本質上,Ext3 mount的過程實際上是inode被替代的過程。?
例如,/dev/sdb塊設備被mount到/mnt/alan目錄。命令:mount -t ext3 /dev/sdb /mnt/alan。
那么mount這個過程所需要解決的問題就是將/mnt/alan的dentry目錄項所指向的inode屏蔽掉,然后重新定位到/dev/sdb所表示的inode索引節點。
在沒有分析閱讀linux vfs mount代碼的時候,我的想法是修改dentry所指向的inode索引節點,以此實現mount文件系統的訪問。
經過分析,在實際的vfs mount實現過程中,還是和我原始的想法略有差別,但是,基本目標還是相同的。
?
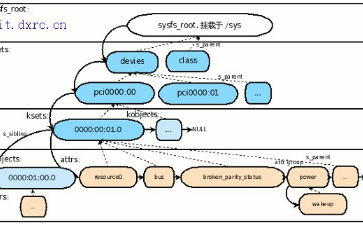
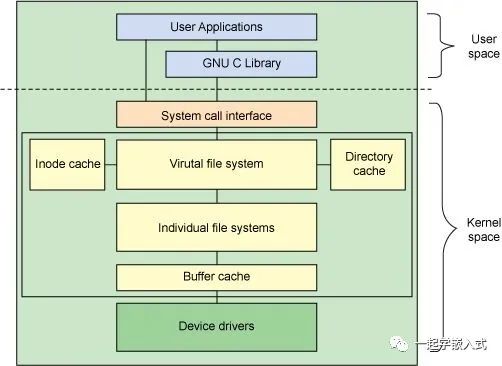
Linux?VFS的mount過程基本原理如下圖所示:
當用戶輸入”mount -t ext3 /dev/sdb /mnt/alan”命令后:
1> Linux會解析/mnt/alan字符串,并且從Dentry Hash表中獲取相關的dentry目錄項,然后將該目錄項標識成DCACHE_MOUNTED。
2> 一旦該dentry被標識成DCACHE_MOUNTED,也就意味著在訪問路徑上對其進行了屏蔽。
3> 在mount /dev/sdb設備上的ext3文件系統時,內核會創建一個該文件系統的superblock對象,并且從/dev/sdb設備上讀取所有的superblock信息,初始化該內存對象。
Linux內核維護了一個全局superblock對象鏈表。
s_root是superblock對象所維護的dentry目錄項,該目錄項是該文件系統的根目錄。即新mount的文件系統內容都需要通過該根目錄進行訪問。
在mount的過程中,VFS會創建一個非常重要的vfsmount對象,該對象維護了文件系統mount的所有信息。
Vfsmount對象通過HASH表進行維護,通過path地址計算HASH值,在這里vfsmount的HASH值通過“/mnt/alan”路徑字符串進行計算得到。
Vfsmount中的mnt_root指向superblock對象的s_root根目錄項。
因此,通過/mnt/alan地址可以檢索VFSMOUNT Hash Table得到被mount的vfsmount對象,進而得到mnt_root根目錄項。
例如,/dev/sdb被mount之后,用戶想要訪問該設備上的一個文件ab.c,假設該文件的地址為:/mnt/alan/ab.c。
1> 在打開該文件的時候,首先需要進行path解析。
2>?在解析到/mnt/alan的時候,得到/mnt/alan的dentry目錄項,并且發現該目錄項已經被標識為DCACHE_MOUNTED。
3> 之后,會采用/mnt/alan計算HASH值去檢索VFSMOUNT Hash Table,得到對應的vfsmount對象。
4>?然后采用vfsmount指向的mnt_root目錄項替代/mnt/alan原來的dentry,從而實現了dentry和inode的重定向。
5> 在新的dentry的基礎上,解析程序繼續執行,最終得到表示ab.c文件的inode對象。
一、關鍵數據結構說明
Linux VFS mount所涉及的關鍵數據結構分析如下。
Vfsmount數據結構
Vfsmount數據結構是vfs mount最為重要的數據結構,其維護了一個mount點的所有信息。
該數據結構描述如下:

struct vfsmount { struct list_head mnt_hash; /* 連接到VFSMOUNT Hash Table */ struct vfsmount *mnt_parent; /* 指向mount樹中的父節點 */ struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; /* 指向mount點的目錄項 */ struct dentry *mnt_root; /* 被mount的文件系統根目錄項 */ struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* 指向被mount的文件系統superblock */ #ifdef CONFIG_SMP struct mnt_pcp __percpu *mnt_pcp; atomic_t mnt_longterm; /* how many of the refs are longterm */ #else int mnt_count; int mnt_writers; #endif struct list_head mnt_mounts; /* 下級(child)vfsmount對象鏈表 */ struct list_head mnt_child; /* 鏈入上級vfsmount對象的鏈表點 */ int mnt_flags; /* 4 bytes hole on 64bits arches without fsnotify */ #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY __u32 mnt_fsnotify_mask; struct hlist_head mnt_fsnotify_marks; #endif const char *mnt_devname; /* 文件系統所在的設備名字,例如/dev/sdb */ struct list_head mnt_list; struct list_head mnt_expire; /* link in fs-specific expiry list */ struct list_head mnt_share; /* circular list of shared mounts */ struct list_head mnt_slave_list;/* list of slave mounts */ struct list_head mnt_slave; /* slave list entry */ struct vfsmount *mnt_master; /* slave is on master->mnt_slave_list */ struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns; /* containing namespace */ int mnt_id; /* mount identifier */ int mnt_group_id; /* peer group identifier */ int mnt_expiry_mark; /* true if marked for expiry */ int mnt_pinned; int mnt_ghosts; };

在Linux內核中不僅存在VFSMOUNT的Hash Table,而且還維護了一棵Mount對象樹,通過該mount樹,我們可以了解到各個文件系統之間的關系。
該mount樹描述如下:
上圖所示為三層mount文件系統樹。
第一層為系統根目錄“/”;
第二層有兩個mount點,一個為/mnt/a,另一個是/mnt/b;
第三層在/mnt/a的基礎上又創建了兩個mount點,分別為/mnt/a/c和/mnt/a/d。
通過mount樹,可以對整個系統的mount結構一目了然。
?
Superblock數據結構
每個文件系統都會擁有一個superblock對象對其基本信息進行描述。
對于像ext3之類的文件系統而言,在磁盤上會持久化存儲一份superblock元數據信息,內存的superblock對象由磁盤上的信息初始化。
對于像block device 之類的“偽文件系統”而言,在mount的時候也會創建superblock對象,只不過很多信息都是臨時生成的,沒有持久化信息。
Vfs superblock數據結構定義如下:

struct super_block { struct list_head s_list; /* 鏈入全局鏈表的對象*/ dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t */ unsigned char s_dirt; unsigned char s_blocksize_bits; unsigned long s_blocksize; loff_t s_maxbytes; /* Max file size */ struct file_system_type *s_type; const struct super_operations *s_op; /* superblock操作函數集 */ const struct dquot_operations *dq_op; const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop; const struct export_operations *s_export_op; unsigned long s_flags; unsigned long s_magic; struct dentry *s_root; /* 文件系統根目錄項 */ struct rw_semaphore s_umount; struct mutex s_lock; int s_count; atomic_t s_active; #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY void *s_security; #endif const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr; struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes */ struct hlist_bl_head s_anon; /* anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting */ #ifdef CONFIG_SMP struct list_head __percpu *s_files; #else struct list_head s_files; #endif /* s_dentry_lru, s_nr_dentry_unused protected by dcache.c lru locks */ struct list_head s_dentry_lru; /* unused dentry lru */ int s_nr_dentry_unused; /* # of dentry on lru */ /* s_inode_lru_lock protects s_inode_lru and s_nr_inodes_unused */ spinlock_t s_inode_lru_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; struct list_head s_inode_lru; /* unused inode lru */ int s_nr_inodes_unused; /* # of inodes on lru */ struct block_device *s_bdev; struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi; struct mtd_info *s_mtd; struct list_head s_instances; struct quota_info s_dquot; /* Diskquota specific options */ int s_frozen; wait_queue_head_t s_wait_unfrozen; char s_id[32]; /* Informational name */ u8 s_uuid[16]; /* UUID */ void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info */ fmode_t s_mode; /* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns. Cannot be worse than a second */ u32 s_time_gran; /* * The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business * even looking at it. You had been warned. */ struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */ /* * Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field * in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype" */ char *s_subtype; /* * Saved mount options for lazy filesystems using * generic_show_options() */ char __rcu *s_options; const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */ /* * Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none) */ int cleancache_poolid; struct shrinker s_shrink; /* per-sb shrinker handle */ };

二、代碼流程分析
Linux中實現mount操作需要一定的代碼量,下面對Linux VFS Mount代碼進行分析說明,整個分析過程按照mount操作函數調用流程進行。
代碼分析基于Linux-3.2版本。
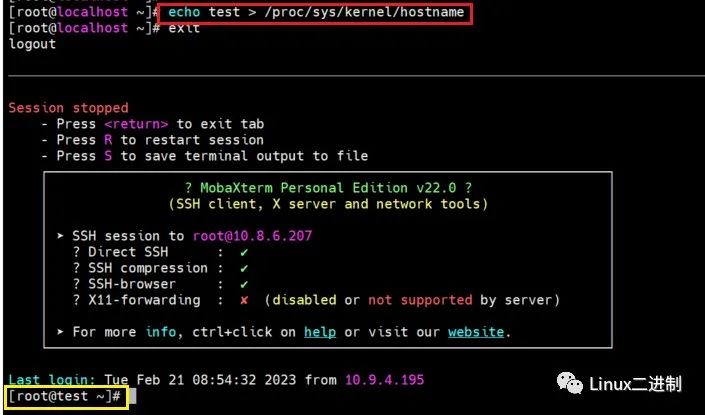
當用戶在用戶層執行mount命令時,會執行系統調用從用戶態陷入linux內核,執行如下函數(namespace.c):

SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name, char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data) { int ret; char *kernel_type; char *kernel_dir; char *kernel_dev; unsigned long data_page; /* 獲取mount類型 */ ret = copy_mount_string(type, &kernel_type); if (ret < 0) goto out_type; /* 獲取mount點目錄字符串 */ kernel_dir = getname(dir_name); if (IS_ERR(kernel_dir)) { ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_dir); goto out_dir; } /* 獲取設備名稱字符串 */ ret = copy_mount_string(dev_name, &kernel_dev); if (ret < 0) goto out_dev; /* 獲取其它選項 */ ret = copy_mount_options(data, &data_page); if (ret < 0) goto out_data; /* 主要函數,執行掛載文件系統的具體操作 */ ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, kernel_dir, kernel_type, flags, (void *) data_page); free_page(data_page); out_data: kfree(kernel_dev); out_dev: putname(kernel_dir); out_dir: kfree(kernel_type); out_type: return ret; }

do_mount()函數是mount操作過程中的核心函數,在該函數中,通過mount的目錄字符串找到對應的dentry目錄項,然后通過do_new_mount()函數完成具體的mount操作。
do_mount()函數分析如下:

long do_mount(char *dev_name, char *dir_name, char *type_page, unsigned long flags, void *data_page) { struct path path; int retval = 0; int mnt_flags = 0; 。。。 /* 通過mount目錄字符串獲取path,path結構中包含有mount目錄的dentry目錄對象 */ retval = kern_path(dir_name, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, &path); if (retval) return retval; 。。。 /* Separate the per-mountpoint flags */ if (flags & MS_NOSUID) mnt_flags |= MNT_NOSUID; if (flags & MS_NODEV) mnt_flags |= MNT_NODEV; if (flags & MS_NOEXEC) mnt_flags |= MNT_NOEXEC; if (flags & MS_NOATIME) mnt_flags |= MNT_NOATIME; if (flags & MS_NODIRATIME) mnt_flags |= MNT_NODIRATIME; if (flags & MS_STRICTATIME) mnt_flags &= ~(MNT_RELATIME | MNT_NOATIME); if (flags & MS_RDONLY) mnt_flags |= MNT_READONLY; flags &= ~(MS_NOSUID | MS_NOEXEC | MS_NODEV | MS_ACTIVE | MS_BORN | MS_NOATIME | MS_NODIRATIME | MS_RELATIME| MS_KERNMOUNT | MS_STRICTATIME); /* remount操作 */ if (flags & MS_REMOUNT) retval = do_remount(&path, flags & ~MS_REMOUNT, mnt_flags, data_page); else if (flags & MS_BIND) retval = do_loopback(&path, dev_name, flags & MS_REC); else if (flags & (MS_SHARED | MS_PRIVATE | MS_SLAVE | MS_UNBINDABLE)) retval = do_change_type(&path, flags); else if (flags & MS_MOVE) retval = do_move_mount(&path, dev_name); else /* 正常的mount操作,完成具體的mount操作 */ retval = do_new_mount(&path, type_page, flags, mnt_flags, dev_name, data_page); dput_out: path_put(&path); return retval; }

do_new_mount()函數主要分成兩大部分:
第一部分建立vfsmount對象和superblock對象,必要時從設備上獲取文件系統元數據;
第二部分將vfsmount對象加入到mount樹和Hash Table中,并且將原來的dentry對象無效掉。
do_new_mount函數說明如下:

static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, char *type, int flags, int mnt_flags, char *name, void *data) { struct vfsmount *mnt; int err; 。。。 /* 在內核建立vfsmount對象和superblock對象 */ mnt = do_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data); if (IS_ERR(mnt)) return PTR_ERR(mnt); /* 將vfsmount對象加入系統,屏蔽原有dentry對象 */ err = do_add_mount(mnt, path, mnt_flags); if (err) mntput(mnt); return err; }

do_new_mount()中的第一步:
調用do_kern_mount()函數,該函數的主干調用路徑如下:
do_kern_mount--> vfs_kern_mount--> mount_fs
在mount_fs()函數中會調用特定文件系統的mount方法,如果mount是ext3文件系統,那么在mount_fs函數中最終會調用ext3的mount方法。
Ext3的mount方法定義在super.c文件中:

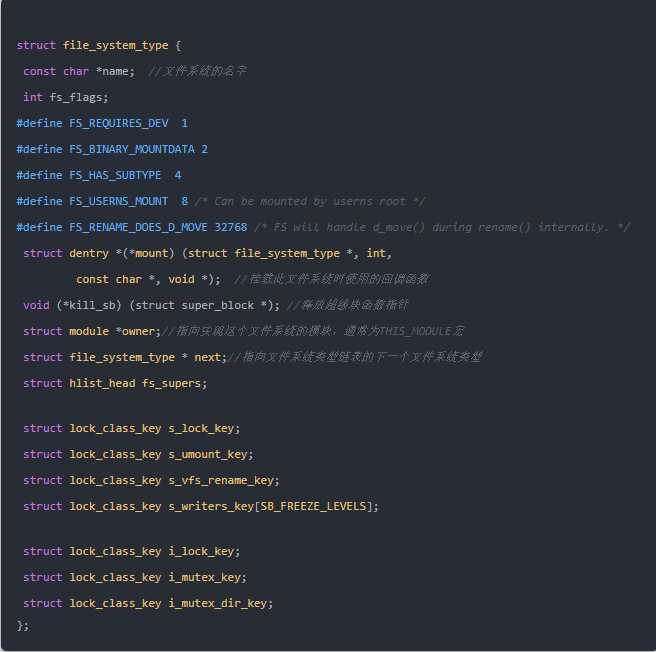
static struct file_system_type ext3_fs_type = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .name = "ext3", .mount = ext3_mount, /* ext3文件系統mount方法 */ .kill_sb = kill_block_super, .fs_flags = FS_REQUIRES_DEV, };

ext3 mount函數主干調用路徑為:
ext3_mount--> mount_bdev。
Mount_bdev()函數主要完成superblock對象的內存初始化,并且加入到全局superblock鏈表中。
該函數說明如下:

struct dentry *mount_bdev(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data, int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int)) { struct block_device *bdev; struct super_block *s; fmode_t mode = FMODE_READ | FMODE_EXCL; int error = 0; if (!(flags & MS_RDONLY)) mode |= FMODE_WRITE; /* 通過設備名字獲取被mount設備的bdev對象 */ bdev = blkdev_get_by_path(dev_name, mode, fs_type); if (IS_ERR(bdev)) return ERR_CAST(bdev); /* * once the super is inserted into the list by sget, s_umount * will protect the lockfs code from trying to start a snapshot * while we are mounting */ mutex_lock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex); if (bdev->bd_fsfreeze_count > 0) { mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex); error = -EBUSY; goto error_bdev; } /* 查找或者創建superblock對象 */ s = sget(fs_type, test_bdev_super, set_bdev_super, bdev); mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex); if (IS_ERR(s)) goto error_s; if (s->s_root) { /* 被mount文件系統的根目錄項已經存在 */ if ((flags ^ s->s_flags) & MS_RDONLY) { deactivate_locked_super(s); error = -EBUSY; goto error_bdev; } /* * s_umount nests inside bd_mutex during * __invalidate_device(). blkdev_put() acquires * bd_mutex and can't be called under s_umount. Drop * s_umount temporarily. This is safe as we're * holding an active reference. */ up_write(&s->s_umount); blkdev_put(bdev, mode); down_write(&s->s_umount); } else { /* 文件系統根目錄項不存在,通過filler_super函數讀取磁盤上的superblock元數據信息,并且初始化superblock內存結構 */ char b[BDEVNAME_SIZE]; s->s_flags = flags | MS_NOSEC; s->s_mode = mode; strlcpy(s->s_id, bdevname(bdev, b), sizeof(s->s_id)); sb_set_blocksize(s, block_size(bdev)); /* 對于ext3文件系統,調用ext3_fill_super函數 */ error = fill_super(s, data, flags & MS_SILENT ? 1 : 0); if (error) { deactivate_locked_super(s); goto error; } s->s_flags |= MS_ACTIVE; bdev->bd_super = s; } /* 正常返回被mount文件系統根目錄項 */ return dget(s->s_root); error_s: error = PTR_ERR(s); error_bdev: blkdev_put(bdev, mode); error: return ERR_PTR(error); }

do_new_mount()函數的第二步:
是將創建的vfsmount對象加入到mount樹和VFSMOUNT Hash Table中,并且將老的dentry目錄項無效掉。
該過程主干函數調用過程如下所示:
do_new_mount--> do_add_mount--> graft_tree--> attach_recursive_mnt
attach_recursive_mnt()函數完成第二步過程的主要操作。
至此,文件系統的mount操作已經完成。
Mount完成之后,如果用戶想要訪問新mount文件系統中的文件,那么需要在path解析過程中重定位dentry,該過程主要在follow_managed()函數中完成。
在該函數中會判斷一個dentry是否已經被標識成DCACHE_MOUNTED,如果該標志位已經被設置,那么通過VFSMOUNT Hash Table可以重定位dentry。
?
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App

























評論