使用 OpenVINO 定制你的 AI 助手丨開發(fā)者實戰(zhàn)
作者:
指導(dǎo):
顏國進 英特爾邊緣計算創(chuàng)新大使
研揚科技針對邊緣 AI 行業(yè)開發(fā)者推出的『哪吒』(Nezha)開發(fā)套件,以信用卡大小(85 x 56mm)的開發(fā)板-『哪吒』(Nezha)為核心,『哪吒』采用 Intel N97 處理器(Alder Lake-N),最大睿頻 3.6GHz,Intel UHD Graphics 內(nèi)核GPU,可實現(xiàn)高分辨率顯示;板載 LPDDR5 內(nèi)存、eMMC 存儲及 TPM 2.0,配備 GPIO 接口,支持 Windows 和 Linux 操作系統(tǒng),這些功能和無風(fēng)扇散熱方式相結(jié)合,為各種應(yīng)用程序構(gòu)建高效的解決方案,專為入門級人工智能應(yīng)用和邊緣智能設(shè)備而設(shè)計。英特爾開發(fā)套件能完美勝人工智能學(xué)習(xí)、開發(fā)、實訓(xùn)、應(yīng)用等不同應(yīng)用場景。適用于如自動化、物聯(lián)網(wǎng)網(wǎng)關(guān)、數(shù)字標(biāo)牌和機器人等應(yīng)用。
1.1
OpenVINO 介紹
OpenVINO 是一個開源工具套件,用于對深度學(xué)習(xí)模型進行優(yōu)化并在云端、邊緣進行部署。它能在諸如生成式人工智能、視頻、音頻以及語言等各類應(yīng)用場景中加快深度學(xué)習(xí)推理的速度,且支持來自 PyTorch、TensorFlow、ONNX 等熱門框架的模型。實現(xiàn)模型的轉(zhuǎn)換與優(yōu)化,并在包括 Intel硬件及各種環(huán)境(本地、設(shè)備端、瀏覽器或者云端)中進行部署。
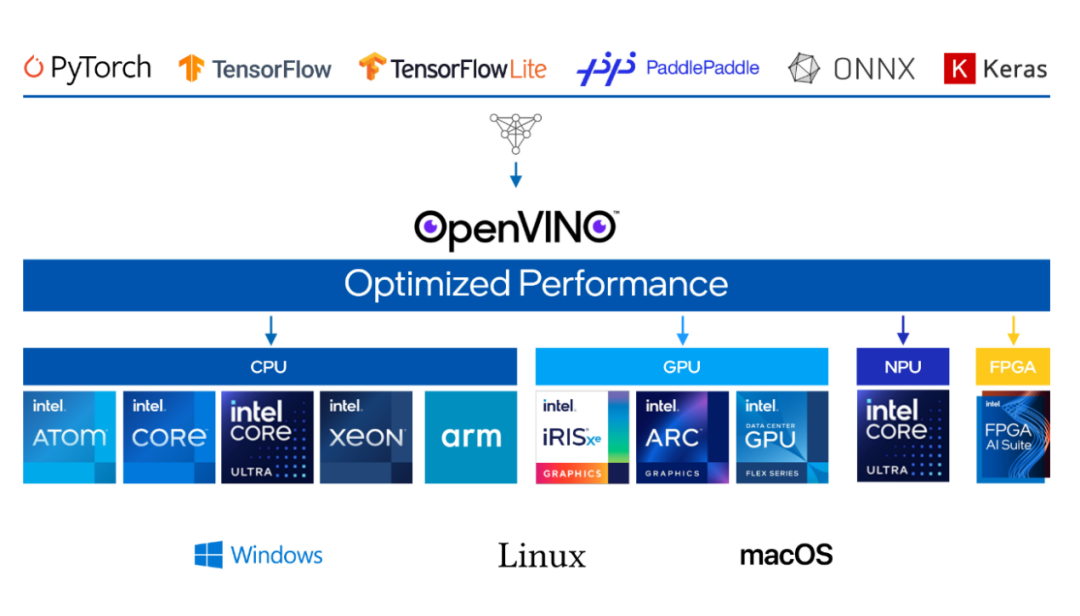
圖1-2 以深度學(xué)習(xí)為基礎(chǔ)的AI技術(shù)在各行各業(yè)應(yīng)用廣泛
1.2
Ubuntu22.04 上的
OpenVINO 環(huán)境配置
OpenVINO 官方文檔 https://docs.openvino.ai 有最新版本的安裝教程,這里使用壓縮包的方式安裝,選擇對應(yīng)的 Ubuntu22 的版本:
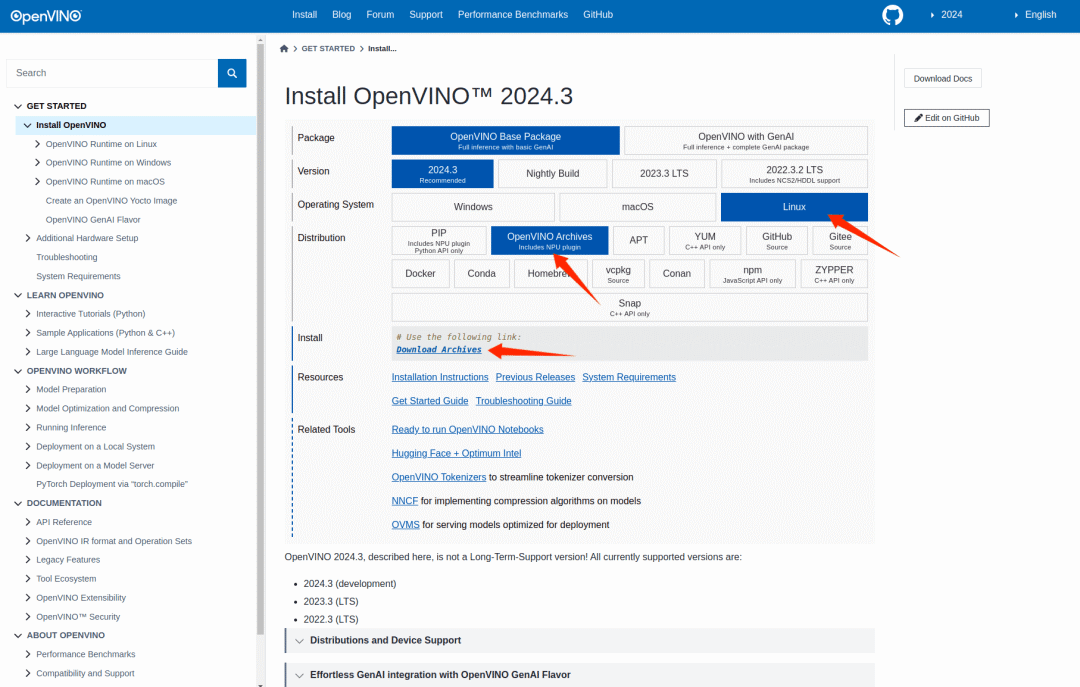
下載到哪吒開發(fā)板上后將壓縮包解壓:
1 tar -zxvf l_openvino_toolkit_ubuntu22_2024.3.0.16041.1e3b88e4e3f_x86_64.tgz
進入解壓目錄,安裝依賴:
1 cd l_openvino_toolkit_ubuntu22_2024.3.0.16041.1e3b88e4e3f_x86_64/ 2 sudo -E ./install_dependencies/install_openvino_dependencies.sh
然后配置環(huán)境變量:
1 source ./setupvars.sh
這樣 OpenVINO 的環(huán)境就配置好了,可以直接在 Intel CPU 上推理模型,如果需要在 Intel iGPU 上推理,還需要另外安裝 OpenCL runtime packages,參考官方文檔:
https://docs.openvino.ai/2024/get-started/configurations/configurations-intel-gpu.html
這里使用 deb 包的方式安裝,按照 Github
https://github.com/intel/compute-runtime
的說明下載7個 deb 包,然后 dpkg 安裝
1 sudo dpkg -i *.deb
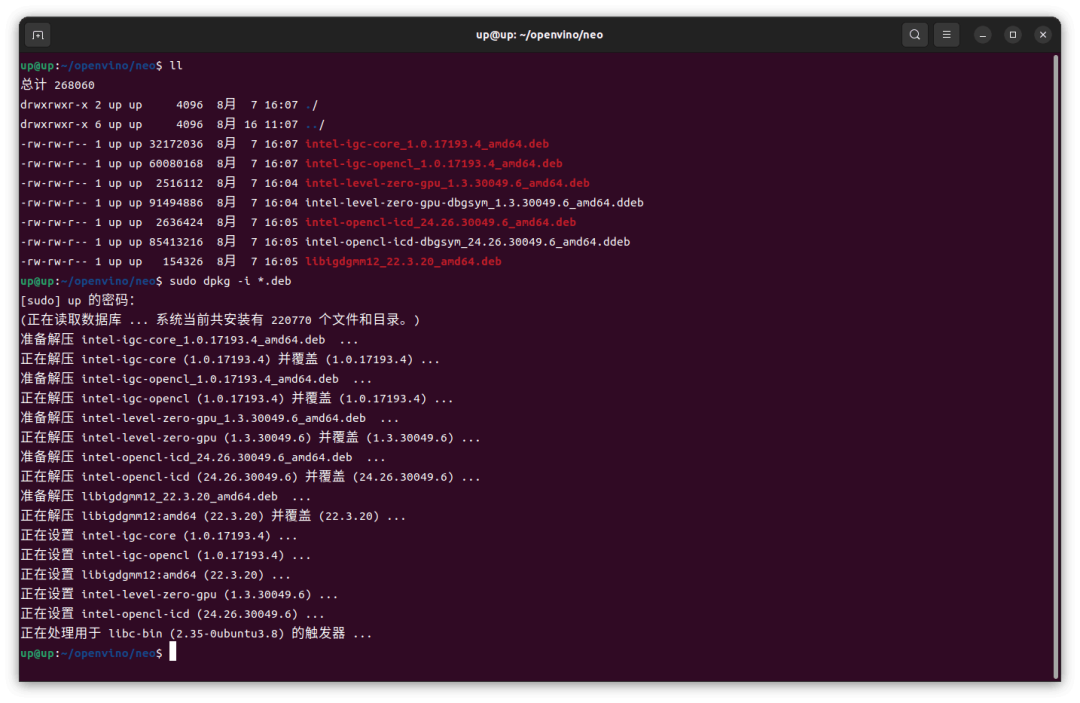
如果 dpkg 安裝出現(xiàn)依賴報錯,就需要先 apt 安裝依賴,然后再 dpkg 安裝7個 deb 包
1 sudo apt install ocl-icd-libopencl1
這樣在哪吒開發(fā)板 Ubuntu22.04 上使用 Intel iGPU 進行 OpenVINO 推理的環(huán)境就配置完成了。
1.3
Transformer模型推理
模型是一個基于 Transformer 結(jié)構(gòu)的模型,訓(xùn)練后生成 ONNX 中間表示,OpenVINO 可以直接使用 ONNX 模型進行推理,也可以轉(zhuǎn)為 OpenVINO IR格式,轉(zhuǎn)換命令如下:
1 ovc model.onnx
默認會生成 FP16 的模型,如果精度有較大損失,可指定 compress_to_fp16 為 False 就不會進行 FP16 量化了:
1 ovc model.onnx --compress_to_fp16=False
轉(zhuǎn)換后將生成.xml和.bin兩個文件,.xml文件描述了模型的結(jié)構(gòu),.bin文件包含了模型各層的參數(shù)。
推理代碼如下:
1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 #include 6 #include 7 #include 8 const int length = 300; 9 void read_csv(const char* filepath, float* input) 10 { 11 std::ifstream file(filepath); 12 std::string line; 13 if (file.is_open()) 14 { 15 std::getline(file, line); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) ? ? ? 17? { ? ? ? ? ? ? 18 std::getline(file, line); ? ? ? ? ? ? 19 std::stringstream ss(line); ? ? ? ? ? ? 20 std::string field; ? ? ? ? ? 21? if (std::getline(ss, field, ',')) ? ? ? ? ? 22? { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 23? if (std::getline(ss, field, ',')) ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 24 { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 25 input[i] = std::stof(field); ? 26 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ? 27? } ? ? ? 28? } ? ? ? 29? file.close(); ? 30 } ? ? 31 float maxVal = *std::max_element(input, input + 300); 32? for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) ? 33 { ? ? ? 34? input[i] /= maxVal; 35? } 36 } 37 std::vector softmax(std::vector input) 38 { 39 ? ? std::vector output(input.size()); ? 40? float sum = 0; ? ? 41 for (int i = 0; i < input.size(); i++) ? ? 42 { ? ? ? ? 43 output[i] = exp(input[i]); ? ? ? ? 44 sum += output[i]; ? ? 45 } ? ? 46 for (int i = 0; i < input.size(); i++) ? 47 { ? ? ? ? 48 output[i] /= sum; ? ? 49 } ? ? 50 return output; 51 } 52 void warmup(ov::InferRequest request) 53 { ? ? 54 std::vector inputData(length); ? 55 memcpy(request.get_input_tensor().data(), inputData.data(), length * sizeof(float)); ? ? 56 request.infer(); 57 } 58 int main() 59 { ? 60 const char* modelFile = "/home/up/openvino/AutoInjector_Transformer/AutoInjector_Transformer/2024-07-17-17-28-00_best_model.xml"; ? ? 61 const char* dirpath = "/home/up/openvino/AutoInjector_Transformer/AutoInjector_Transformer/data"; ? ? 62 const char* device = "GPU"; ? ? 63 std::vector inputs(length); ? ? 64 std::vector outputs(length * 4); ? ? 65 ov::Core core; ? 66? // Load Model 67? ? std::cout << "Loading Model" << std::endl; ? ? 68 auto start_load_model = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); 69? ? auto model = core.read_model(modelFile); ? ? 70 auto compiled_model = core.compile_model(model, device); ? 71? ov::InferRequest request = compiled_model.create_infer_request(); ? ? 72 std::cout << "Model Loaded, " << "time: " << std::chrono::duration_cast(std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now() - start_load_model).count() << "ms" << std::endl; ? ? 73 request.get_input_tensor().set_shape(std::vector{1, length}); ? ? 74 // Warmup ? ? 75 warmup(request); ? ? 76 for (auto& filename : std::filesystem::directory_iterator(dirpath)) ? ? 77 { ? ? ? ? 78 std::string pathObj = filename.path().string(); ? ? ? ? 79 const char* filepath = pathObj.c_str(); ? ? ? ? 80 std::cout << "Current File: " << filepath << std::endl; ? ? ? ? 81 // Read CSV ? ? ? ? 82 auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); ? ? ? ? 83 read_csv(filepath, inputs.data()); ? ? ? 84? memcpy(request.get_input_tensor().data(), inputs.data(), length * sizeof(float)); ? ? ? ? 85 // Infer ? ? ? ? 86 request.infer(); ? ? ? ? 87 // Get Output Data ? ? ? ? 88 memcpy(outputs.data(), request.get_output_tensor().data(), length * sizeof(float) * 4); ? ? ? ? 89 // Softmax ? ? ? ? 90 std::vector softmax_results(length); ? ? ? ? 91 std::vector temp(4); ? ? ? ? 92 std::vector softmax_tmp(4); ? ? ? ? 93 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) ? ? ? 94? { ? ? ? ? ? ? 95 for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) ? ? ? ? ? 96? { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 97 temp[j] = outputs[j * length + i]; ? ? ? ? ? 98? } ? ? ? ? ? ? 99 softmax_tmp = softmax(temp); ? ? ? ? ? ? 100 auto maxVal = std::max_element(softmax_tmp.begin(), softmax_tmp.end()); ? ? ? ? ? ? 101 auto maxIndex = std::distance(softmax_tmp.begin(), maxVal); ? ? ? ? ? ? 102 softmax_results[i] = maxIndex; ? ? ? ? 103 } ? ? ? ? 104 std::cout << "Infer time: " << std::chrono::duration_cast(std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now() - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; 105 106? ? ? ? ? // Print outputs ? ? ? ? 107 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) ? ? ? 108? { ? ? ? ? ? ? 109 std::cout << softmax_results[i] << " "; ? ? ? 110? } ? ? 111 } ? ? 112 return 0; 113 }
使用 cmake 進行構(gòu)建,在 CMakeLists.txt 中指定變量 ${OpenVino_ROOT} 為前面解壓的 OpenVINO 壓縮包路徑:
1 cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10.0) 2 3 project(AutoInjector_Transformer) 4 5 set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 20) 6 set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON) 7 set(OpenVino_ROOT /home/up/openvino/l_openvino_toolkit_ubuntu22_2024.3.0.16041.1e3b88e4e3f_x86_64/runtime) 8 set(OpenVINO_DIR ${OpenVino_ROOT}/cmake) 9 10 find_package(OpenVINO REQUIRED) 11 12 include_directories( 13 ${OpenVino_ROOT}/include 14 ${OpenVino_ROOT}/include/openvino 15 ) 16 17 link_directories( 18 ${OpenVino_ROOT}/lib 19 ${OpenVino_ROOT}/lib/intel64 20 ) 21 22 add_executable(AutoInjector_Transformer AutoInjector_Transformer.cpp) 23 target_link_libraries(AutoInjector_Transformer openvino)
然后 cmake 構(gòu)建項目:
1 mkdir build && cd build 2 cmake .. 3 make
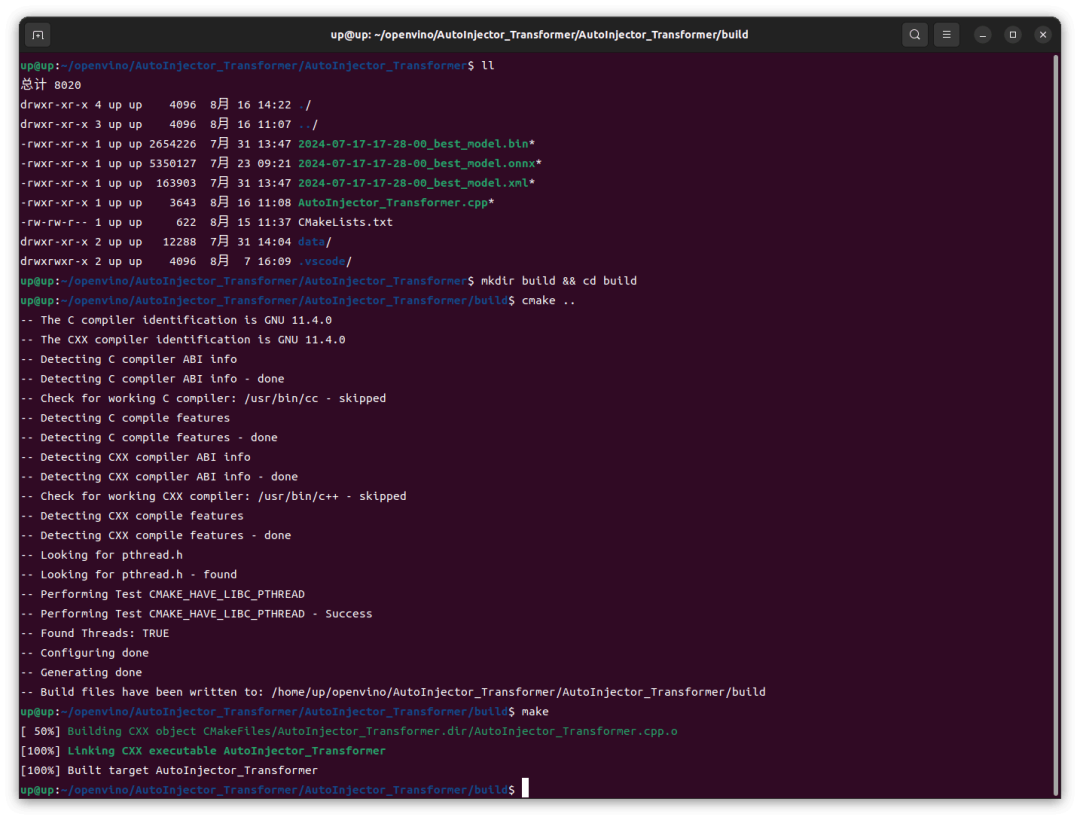
然后運行生成的可執(zhí)行文件:
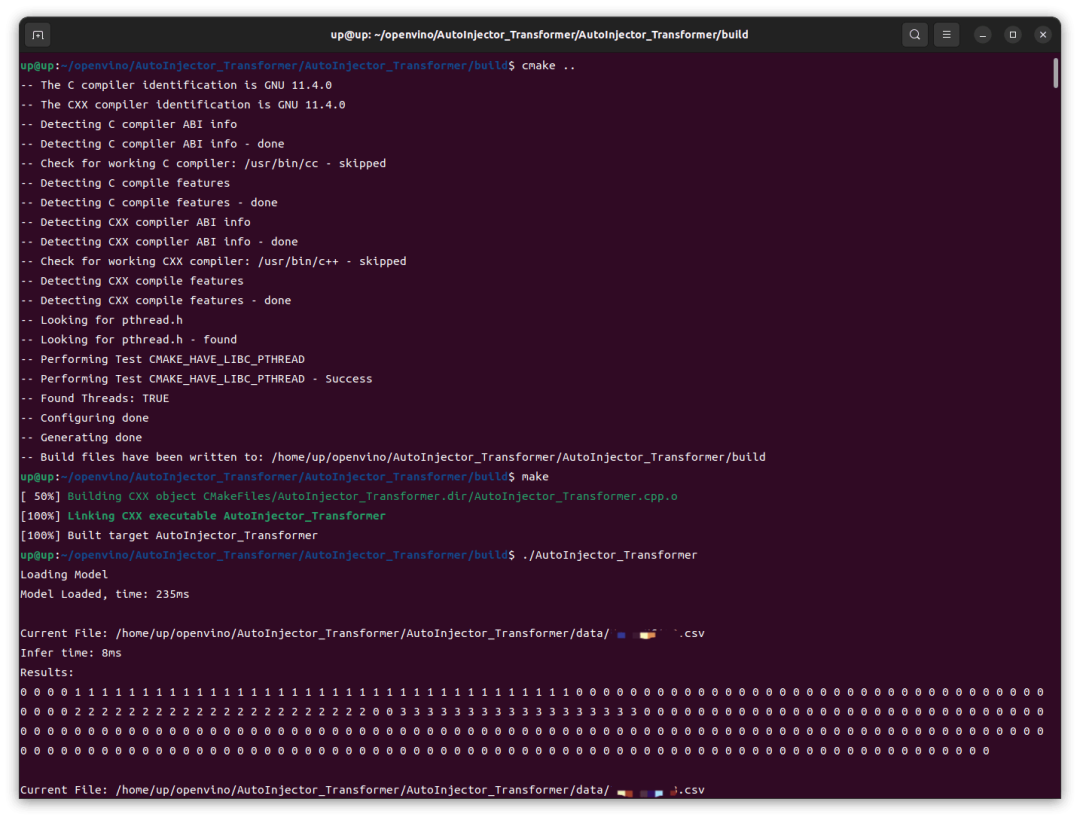
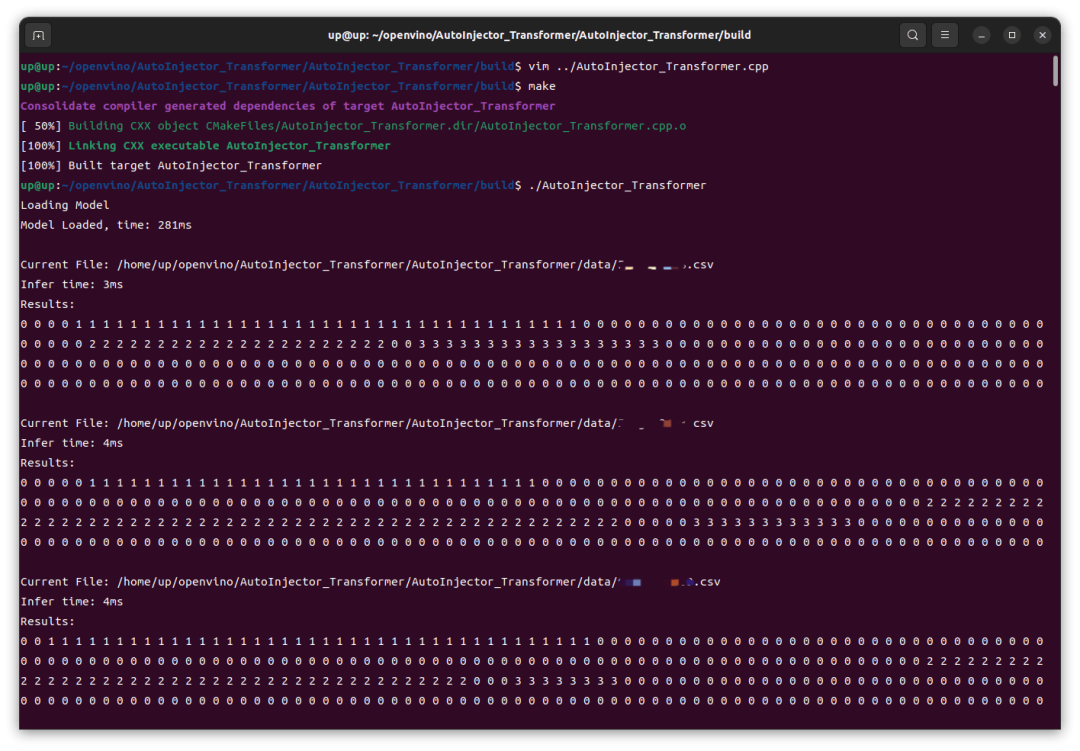
可以看到,在 Intel iGPU 上的推理速度還是很快的,前幾次推理稍慢,8ms,后續(xù)基本穩(wěn)定在 4ms,這跟我之前在 RTX4060 GPU 上用 TensorRT 推理并沒有慢多少。然后我這里修改了代碼改為 CPU 運行,重新編譯、運行,結(jié)果在 Intel CPU 上的速度還要更快一點。
-
編程
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
88文章
3614瀏覽量
93686 -
開發(fā)板
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
25文章
5032瀏覽量
97371 -
開發(fā)教程
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
8瀏覽量
9471 -
OpenVINO
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
92瀏覽量
196
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
基于英特爾開發(fā)板開發(fā)ROS應(yīng)用
使用OpenVINO Model Server在哪吒開發(fā)板上部署模型
使用OpenVINO C++在哪吒開發(fā)板上推理Transformer模型

i.MX Linux開發(fā)實戰(zhàn)指南—基于野火i.MX系列開發(fā)板
KaihongOS 4.1.2開發(fā)者預(yù)覽版正式上線,誠邀開發(fā)者免費試用!
【飛凌嵌入式OK3576-C開發(fā)板體驗】rkllm板端推理
OpenVINO2024 C++推理使用技巧
迅為RK3568手冊上新 | RK3568開發(fā)板NPU例程測試
英特爾開發(fā)套件『哪吒』在Java環(huán)境實現(xiàn)ADAS道路識別演示 | 開發(fā)者實戰(zhàn)

【轉(zhuǎn)載】英特爾開發(fā)套件“哪吒”快速部署YoloV8 on Java | 開發(fā)者實戰(zhàn)

基于英特爾哪吒開發(fā)者套件平臺來快速部署OpenVINO Java實戰(zhàn)
RISC-V SoC + AI | 在全志 D1「哪吒」開發(fā)板上,跑個 ncnn 神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)推理框架的 demo
使用愛芯派Pro開發(fā)板部署人體姿態(tài)估計模型

OpenVINO? 賦能千元級『哪吒』AI開發(fā)套件大語言模型 | 開發(fā)者實戰(zhàn)





 OpenVINO? C++ 在哪吒開發(fā)板上推理 Transformer 模型|開發(fā)者實戰(zhàn)
OpenVINO? C++ 在哪吒開發(fā)板上推理 Transformer 模型|開發(fā)者實戰(zhàn)











評論