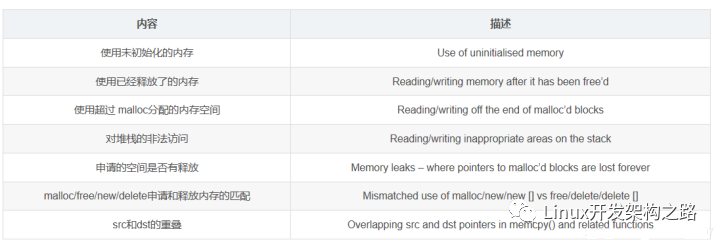
內(nèi)存泄漏原因
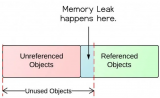
內(nèi)存泄漏在C/C++這種不帶GC(Garbage Collection)的語(yǔ)言里,是一個(gè)經(jīng)常發(fā)生的問(wèn)題。因?yàn)闆](méi)有GC,所以分配的內(nèi)存需要程序員自己調(diào)用釋放。內(nèi)存泄漏的根本原因是程序?qū)τ谠谏暾?qǐng)的內(nèi)存沒(méi)有進(jìn)行釋放。
{
void *p1 = malloc(10);
void *p2 = malloc(20);
free(p1);
}
上面的代碼段,申請(qǐng)了兩塊內(nèi)存p1,p2,只釋放了p1,沒(méi)有釋放p2,產(chǎn)生了內(nèi)存泄漏。
內(nèi)存泄漏會(huì)產(chǎn)生哪些后果?
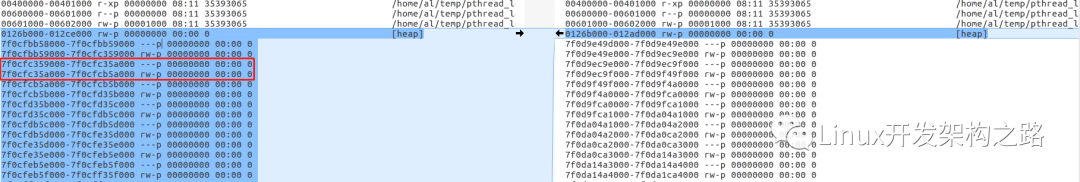
隨著程序運(yùn)行時(shí)間越來(lái)越久,內(nèi)存有分配沒(méi)有釋放,會(huì)使得進(jìn)程堆中的內(nèi)存會(huì)越來(lái)越少,直到耗盡。會(huì)造成后面的運(yùn)行時(shí)代碼不能成功分配內(nèi)存。
內(nèi)存泄漏如何解決?
方案一 引入gc,從語(yǔ)言層面解決內(nèi)存泄漏;
方案二 當(dāng)發(fā)生內(nèi)存泄漏的時(shí)候,能夠精準(zhǔn)的定位代碼那個(gè)文件、那個(gè)函數(shù)、哪一行所引起的。
我們實(shí)現(xiàn)的是方案二,核心需求有兩個(gè)。
需求1: 能夠檢測(cè)出內(nèi)存泄漏
需求2:能夠指出是由代碼的哪個(gè)文件、哪個(gè)函數(shù)、哪一行引起的內(nèi)存泄漏
內(nèi)存泄漏檢測(cè)如何實(shí)現(xiàn)?
內(nèi)存泄漏檢測(cè)實(shí)現(xiàn)的核心思想就是對(duì)系統(tǒng)的malloc/free進(jìn)行hook,用我們自己的malloc/free代替系統(tǒng)調(diào)用,將free的地址和malloc的地址進(jìn)行匹配,查看最后又哪些malloc沒(méi)有進(jìn)行free,并將沒(méi)有free的malloc操作的代碼段地址進(jìn)行記錄,通過(guò)代碼段定位所在的文件、函數(shù)、代碼行。
方案一
采用__libc_malloc, libc_free與__builtin_return_address。它們是gcc提供的函數(shù)。
__libc_malloc, libc_free用來(lái)代替malloc/free。可以用來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)hook。需要注意的是,我們實(shí)現(xiàn)的malloc/free函數(shù),內(nèi)部會(huì)有一些函數(shù)如printf,fopen,需要防止它們會(huì)嵌套調(diào)用malloc/free。
__builtin_return_address,能夠返回調(diào)用所在函數(shù)的代碼段的地址。能夠定位內(nèi)存泄漏的具體位置。
malloc的時(shí)候,創(chuàng)建一個(gè)文件,文件名使用申請(qǐng)內(nèi)存的地址,并記錄申請(qǐng)?jiān)搩?nèi)存的代碼段的地址;free的時(shí)候,刪除對(duì)應(yīng)的文件。
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdio.h >
#include < unistd.h >
int enable_malloc_hook = 1;
extern void *__libc_malloc(size_t size);
int enable_free_hook = 1;
extern void *__libc_free(void *p);
void *malloc(size_t size) {
if (enable_malloc_hook) {
enable_malloc_hook = 0;
void *p = __libc_malloc(size);
void *caller = __builtin_return_address(0);
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
FILE *fp = fopen(buff, "w");
fprintf(fp, "[+%p]malloc -- > addr:%p size:%lun", caller, p, size);
fflush(fp);
enable_malloc_hook = 1;
return p;
} else {
return __libc_malloc(size);
}
return NULL;
}
void free(void *p) {
if (enable_free_hook) {
enable_free_hook = 0;
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
if (unlink(buff) < 0) {
printf("double free: %pn", p);
}
__libc_free(p);
enable_free_hook = 1;
} else {
__libc_free(p);
}
}
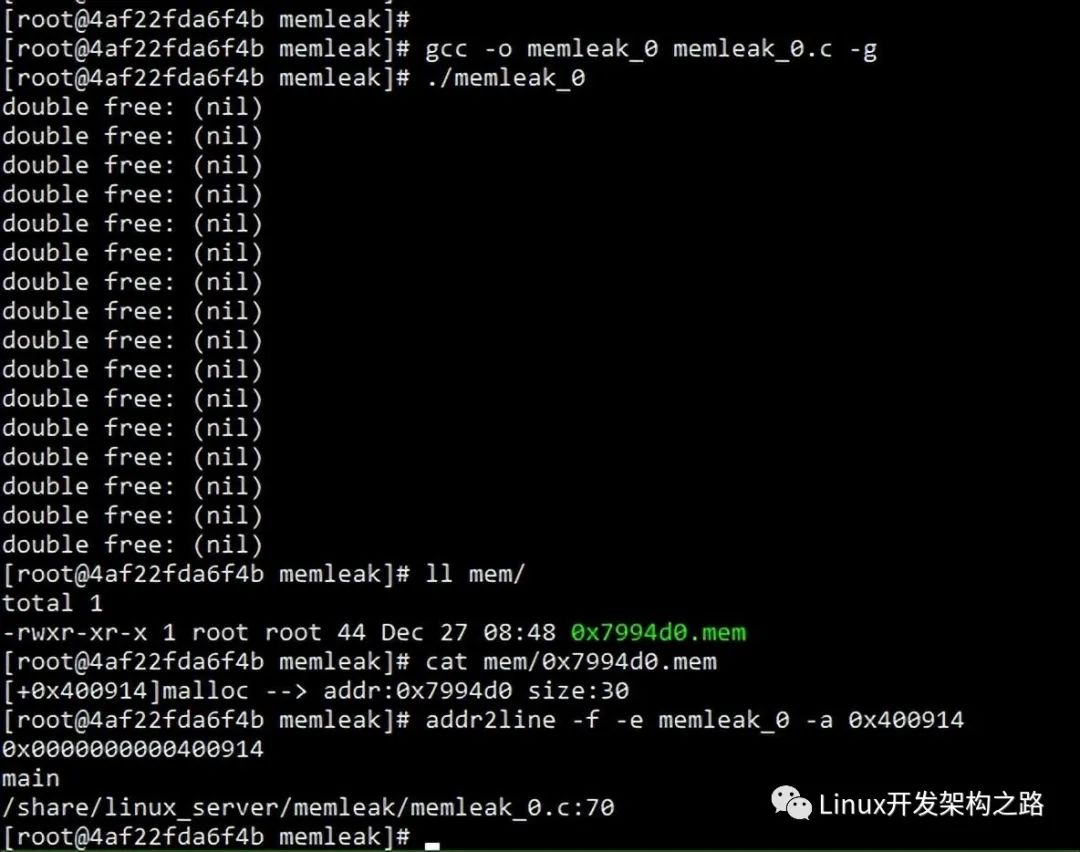
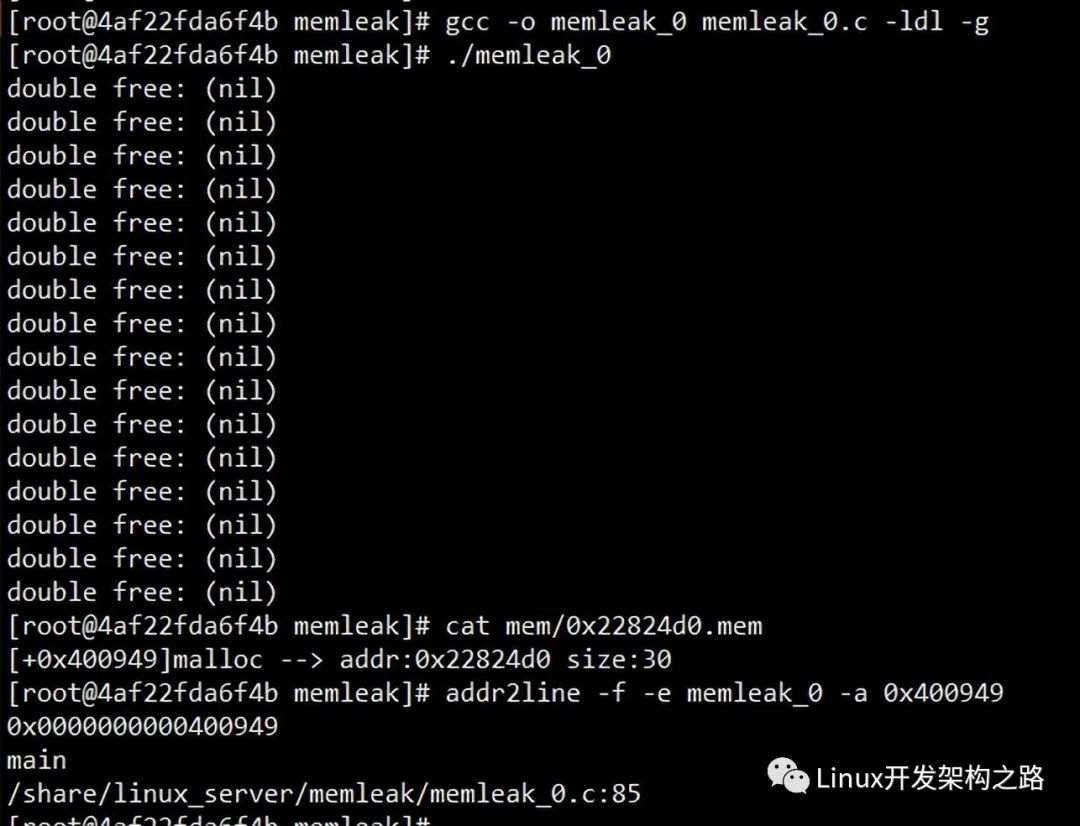
// gcc -o memleak_0 memleak_0.c -g
// addr2line -f -e memleak_0 -a 0x4006d8
int main() {
void *p1 = malloc(10);
void *p2 = malloc(20);
free(p1);
void *p3 = malloc(30);
void *p4 = malloc(40);
free(p2);
free(p4);
return 0;
}
方案二
使用宏定義, 開(kāi)啟宏定義使用我們的版本,不開(kāi)啟就使用系統(tǒng)的。可以方便debug。
內(nèi)存泄漏檢測(cè)使用malloc_hook/free_hook, 定位內(nèi)存泄漏位置,使用__FILE__, LINE .
#define malloc(size) malloc_hook(size, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#define free(p) free_hook(p, __FILE__, __LINE__)
可以使用fclose,沒(méi)有double free的問(wèn)題了
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdio.h >
#include < unistd.h >
void *malloc_hook(size_t size, const char *file, int line) {
void *p = malloc(size);
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
FILE *fp = fopen(buff, "w");
fprintf(fp, "[+%s:%d]malloc -- > addr:%p size:%lun", file, line, p, size);
fflush(fp);
fclose(fp);
return p;
}
void free_hook(void *p, const char *file, int line) {
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
if (unlink(buff) < 0) {
printf("double free: %pn", p);
return;
}
free(p);
}
#define malloc(size) malloc_hook(size, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#define free(p) free_hook(p, __FILE__, __LINE__)
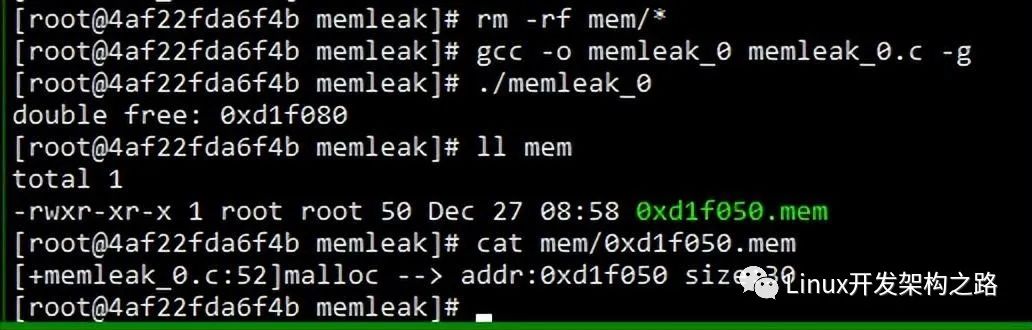
// gcc -o memleak_0 memleak_0.c -g
// addr2line -f -e memleak_0 -a 0x4006d8
int main() {
void *p1 = malloc(10);
void *p2 = malloc(20);
free(p1);
void *p3 = malloc(30); // memory leak
void *p4 = malloc(40);
free(p2);
free(p4);
free(p4); // double free
return 0;
}
檢測(cè)出兩個(gè)問(wèn)題,一次內(nèi)存泄漏 p3,一次double free p4。結(jié)果OK。
方案三
使用malloc.h中提供的hook: __malloc_hook, __free_hook.
這兩個(gè)hook,默認(rèn)是malloc,free。
參考mtrace的做法,通過(guò)改變這兩個(gè)值來(lái)進(jìn)行檢測(cè)。
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdio.h >
#include < unistd.h >
#include < malloc.h >
typedef void *(*malloc_hoot_t)(size_t size, const void *caller);
malloc_hoot_t malloc_f;
typedef void (*free_hook_t)(void *p, const void *caller);
free_hook_t free_f;
void mem_trace(void);
void mem_untrace(void);
void *malloc_hook_f(size_t size, const void *caller) {
mem_untrace();
void *ptr = malloc(size);
// printf("+%p: addr[%p]n", caller, ptr);
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", ptr);
FILE *fp = fopen(buff, "w");
fprintf(fp, "[+%p]malloc -- > addr:%p size:%lun", caller, ptr, size);
fflush(fp);
fclose(fp);
mem_trace();
return ptr;
}
void free_hook_f(void *p, const void *caller) {
mem_untrace();
// printf("-%p: addr[%p]n", caller, p);
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
if (unlink(buff) < 0) {
printf("double free: %pn", p);
}
free(p);
mem_trace();
}
void mem_trace(void) {
malloc_f = __malloc_hook;
free_f = __free_hook;
__malloc_hook = malloc_hook_f;
__free_hook = free_hook_f;
}
void mem_untrace(void) {
__malloc_hook = malloc_f;
__free_hook = free_f;
}
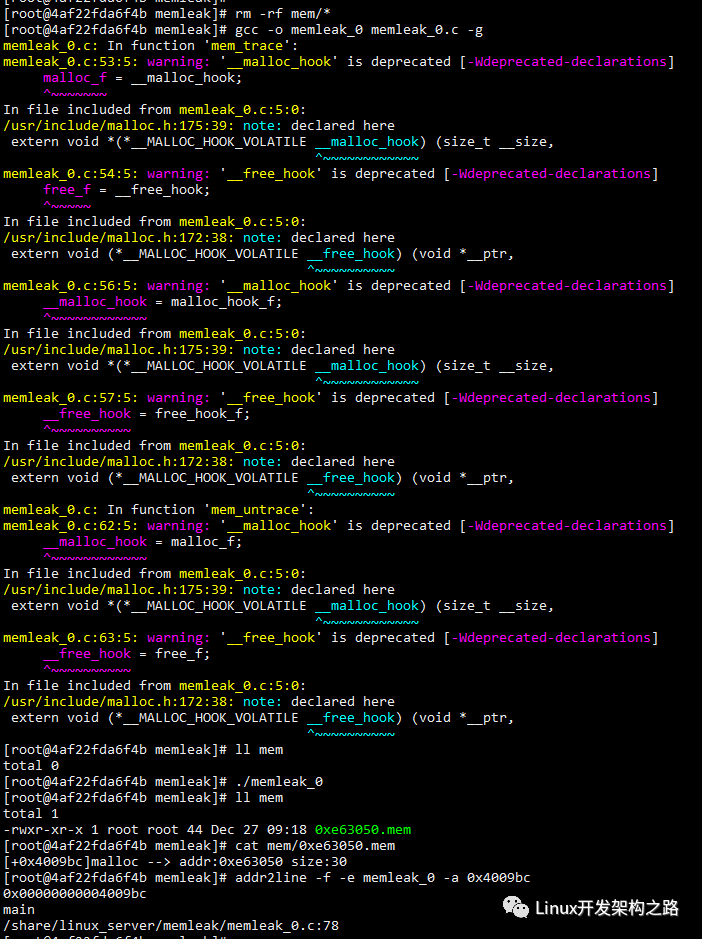
// gcc -o memleak_0 memleak_0.c -g
// addr2line -f -e memleak_0 -a 0x4006d8
int main() {
mem_trace();
void *p1 = malloc(10);
void *p2 = malloc(20);
free(p1);
void *p3 = malloc(30);
void *p4 = malloc(40);
free(p2);
free(p4);
mem_untrace();
return 0;
}
方案四
使用mtrace
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdio.h >
#include < unistd.h >
#include < malloc.h >
#include < mcheck.h >
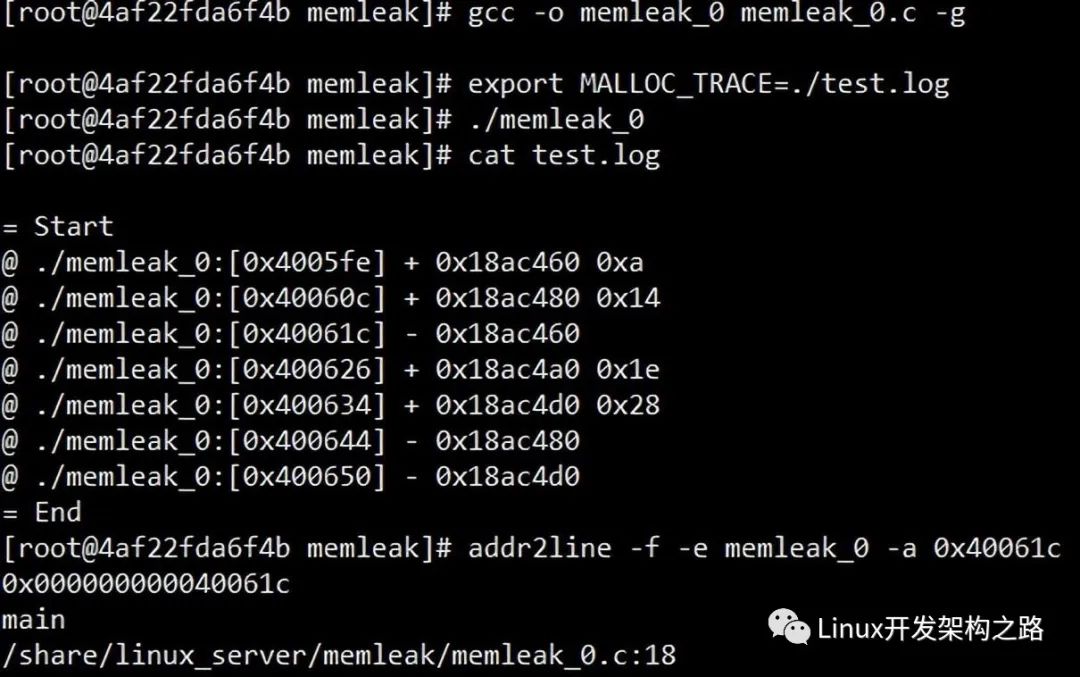
// gcc -o memleak_0 memleak_0.c -g
// addr2line -f -e memleak_0 -a 0x4006d8
int main() {
// export MALLOC_TRACE=./test.log
mtrace();
void *p1 = malloc(10);
void *p2 = malloc(20);
free(p1);
void *p3 = malloc(30);
void *p4 = malloc(40);
free(p2);
free(p4);
muntrace();
#endif
return 0;
}
方案五
使用dlsym對(duì)malloc,free進(jìn)行hook。
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include < dlfcn.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdio.h >
#include < unistd.h >
typedef void *(*malloc_t)(size_t size);
malloc_t malloc_f;
typedef void (*free_t)(void *p);
free_t free_f;
int enable_malloc_hook = 1;
int enable_free_hook = 1;
void *malloc(size_t size) {
if (enable_malloc_hook) {
enable_malloc_hook = 0;
void *p = malloc_f(size);
void *caller = __builtin_return_address(0);
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
FILE *fp = fopen(buff, "w");
fprintf(fp, "[+%p]malloc -- > addr:%p size:%lun", caller, p, size);
fflush(fp);
enable_malloc_hook = 1;
return p;
} else {
return malloc_f(size);
}
return NULL;
}
void free(void *p) {
if (enable_free_hook) {
enable_free_hook = 0;
char buff[128] = {0};
sprintf(buff, "./mem/%p.mem", p);
if (unlink(buff) < 0) {
printf("double free: %pn", p);
}
free_f(p);
enable_free_hook = 1;
} else {
free_f(p);
}
}
static int init_hook() {
malloc_f = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "malloc");
free_f = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "free");
}
// gcc -o memleak_0 memleak_0.c -ldl -g
// addr2line -f -e memleak_0 -a 0x4006d8
int main() {
init_hook();
void *p1 = malloc(10);
void *p2 = malloc(20);
free(p1);
void *p3 = malloc(30);
void *p4 = malloc(40);
free(p2);
free(p4);
return 0;
}
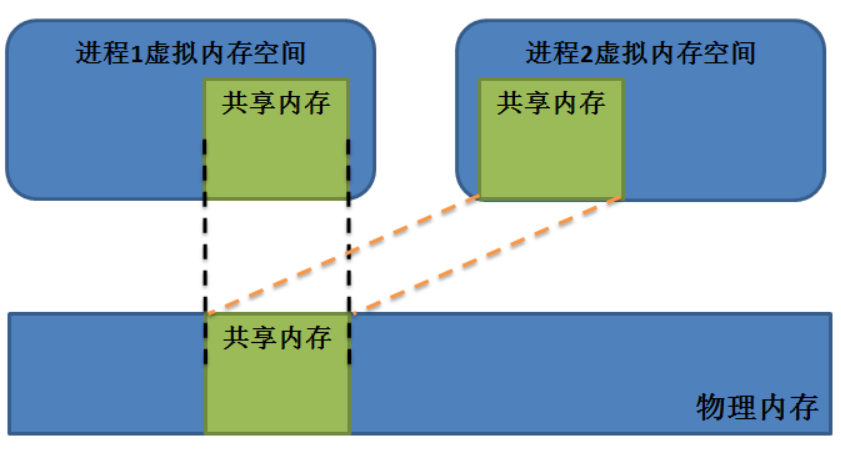
共享內(nèi)存
mmap方法1
匿名mmap
#include < stdio.h >
#include < sys/mman.h >
#include < unistd.h >
void *shm_mmap_alloc(int size) {
void *addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
MAP_ANON | MAP_SHARED, -1, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED) {
return NULL;
}
return addr;
}
int shm_mmap_free(void *addr, int size) {
return munmap(addr, size);
}
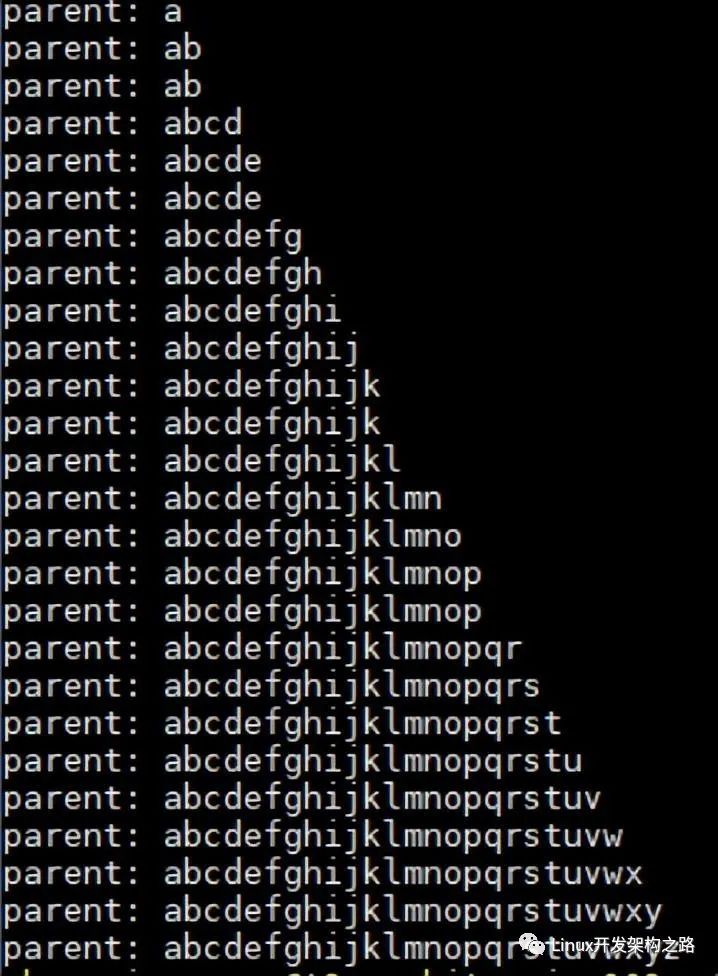
int main() {
char *addr = (char *)shm_mmap_alloc(1024);
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
// child
int i = 0;
while(i < 26) {
addr[i] = 'a' + i++;
addr[i] = '?';
sleep(1);
}
} else if (pid > 0) {
int i = 0;
while (i++ < 26) {
printf("parent: %sn", addr);
sleep(1);
}
}
shm_mmap_free(addr, 1024);
}
mmap方法2
/dev/zero
#include < stdio.h >
#include < sys/mman.h >
#include < unistd.h >
#include < sys/types.h >
#include < sys/stat.h >
#include < fcntl.h >
void *shm_mmap_alloc(int size) {
int fd = open("/dev/zero", O_RDWR);
void *addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
close(fd);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED) {
return NULL;
}
return addr;
}
int shm_mmap_free(void *addr, int size) {
return munmap(addr, size);
}
int main() {
char *addr = (char *)shm_mmap_alloc(1024);
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
// child
int i = 0;
while(i < 26) {
addr[i] = 'a' + i++;
addr[i] = '?';
sleep(1);
}
} else if (pid > 0) {
int i = 0;
while (i++ < 26) {
printf("parent: %sn", addr);
sleep(1);
}
}
shm_mmap_free(addr, 1024);
}
shmget方法
#include < stdio.h >
#include < sys/mman.h >
#include < unistd.h >
#include < sys/types.h >
#include < sys/stat.h >
#include < fcntl.h >
#include < sys/types.h >
#include < sys/shm.h >
void *shm_alloc(int size) {
int segment_id = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, size,
IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
char *addr = (char *)shmat(segment_id, NULL, 0);
return addr;
}
int shm_free(void *addr) {
return shmdt(addr);
}
int main() {
char *addr = (char *)shm_alloc(1024);
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
// child
int i = 0;
while(i < 26) {
addr[i] = 'a' + i++;
addr[i] = '?';
sleep(1);
}
} else if (pid > 0) {
int i = 0;
while (i++ < 26) {
printf("parent: %sn", addr);
sleep(1);
}
}
shm_free(addr);
}
-
語(yǔ)言
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
97瀏覽量
24242 -
C++
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
22文章
2108瀏覽量
73619 -
代碼
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
30文章
4779瀏覽量
68522 -
內(nèi)存泄漏
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
39瀏覽量
9215
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
Linux內(nèi)存泄漏檢測(cè)實(shí)現(xiàn)原理與實(shí)現(xiàn)
內(nèi)存泄漏定位該如何去實(shí)現(xiàn)呢
C++內(nèi)存泄漏
ThreadLocal發(fā)生內(nèi)存泄漏的原因
內(nèi)存泄漏的特點(diǎn)和類(lèi)型
內(nèi)存泄漏問(wèn)題原理及檢視方法
基于機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)的內(nèi)存泄漏測(cè)試腳本預(yù)測(cè)方法
Windows CE中的內(nèi)存泄漏問(wèn)題
什么是內(nèi)存泄漏?內(nèi)存泄漏有哪些現(xiàn)象
什么是內(nèi)存泄漏?如何避免JavaScript內(nèi)存泄漏
內(nèi)存泄漏如何避免
線程內(nèi)存泄漏問(wèn)題的定位




 內(nèi)存泄漏會(huì)產(chǎn)生哪些后果
內(nèi)存泄漏會(huì)產(chǎn)生哪些后果










評(píng)論