在 java 中,程序通常會和其他外部設備進行數據交互,比如寫入磁盤,網絡發送數據等等,今天我們來學學 java 中 基礎的 IO 流。
IO 流
與其他外部設備進行數據交互,比如將數據從內存中保存到磁盤文件中或者從網絡上下載數據并加載到內存中,這個過程都是一種單向且有順序的數據傳輸,被稱之為流。
IO 就是 Input 輸入和 Output 輸出。輸入輸出以內存為中心的流向劃分的。傳輸數據到內存就是輸入流,從內存中輸出數據就是輸出流。
InputStream
InputStream 是所有輸入流的父類,是一個抽象類,讀取的數據單位是字節(byte)。
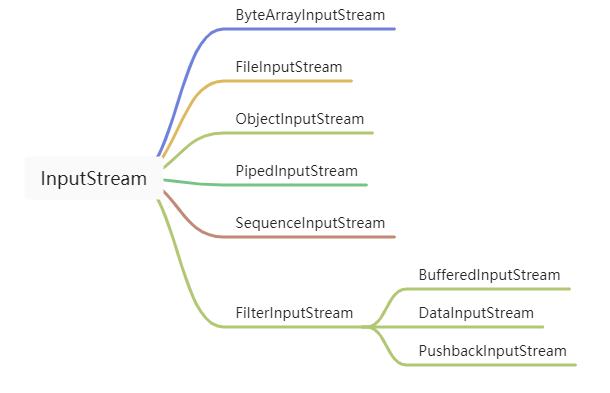
主要的抽象方法是 read(),這個方法就是讀取數據內容并返回 -1~255 的 int 值。read() 方法是一個阻塞的方法,只有將內容全部讀取完成之后才能運行下一行代碼。
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
以 FileInputStream 實現類作為示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// input.txt 內容為 hello, inputStream
InputStream input = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
int n = 0;
while((n = input.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) n);
}
input.close();
}
示例中的 read() 方法只能一個字節的一個字節讀取數據,效率不高,當文件中存在多個字節為一個漢字的中文時,上面的示例將打印出亂碼。
InputStream 支持將一次性讀取多個字節到緩沖區,利用緩沖區提高效率。返回值的數據不再是讀取的數據字節,而是讀取的字節數。并且可以正常的打印出中文字符。
// 將讀取的內容填充到 byte 數組
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException
// 將讀取的內容填充 byte 數組中 off 開始,len 長度的區域
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException
將緩沖區大小設置為 1024 個字節示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//input.txt 文件內容為 你好, inputStream
InputStream input = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
byte[] result = new byte[1024];
while(input.read(result) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(result, "utf-8"));
}
input.close();
}
OutputStream
OutputStream 是所有輸出流的父類。和 InputStream 一樣是一個抽象類。
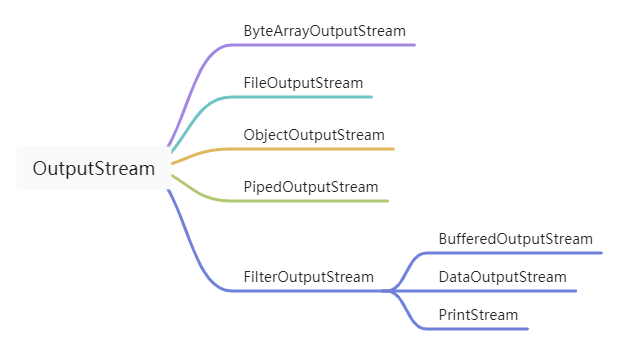
主要的抽象方法是 write(),也是一個阻塞的方法,只有將內容全部寫完成之后才能運行下一行代碼。write() 方法和 read() 方法一樣都是一個字節一個字節的操作的。
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException;
以 FileInputStream 實現類作為示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("out.txt");
try {
out.write("h".getBytes());
out.write("e".getBytes());
out.write("l".getBytes());
out.write("l".getBytes());
out.write("0".getBytes());
} finally {
if(out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
write() 按單個字節寫入磁盤的效率比較低下,OutputStream 提供了 write(byte[]) 一次性大批量的將字節輸出到磁盤。對于 IO 設備來說,一次性寫入 1 個字節和寫入 1000 個字節的時間都是差不多的。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("out.txt");
try {
out.write("哈嘍,outputStream".getBytes());
} finally {
if(out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
關閉資源
不管是 InputStream 還是 OutputStream 在使用資源之后都需要調用 close()方法。在示例中如果在 close() 方法調用之前拋出異常則不會自動關閉資源。以下兩種方式都可以關閉資源:
- try..finally 方式
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream input = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
try {
byte[] result = new byte[1024];
while(input.read(result) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(result, "utf-8"));
}
} finally {
if(input != null) {
input.close();
}
}
}
- try(resource)
實現了 Closeable 接口的 InputStream 和 OutputStream 使用 try(resource) 時,編譯器會自動增加 finally。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("out.txt")){
out.write("編譯器會添加 finally".getBytes());
}
}
總結
今天就是簡單地給大家介紹 Java 的 IO 流,為接下來學其他 IO 類打個基礎。
-
IO
+關注
關注
0文章
448瀏覽量
39203 -
數據
+關注
關注
8文章
7080瀏覽量
89175 -
內存
+關注
關注
8文章
3034瀏覽量
74137 -
JAVA
+關注
關注
19文章
2971瀏覽量
104854 -
磁盤
+關注
關注
1文章
379瀏覽量
25224
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
IO與NIO有何區別
java中的IO流與Guava工具
Java中的輸入輸出流盤點
java流與文件實驗
java中的io流分析





 Java中基礎的 IO 流
Java中基礎的 IO 流










評論