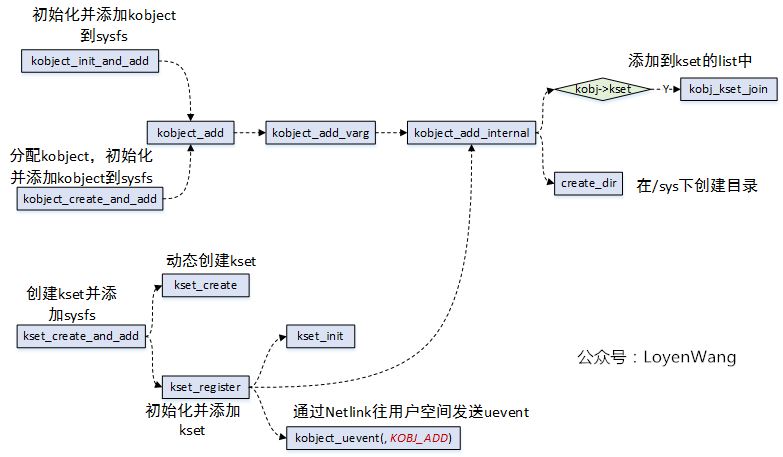
- 完成的工作基本就是分配結(jié)構(gòu)體,初始化各個結(jié)構(gòu)體字段,構(gòu)建拓撲關(guān)系(主要是添加到kset的list中,parent的指向等)等,看懂了結(jié)構(gòu)體的組織,這部分的代碼理解起來就很輕松了;
示例
先上一個原理圖:

代碼
#include < linux/kernel.h >
#include < linux/module.h >
#include < linux/slab.h >
#include < linux/kobject.h >
//自定義一個結(jié)構(gòu),包含了struct kobject子結(jié)構(gòu)
struct test_kobj {
int value;
struct kobject kobj;
};
//自定義個屬性結(jié)構(gòu)體,包含了struct attribute結(jié)構(gòu)
struct test_kobj_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count);
};
//聲明一個全局結(jié)構(gòu)用于測試
struct test_kobj *obj;
//用于初始化sysfs_ops中的函數(shù)指針
static ssize_t test_kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct test_kobj_attribute *test_kobj_attr;
ssize_t ret = -EIO;
test_kobj_attr = container_of(attr, struct test_kobj_attribute, attr);
//回調(diào)到具體的實現(xiàn)函數(shù)
if (test_kobj_attr- >show)
ret = test_kobj_attr- >show(container_of(kobj, struct test_kobj, kobj), test_kobj_attr, buf);
return ret;
}
//用于初始化sysfs_ops中的函數(shù)指針
static ssize_t test_kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count)
{
struct test_kobj_attribute *test_kobj_attr;
ssize_t ret = -EIO;
test_kobj_attr = container_of(attr, struct test_kobj_attribute, attr);
//回調(diào)到具體的實現(xiàn)函數(shù)
if (test_kobj_attr- >store)
ret = test_kobj_attr- >store(container_of(kobj, struct test_kobj, kobj), test_kobj_attr, buf, count);
return ret;
}
//用于初始化kobj_ktype
const struct sysfs_ops test_kobj_sysfs_ops = {
.show = test_kobj_attr_show,
.store = test_kobj_attr_store,
};
//用于初始化kobj_ktype,最終用于釋放kobject
void obj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
struct test_kobj *obj = container_of(kobj, struct test_kobj, kobj);
printk(KERN_INFO "test kobject release %sn", kobject_name(&obj- >kobj));
kfree(obj);
}
//定義kobj_ktype,用于指定kobject的類型,初始化的時候使用
static struct kobj_type test_kobj_ktype = {
.release = obj_release,
.sysfs_ops = &test_kobj_sysfs_ops,
};
//show函數(shù)的具體實現(xiàn)
ssize_t name_show(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, char *buffer)
{
return sprintf(buffer, "%sn", kobject_name(&obj- >kobj));
}
//show函數(shù)的具體實現(xiàn)
ssize_t value_show(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, char *buffer)
{
return sprintf(buffer, "%dn", obj- >value);
}
//store函數(shù)的具體實現(xiàn)
ssize_t value_store(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, const char *buffer, size_t size)
{
sscanf(buffer, "%d", &obj- >value);
return size;
}
//定義屬性,最終注冊進sysfs系統(tǒng)
struct test_kobj_attribute name_attribute = __ATTR(name, 0664, name_show, NULL);
struct test_kobj_attribute value_attribute = __ATTR(value, 0664, value_show, value_store);
struct attribute *test_kobj_attrs[] = {
&name_attribute.attr,
&value_attribute.attr,
NULL,
};
//定義組
struct attribute_group test_kobj_group = {
.name = "test_kobj_group",
.attrs = test_kobj_attrs,
};
//模塊初始化函數(shù)
static int __init test_kobj_init(void)
{
int retval;
printk(KERN_INFO "test_kobj_initn");
obj = kmalloc(sizeof(struct test_kobj), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!obj) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
obj- >value = 1;
memset(&obj- >kobj, 0, sizeof(struct kobject));
//添加進sysfs系統(tǒng)
kobject_init_and_add(&obj- >kobj, &test_kobj_ktype, NULL, "test_kobj");
//在sys文件夾下創(chuàng)建文件
retval = sysfs_create_files(&obj- >kobj, (const struct attribute **)test_kobj_attrs);
if (retval) {
kobject_put(&obj- >kobj);
return retval;
}
//在sys文件夾下創(chuàng)建group
retval = sysfs_create_group(&obj- >kobj, &test_kobj_group);
if (retval) {
kobject_put(&obj- >kobj);
return retval;
}
return 0;
}
//模塊清理函數(shù)
static void __exit test_kobj_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "test_kobj_exitn");
kobject_del(&obj- >kobj);
kobject_put(&obj- >kobj);
return;
}
module_init(test_kobj_init);
module_exit(test_kobj_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("LoyenWang");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m:=test_kobject.o
else
KERDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD:=$(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KERDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.symvers *.cmd *.cmd.o modules.* *.mod.c
endif
Makefile沒有太多好說的,注意Tab的使用,否則容易出錯;
測試結(jié)果

- 在/sys目錄下創(chuàng)建了test_kobj文件夾,在該文件夾下除了
name和value外,還有一個test_kobj_group的子文件夾; - 可以通過
cat/echo的操作,來操作name和value,分別會調(diào)用到底層的xxx_show和xxx_store函數(shù); - 對著代碼看這個圖,一目了然;
聲明:本文內(nèi)容及配圖由入駐作者撰寫或者入駐合作網(wǎng)站授權(quán)轉(zhuǎn)載。文章觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表電子發(fā)燒友網(wǎng)立場。文章及其配圖僅供工程師學(xué)習(xí)之用,如有內(nèi)容侵權(quán)或者其他違規(guī)問題,請聯(lián)系本站處理。
舉報投訴
-
嵌入式
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
5153文章
19708瀏覽量
318087 -
Linux
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
87文章
11519瀏覽量
214001 -
設(shè)備
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
2文章
4670瀏覽量
71808 -
模型
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
3527瀏覽量
50497 -
結(jié)構(gòu)體
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
131瀏覽量
11127
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
熱點推薦
詳解linux設(shè)備驅(qū)動模型架構(gòu)
LDD3中說:“Linux內(nèi)核需要一個對系統(tǒng)結(jié)構(gòu)的一般性描述。”這個描述就是linux設(shè)備驅(qū)動模型(下面簡稱為LDDM)。LDDM不是獨立存在,其體系如下圖所示:
發(fā)表于 07-25 07:25
Linux設(shè)備驅(qū)動模型摘抄
Linux2.6 內(nèi)核提供了新的設(shè)備模型,目的是為了對計算機上的所有設(shè)備進行統(tǒng)一地表示和操作,包括設(shè)備本身和
發(fā)表于 03-19 15:15
?39次下載
Linux設(shè)備模型之一:Kobject
Kobject是Linux設(shè)備模型的基礎(chǔ),也是設(shè)備模型中最難理解的一部分(可參考Documentation/kobject.txt的表述)。
發(fā)表于 05-06 15:51
?3474次閱讀
Linux設(shè)備模型:Bus
在Linux設(shè)備模型中,Bus(總線)是一類特殊的設(shè)備,它是連接處理器和其它設(shè)備之間的通道(channel)。為了方便
發(fā)表于 05-10 11:24
?1265次閱讀
Linux設(shè)備模型學(xué)習(xí)筆記(1)
Linux設(shè)備模型學(xué)習(xí)筆記1KobjectKobject, Kset和KtypeUeventsysfs文件系統(tǒng)wowo這里寫的很好了:http://www.wowotech.net
發(fā)表于 12-22 18:52
?0次下載





















評論