作者根據每周發布總結的系列文章,匯總了2018年針對數據科學家/AI的最佳庫、repos、包和工具。本文對其進行了梳理,列舉了人工智能和數據科學的七大Python庫。
本文作者Favio Vázquez從2018年開始發布《數據科學和人工智能每周文摘:Python & R》系列文章,為數據科學家介紹最好的庫、repos、packages以及工具。
一年結束,作者列出了2018年的7大最好的Python庫,這些庫確實地改進了研究人員的工作方式。
7. AdaNet?———快速靈活的AutoML框架
https://github.com/tensorflow/adanet
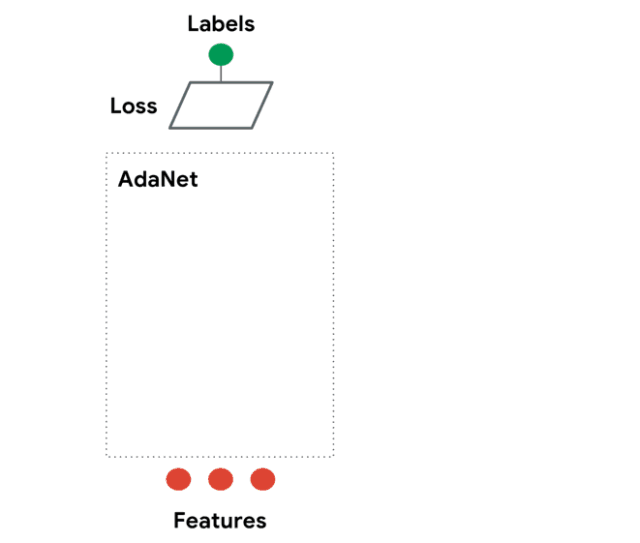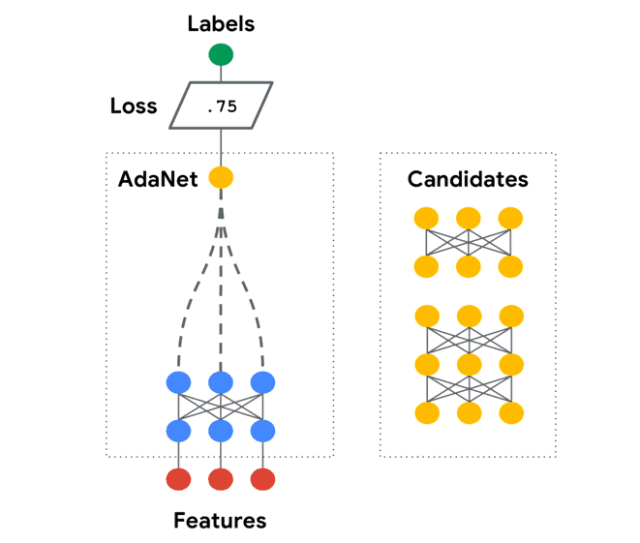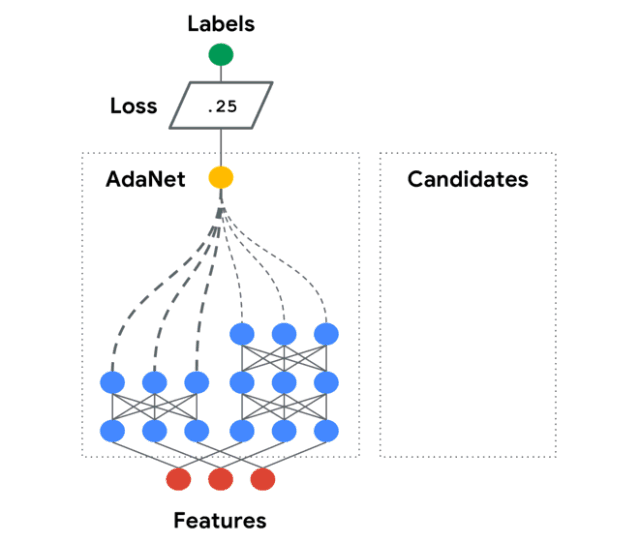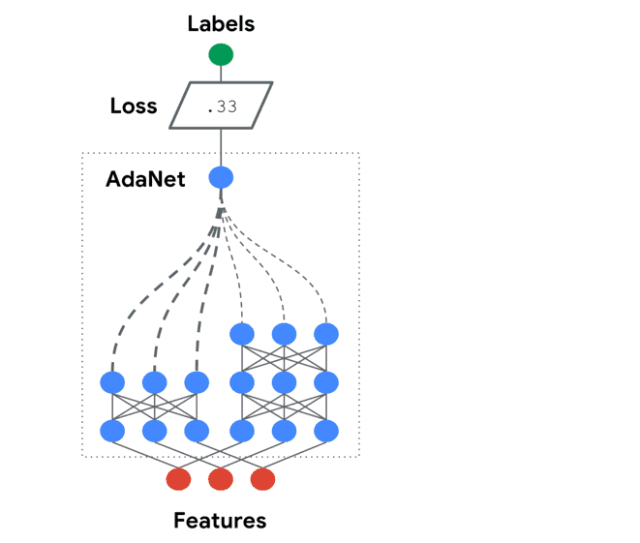
AdaNet是一個輕量級的、可擴展的TensorFlow AutoML框架,用于使用AdaNet算法訓練和部署自適應神經網絡[Cortes et al. ICML 2017]。AdaNet結合了多個學習子網絡,以減輕設計有效的神經網絡所固有的復雜性。
這個軟件包將幫助你選擇最優的神經網絡架構,實現一種自適應算法,用于學習作為子網絡集合的神經架構。
你需要了解TensorFlow才能使用這個包,因為它實現了TensorFlow Estimator,但這將通過封裝訓練、評估、預測和導出服務來幫助你簡化機器學習編程。
你可以構建一個神經網絡的集合,這個庫將幫助你優化一個目標,以平衡集合在訓練集上的性能和將其泛化到未見過數據的能力之間的權衡。
安裝
安裝adanet之前需將TensorFlow升級到1.7或以上:
$pipinstall"tensorflow>=1.7.0"
從源代碼安裝
要從源代碼進行安裝,首先需要安裝bazel。
下一步,復制adanet和cd到它的根目錄:
$gitclonehttps://github.com/tensorflow/adanet&&cdadanet
從adanet根目錄運行測試:
$cdadanet$bazeltest-copt//...
確認一切正常后,將adanet安裝為pip包。
現在,可以對adanet進行試驗了。
importadanet
用法
有關AdaNet的詳細用法,請閱讀官方教程:
https://github.com/tensorflow/adanet/tree/master/adanet/examples/tutorials
https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/10/introducing-adanet-fast-and-flexible.html?m=1
6. TPOT——一個自動化的Python機器學習工具
https://github.com/EpistasisLab/tpot
之前我介紹過Auto-Keras,這是一個很棒的AutoML庫。現在我們有另一個非常有趣的工具——TPOT。
TPOT全稱是基于樹的pipeline優化工具(Tree-based Pipeline Optimization Tool),這是一個非常棒Python自動機器學習工具,使用遺傳編程優化機器學習pipeline。

TPOT可以自動化許多東西,包括生命特性選擇、模型選擇、特性構建等等。如果你是Python機器學習者,很幸運,TPOT是構建在Scikit-learn之上的,所以它生成的所有代碼看起來應該很熟悉。
它的作用是通過智能地探索數千種可能的pipeline來自動化機器學習中最繁瑣的部分,找到最適合你的數據的pipeline,然后為你提供最佳的 Python 代碼。
它的工作原理如下:

安裝
安裝TPOT之前,請先閱讀教程:
http://epistasislab.github.io/tpot/installing/
然后,運行以下代碼:
pipinstalltpot
例子:
首先讓我們從基本的Iris數據集開始:
1fromtpotimportTPOTClassifier 2fromsklearn.datasetsimportload_iris 3fromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_split 4 5#Loadirisdataset 6iris=load_iris() 7 8#Splitthedata 910X_trainX_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,11train_size=0.75,test_size=0.25)1213#FittheTPOTclassifier1415tpot=TPOTClassifier(verbosity=2,max_time_mins=2)16tpot.fit(X_train,y_train)1718#Exportthepipeline19tpot.export('tpot_iris_pipeline.py')
我們在這里構建了一個非常基本的TPOT pipeline,它將嘗試尋找最佳ML pipeline來預測iris.target。然后保存這個pipeline。之后,我們要做的就非常簡單了——加載生成的.py文件,你將看到:
1importnumpyasnp 2fromsklearn.kernel_approximationimportRBFSampler 3fromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_split 4fromsklearn.pipelineimportmake_pipeline 5fromsklearn.treeimportDecisionTreeClassifier 6#NOTE:Makesurethattheclassislabeled'class'inthedatafile 7tpot_data=np.recfromcsv('PATH/TO/DATA/FILE',delimiter='COLUMN_SEPARATOR',dtype=np.float64) 8features=np.delete(tpot_data.view(np.float64).reshape(tpot_data.size,-1),tpot_data.dtype.names.index('class'),axis=1) 9training_features,testing_features,training_classes,testing_classes=10train_test_split(features,tpot_data['class'],random_state=42)11exported_pipeline=make_pipeline(12RBFSampler(gamma=0.8500000000000001),13DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy",max_depth=3,min_samples_leaf=4,min_samples_split=9)14)15exported_pipeline.fit(training_features,training_classes)16results=exported_pipeline.predict(testing_features)
就是這樣。你已經以一種簡單但強大的方式為Iris數據集構建一個分類器。
現在我們來看看MNIST的數據集:
1fromtpotimportTPOTClassifier 2fromsklearn.datasetsimportload_digits 3fromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_split 4 5#loadandsplitdataset 6digitsdigits==load_digitsload_di() 7X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(digits.data,digits.target, 8train_size=0.75,test_size=0.25) 910#FittheTPOTclassifier11tpot=TPOTClassifier(verbosity=2,max_time_mins=5,population_size=40)12tpot.fit(X_train,y_train)1314#Exportpipeline15tpot.export('tpot_mnist_pipeline.py')
接下來我們再次加載生成的 .py文件,你將看到:
1importnumpyasnp 2fromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_split 3fromsklearn.neighborsimportKNeighborsClassifier 4#NOTE:Makesurethattheclassislabeled'class'inthedatafile 5tpot_data=np.recfromcsv('PATH/TO/DATA/FILE',delimiter='COLUMN_SEPARATOR',dtype=np.float64) 6features=np.delete(tpot_data.view(np.float64).reshape(tpot_data.size,-1),tpot_data.dtype.names.index('class'),axis=1) 7training_features,testing_features,training_classes,testing_classes= 8train_test_split(features,tpot_data['class'],random_state=42) 9exported_pipeline=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=4,p=2,weights="distance")10exported_pipeline.fit(training_features,training_classes)11results=exported_pipeline.predict(testing_features)
5. SHAP?——一個解釋任何機器模型輸出的統一方法
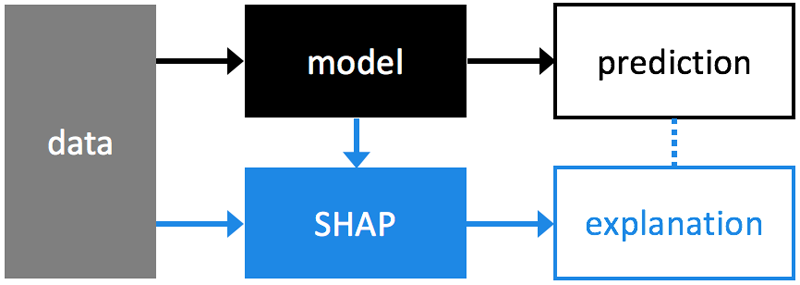
https://github.com/slundberg/shap
解釋機器學習模型并不容易。然而,它對許多商業應用程序來說非常重要。幸運的是,有一些很棒的庫可以幫助我們完成這項任務。在許多應用程序中,我們需要知道、理解或證明輸入變量在模型中的運作方式,以及它們如何影響最終的模型預測。
SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations)是一種解釋任何機器學習模型輸出的統一方法。SHAP將博弈論與局部解釋聯系起來,并結合了之前的幾種方法。
安裝
SHAP可以從PyPI安裝
pipinstallshap
或conda -forge
condainstall-cconda-forgeshap
用法
有很多不同的模型和方法可以使用這個包。在這里,我將以DeepExplainer中的一個例子為例。
Deep SHAP是深度學習模型中SHAP值的一種高速近似算法,它基于與DeepLIFT的連接,如SHAP的NIPS論文所述(https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03888)。
下面這個例子可以看到SHAP如何被用來解釋MNIST數據集的Keras模型結果:
#thisisthecodefromhttps://github.com/keras-team/keras/blob/master/examples/mnist_cnn.pyfrom__future__importprint_functionimportkerasfromkeras.datasetsimportmnistfromkeras.modelsimportSequentialfromkeras.layersimportDense,Dropout,Flattenfromkeras.layersimportConv2D,MaxPooling2DfromkerasimportbackendasKbatch_size=128num_classes=10epochs=12#inputimagedimensionsimg_rows,img_cols=28,28#thedata,splitbetweentrainandtestsets(x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test)=mnist.load_data()ifK.image_data_format()=='channels_first':x_train=x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0],1,img_rows,img_cols)x_test=x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0],1,img_rows,img_cols)input_shape=(1,img_rows,img_cols)else:x_train=x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0],img_rows,img_cols,1)x_test=x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0],img_rows,img_cols,1)input_shape=(img_rows,img_cols,1)x_train=x_train.astype('float32')x_test=x_test.astype('float32')x_train/=255x_test/=255print('x_trainshape:',x_train.shape)print(x_train.shape[0],'trainsamples')print(x_test.shape[0],'testsamples')#convertclassvectorstobinaryclassmatricesy_train=keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train,num_classes)y_test=keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test,num_classes)model=Sequential()model.add(Conv2D(32,kernel_size=(3,3),activation='relu',input_shape=input_shape))model.add(Conv2D(64,(3,3),activation='relu'))model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2)))model.add(Dropout(0.25))model.add(Flatten())model.add(Dense(128,activation='relu'))model.add(Dropout(0.5))model.add(Dense(num_classes,activation='softmax'))model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adadelta(),metrics=['accuracy'])model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=batch_size,epochs=epochs,verbose=1,validation_data=(x_test,y_test))score=model.evaluate(x_test,y_test,verbose=0)print('Testloss:',score[0])print('Testaccuracy:',score[1])
更多示例:
https://github.com/slundberg/shap#sample-notebooks
4. Optimus——使用 Python 和 Spark 輕松實現敏捷數據科學工作流
https://github.com/ironmussa/Optimus
Optimus V2旨在讓數據清理更容易。這個API的設計對新手來說超級簡單,對使用pandas的人來說也非常熟悉。Optimus擴展了Spark DataFrame功能,添加了.rows和.cols屬性。
使用Optimus,你可以以分布式的方式清理數據、準備數據、分析數據、創建分析器和圖表,并執行機器學習和深度學習,因為它的后端有Spark、TensorFlow和Keras。
Optimus是數據科學敏捷方法的完美工具,因為它幾乎可以幫助你完成整個過程的所有步驟,并且可以輕松地連接到其他庫和工具。
Installation (pip):
pipinstalloptimuspyspark
用法
在這個示例中,你可以從 URL 加載數據,對其進行轉換,并應用一些預定義的清理功能:
fromoptimusimportOptimusop=Optimus()#Thisisacustomfunctiondeffunc(value,arg):return"thiswasanumber"df=op.load.url("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ironmussa/Optimus/master/examples/foo.csv")df.rows.sort("product","desc").cols.lower(["firstName","lastName"]).cols.date_transform("birth","new_date","yyyy/MM/dd","dd-MM-YYYY").cols.years_between("birth","years_between","yyyy/MM/dd").cols.remove_accents("lastName").cols.remove_special_chars("lastName").cols.replace("product","taaaccoo","taco").cols.replace("product",["piza","pizzza"],"pizza").rows.drop(df["id"]<7)????.cols.drop("dummyCol")????.cols.rename(str.lower)????.cols.apply_by_dtypes("product",func,"string",?data_type="integer")????.cols.trim("*")????.show()
你可以將這個表格
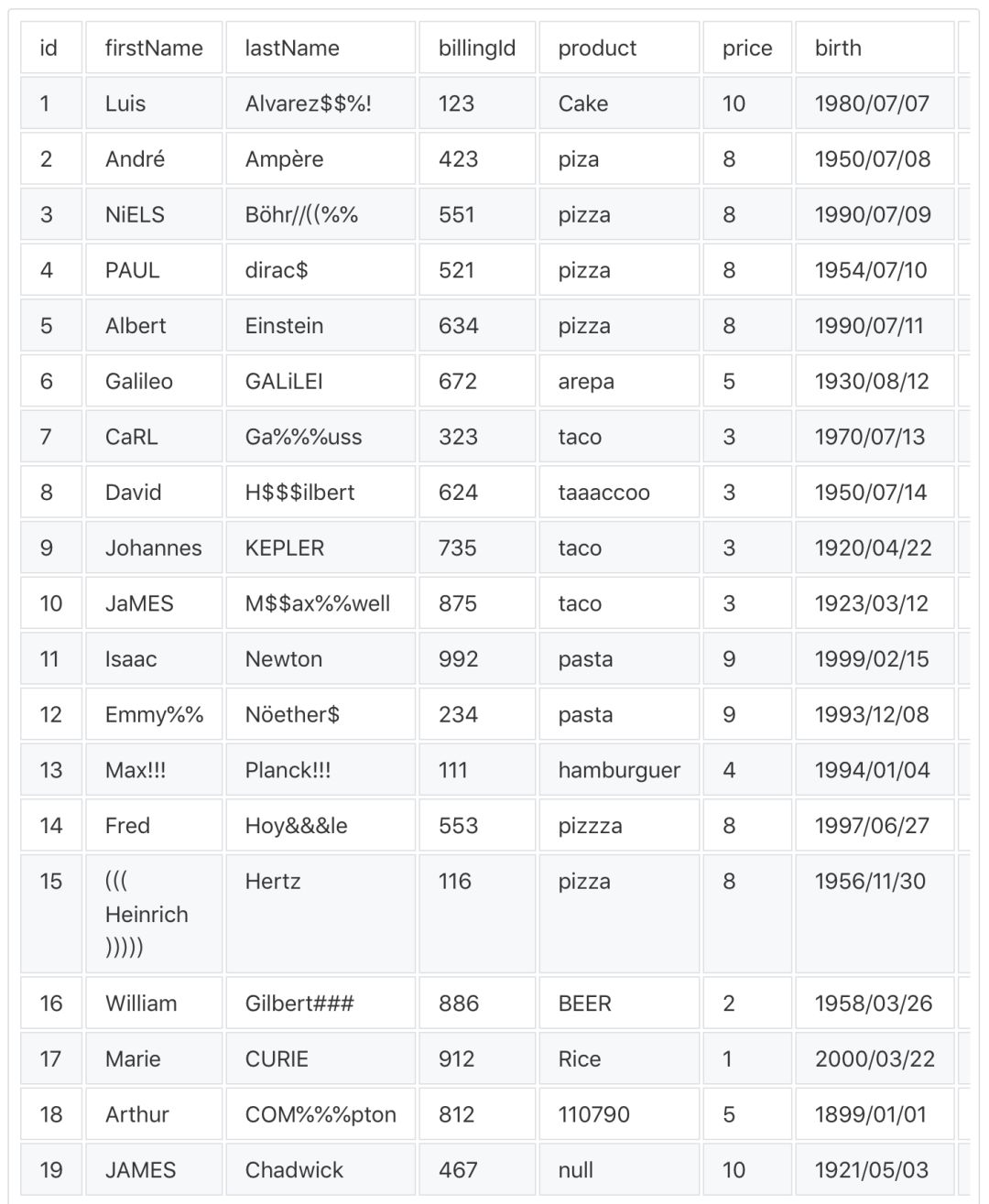
轉換為這樣:
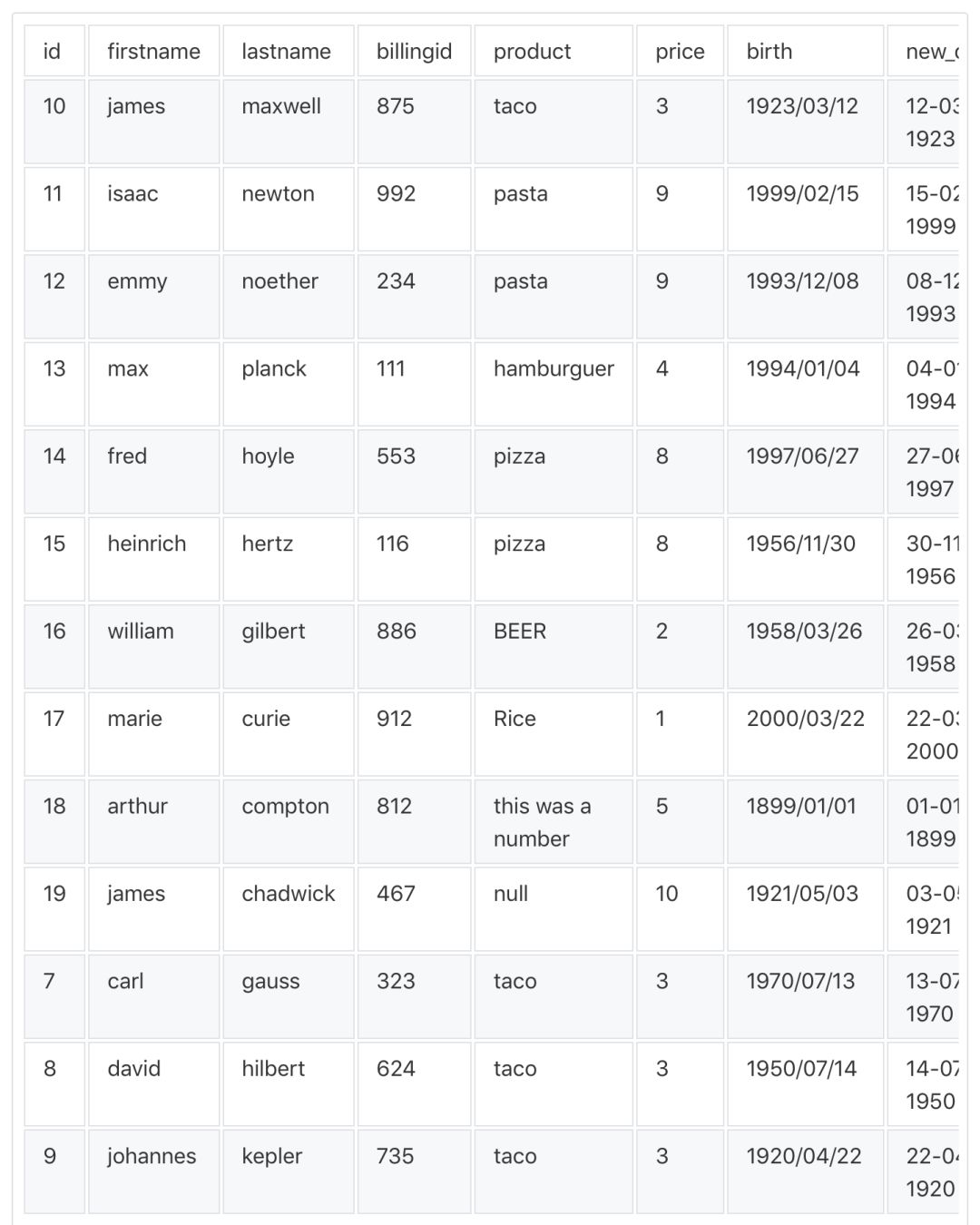
是不是很酷?這個庫還可以做更多事情,具體請閱讀:
https://www.hioptimus.com/
3. spacy——使用Python和Cython的工業級自然語言處理
https://spacy.io/
spaCy旨在幫助你完成實際的工作——構建真實的產品,或收集真實的見解。這個庫尊重你的時間,盡量避免浪費。它易于安裝,而且它的API簡單而高效。spaCy被視為自然語言處理的Ruby on Rails。
spaCy是為深度學習準備文本的最佳方法。它與TensorFlow、PyTorch、Scikit-learn、Gensim以及Python強大的AI生態系統的其他部分無縫交互。使用spaCy,你可以很容易地為各種NLP問題構建語言復雜的統計模型。
安裝
pip3installspacy$python3-mspacydownloaden
這里,我們還下載了英語語言模型。你可以在這里找到德語,西班牙語,意大利語,葡萄牙語,法國語等版本的模型:
https://spacy.io/models/
下面是主頁面的一個示例:
#python-mspacydownloaden_core_web_smimportspacy#LoadEnglishtokenizer,tagger,parser,NERandwordvectorsnlp=spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')#Processwholedocumentstext=(u"WhenSebastianThrunstartedworkingonself-drivingcarsat"u"Googlein2007,fewpeopleoutsideofthecompanytookhim"u"seriously.“IcantellyouveryseniorCEOsofmajorAmerican"u"carcompanieswouldshakemyhandandturnawaybecauseIwasn’t"u"worthtalkingto,”saidThrun,nowtheco-founderandCEOof"u"onlinehighereducationstartupUdacity,inaninterviewwith"u"Recodeearlierthisweek.")doc=nlp(text)#Findnamedentities,phrasesandconceptsforentityindoc.ents:print(entity.text,entity.label_)#Determinesemanticsimilaritiesdoc1=nlp(u"myfriesweresupergross")doc2=nlp(u"suchdisgustingfries")similarity=doc1.similarity(doc2)print(doc1.text,doc2.text,similarity)
在這個示例中,我們首先下載English tokenizer, tagger, parser, NER和word vectors。然后創建一些文本,打印找到的實體、短語和概念,最后確定兩個短語的語義相似性。運行這段代碼,你會得到:
SebastianThrunPERSONGoogleORG2007DATEAmericanNORPThrunPERSONRecodeORGearlierthisweekDATEmyfriesweresupergrosssuchdisgustingfries0.7139701635071919
2. jupytext
對我來說,jupytext是年度最佳。幾乎所有人都在像Jupyter這樣的筆記本上工作,但是我們也在項目的更核心部分使用像PyCharm這樣的IDE。
好消息是,你可以在自己喜歡的IDE中起草和測試普通腳本,在使用Jupytext時可以將IDE作為notebook在Jupyter中打開。在Jupyter中運行notebook以生成輸出,關聯.ipynb表示,并作為普通腳本或傳統Jupyter notebook 進行保存和分享。
下圖展示了這個包的作用:
可點擊下方鏈接查看原文中的GIF展示:
https://heartbeat.fritz.ai/top-7-libraries-and-packages-of-the-year-for-data-science-and-ai-python-r-6b7cca2bf000
安裝
pipinstalljupytext--upgrade
然后,配置Jupyter使用Jupytext:
使用jupyter notebook --generate-config生成Jupyter配置
編輯.jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py,并附加以下代碼:
c.NotebookApp.contents_manager_class="jupytext.TextFileContentsManager"
重啟Jupyter,即運行:
jupyternotebook
你可以在這里試試:
https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/mwouts/jupytext/master?filepath=demo
1.Chartify?——讓數據科學家很容易創建圖表的Python庫
https://xkcd.com/1945/
Chartify是Python的年度最佳庫。
在Python世界中創建一個像樣的圖很費時間。幸運的是,我們有像Seaborn之類的庫,但問題是他們的plots不是動態的。
然后就出現了Bokeh——這是一個超棒的庫,但用它來創造互動情節仍很痛苦。
Chartify建立在Bokeh之上,但它簡單得多。
Chartify的特性:
一致的輸入數據格式:轉換數據所需的時間更少。所有繪圖函數都使用一致、整潔的輸入數據格式。
智能默認樣式:創建漂亮的圖表,幾乎不需要自定義。
簡單API:API盡可能直觀和容易學習。
靈活性:Chartify是建立在Bokeh之上的,所以如果你需要更多的控制,你可以使用Bokeh的API。
安裝
Chartify可以通過pip安裝:
pip3installchartify
用法
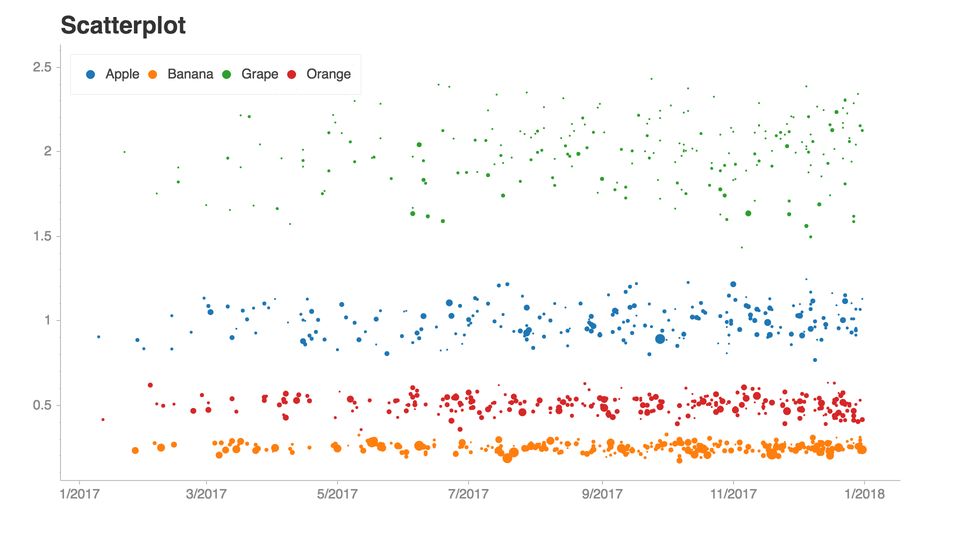
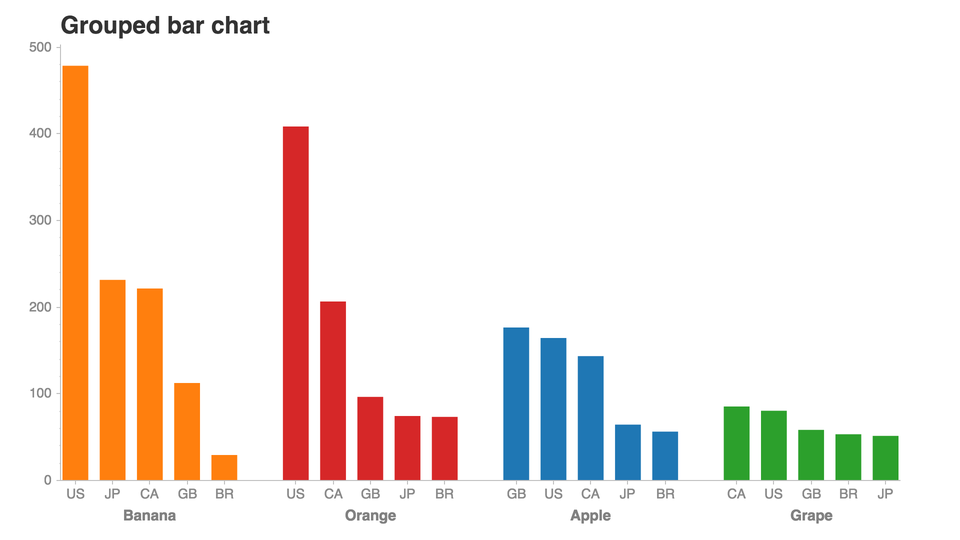
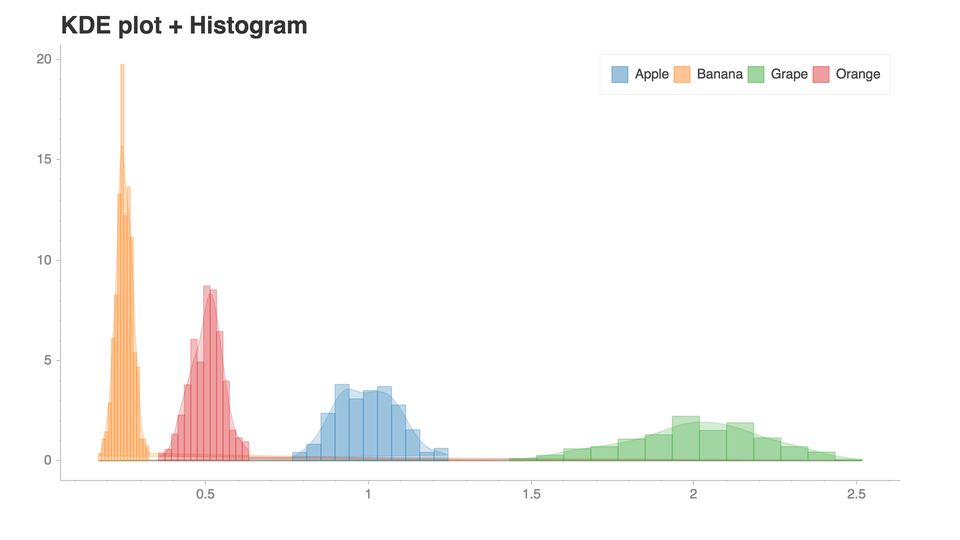
假設我們想要創建這個圖表:

importpandasaspdimportchartify#Generateexampledatadata=chartify.examples.example_data()
現在,我們已經加載了一些示例數據,讓我們來做一些轉換:
total_quantity_by_month_and_fruit=(data.groupby([data['date']+pd.offsets.MonthBegin(-1),'fruit'])['quantity'].sum().reset_index().rename(columns={'date':'month'}).sort_values('month'))print(total_quantity_by_month_and_fruit.head())monthfruitquantity02017-01-01Apple712017-01-01Banana622017-01-01Grape132017-01-01Orange242017-02-01Apple8
現在我們可以把它畫出來:
#Plotthedatach=chartify.Chart(blank_labels=True,x_axis_type='datetime')ch.set_title("Stackedarea")ch.set_subtitle("Representchangesindistribution.")ch.plot.area(data_frame=total_quantity_by_month_and_fruit,x_column='month',y_column='quantity',color_column='fruit',stacked=True)ch.show('png')
超級容易創建一個互動的plot。
更多示例:
-
神經網絡
+關注
關注
42文章
4771瀏覽量
100720 -
機器學習
+關注
關注
66文章
8408瀏覽量
132569 -
python
+關注
關注
56文章
4792瀏覽量
84631
原文標題:必備!人工智能和數據科學的七大 Python 庫
文章出處:【微信號:AI_era,微信公眾號:新智元】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦




 2018年的7大最好的Python庫
2018年的7大最好的Python庫










評論