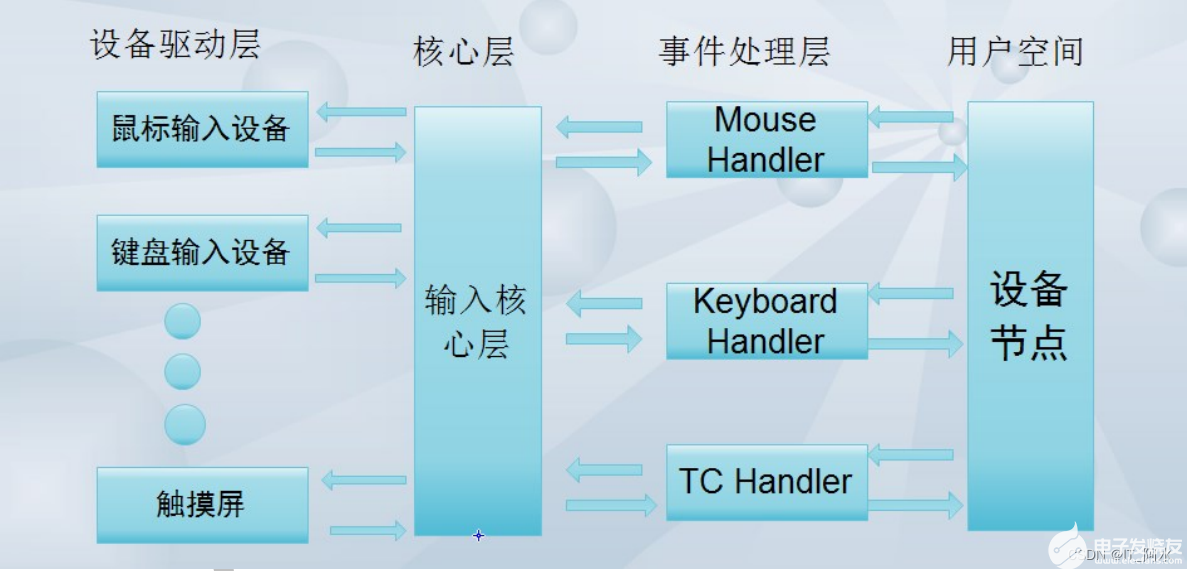
簡(jiǎn)介
在linux聲卡的驅(qū)動(dòng)中存在兩種架構(gòu),一種是OSS(開放聲音系統(tǒng)),一種是ALSA(先進(jìn)Linux聲音架構(gòu))。OSS是一個(gè)商業(yè)聲卡驅(qū)動(dòng)程序,需要花錢購(gòu)買。一般我們現(xiàn)在使用的是ALSA的聲音架構(gòu)。OOS(Open Sound System),在這里主要介紹兩個(gè)設(shè)備,DSP與MIXER.DSP: 用來采樣和播放的文件,對(duì)該設(shè)備寫操作就是播放,對(duì)該設(shè)備讀就是錄音操作。
這個(gè)設(shè)備可以有多個(gè)。對(duì)該設(shè)備操作時(shí)應(yīng)注意一次寫入數(shù)據(jù)塊的大小,如果數(shù)據(jù)塊過大會(huì)引起設(shè)備的block操作。屬于應(yīng)用范疇的內(nèi)容不在此介紹了。
MIXER: 應(yīng)用程序?qū)煲羝鞯能浖?a target="_blank">接口。混音器電路通常由兩個(gè)部分組成:input mixer和ouput mixer. 該設(shè)備的大部分操作都是由ioctl實(shí)現(xiàn)的, mixer設(shè)備允許同時(shí)多個(gè)用戶同時(shí)訪問。 主要設(shè)備的參數(shù)有Rate ,Channel, Format. Volume, Standby等
主要參數(shù)
Oss系統(tǒng)的主要文件:
sound/sound_core.c
include/linux/sound.h
sound/sound_core.h
sound/sound_core.cinclude/linux/sound.hsound/sound_core.h
Oss系統(tǒng)的主要結(jié)構(gòu)介紹:
structsound_unit
{
int unit_minor;
const struct file_operations *unit_fops;
struct sound_unit *next;
char name[32];
};
structsound_unit{int unit_minor;const struct file_operations *unit_fops;struct sound_unit *next;char name[32];};
每個(gè)sound設(shè)備都會(huì)對(duì)應(yīng)這樣一個(gè)結(jié)構(gòu),unit_minor對(duì)應(yīng)子設(shè)備號(hào), unit_fops對(duì)應(yīng)操作
函數(shù),這個(gè)是由各廠商應(yīng)現(xiàn),在注冊(cè)設(shè)備的時(shí)候傳入。Next指向下一個(gè)同類形設(shè)備,name
就不需多說了。
sound_class /sys/class/sound類
static struct sound_unit*chains[SOUND_STEP];
/*整個(gè)OSS系統(tǒng)的鏈表數(shù)組,數(shù)組的每一項(xiàng)代表一種聲卡設(shè)備,如下表所示:*/
* 0 *16 Mixers
* 1 *8 Sequencers
* 2 *16 Midi
* 3 *16 DSP
* 4 *16 SunDSP
* 5 *16 DSP16
* 6 -- sndstat (obsolete)
* 7 *16 unused
* 8 -- alternate sequencer (see above)
* 9 *16 raw synthesizer access
* 10 *16 unused
* 11 *16 unused
* 12 *16 unused
* 13 *16 unused
* 14 *16 unused
* 15 *16 unused
sound_class /sys/class/sound類static struct sound_unit*chains[SOUND_STEP];/*整個(gè)OSS系統(tǒng)的鏈表數(shù)組,數(shù)組的每一項(xiàng)代表一種聲卡設(shè)備,如下表所示:*/* 0 *16 Mixers* 1 *8 Sequencers* 2 *16 Midi* 3 *16 DSP* 4 *16 SunDSP* 5 *16 DSP16* 6 -- sndstat (obsolete)* 7 *16 unused* 8 -- alternate sequencer (see above)* 9 *16 raw synthesizer access* 10 *16 unused* 11 *16 unused* 12 *16 unused* 13 *16 unused* 14 *16 unused* 15 *16 unused
OSS系統(tǒng)的注冊(cè)過程:
本節(jié)描述soundclass的注冊(cè)過程,與及實(shí)例說明dsp與mixer設(shè)備的注冊(cè)過程,用戶層
是如何通過設(shè)備節(jié)點(diǎn)訪問到各廠商提供設(shè)備的操作函數(shù)的。
static int __init init_soundcore(void)
{
intrc;
rc= init_oss_soundcore();
if(rc)
returnrc;
/*注意這里的sound_class是全局函數(shù),用于保存sound類*/
sound_class= class_create(THIS_MODULE, “sound”); //注冊(cè)/sys/class/sound類
if(IS_ERR(sound_class)) {
cleanup_oss_soundcore();
returnPTR_ERR(sound_class);
}
sound_class-》devnode= sound_devnode;
return0;
}
static int __init init_soundcore(void){intrc;rc= init_oss_soundcore();if(rc)returnrc;/*注意這里的sound_class是全局函數(shù),用于保存sound類*/sound_class= class_create(THIS_MODULE, “sound”); //注冊(cè)/sys/class/sound類if(IS_ERR(sound_class)) {cleanup_oss_soundcore();returnPTR_ERR(sound_class);}sound_class-》devnode= sound_devnode;return0;}
在系統(tǒng)啟動(dòng)階段,kernel會(huì)調(diào)用到module_init,進(jìn)入init_soundcore,初始化
init_oss_soundcore, 并注冊(cè)sound類,這樣在/sys/class/下就有了sound類了, sound_devnode()
也決定了相應(yīng)的設(shè)備節(jié)點(diǎn)也將會(huì)出現(xiàn)在/dev/snd/下面。
static void __exit cleanup_soundcore(void)
{
cleanup_oss_soundcore();
class_destroy(sound_class);
}
module_init(init_soundcore);
module_exit(cleanup_soundcore);
static void __exit cleanup_soundcore(void){cleanup_oss_soundcore();class_destroy(sound_class);}module_init(init_soundcore);module_exit(cleanup_soundcore);
cleanup_soundcore函數(shù)對(duì)應(yīng)于init_soundcore,主要用于清除oss_soundcore, 并銷毀
sound_class類。
下面主要介紹一下,mixer與dsp設(shè)備的注冊(cè)過程, 其它設(shè)備雷同:
int register_sound_dsp(const structfile_operations *fops, int dev)
{
returnsound_insert_unit(&chains[3], fops, dev, 3, 131,
“dsp”, S_IWUSR | S_IRUSR, NULL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(register_sound_dsp);“font-family: Arial, Verdana, sans-serif; white-space: normal; ”》
int register_sound_dsp(const structfile_operations *fops, int dev){returnsound_insert_unit(&chains[3], fops, dev, 3, 131,“dsp”, S_IWUSR | S_IRUSR, NULL);}EXPORT_SYMBOL(register_sound_dsp);
register_sound_dsp是注冊(cè)dsp設(shè)備的函數(shù),需要傳入dsp設(shè)備的fops, 就是dsp設(shè)備的
具體操作方法實(shí)現(xiàn)。register_sound_dsp調(diào)用sound_insert_unit函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)注冊(cè), 這時(shí)傳入
的chains[3]就是在聲卡數(shù)組鏈表的3上注冊(cè)dsp設(shè)備,如果注冊(cè)mixer設(shè)備就是chains[0]了。
static intsound_insert_unit(struct sound_unit **list, const struct file_operations
*fops,int index, int low, int top, const char *name, umode_t mode, struct device *dev)
{
struct sound_unit *s =kmalloc(sizeof(*s), GFP_KERNEL); //分配聲卡設(shè)備內(nèi)存
int r;
………………………。
r = __sound_insert_unit(s, list, fops,index, low, top); //注冊(cè)聲卡設(shè)備到list上
spin_unlock(&sound_loader_lock);
………………………
device_create(sound_class, dev,MKDEV(SOUND_MAJOR, s-》unit_minor),
NULL, s-》name+6);
//調(diào)用device_create廣播設(shè)備信息到userspace,udev創(chuàng)建
static intsound_insert_unit(struct sound_unit **list, const struct file_operations*fops,int index, int low, int top, const char *name, umode_t mode, struct device *dev){struct sound_unit *s =kmalloc(sizeof(*s), GFP_KERNEL); //分配聲卡設(shè)備內(nèi)存int r;……………………….r = __sound_insert_unit(s, list, fops,index, low, top); //注冊(cè)聲卡設(shè)備到list上spin_unlock(&sound_loader_lock);………………………device_create(sound_class, dev,MKDEV(SOUND_MAJOR, s-》unit_minor),NULL, s-》name+6);//調(diào)用device_create廣播設(shè)備信息到userspace,udev創(chuàng)建
現(xiàn)在就進(jìn)入分析__sound_insert_unit,分析這里就有點(diǎn)技巧了,大家C基本功可得過關(guān),
分得清指針數(shù)組和數(shù)組指針,指針數(shù)組就是存在一個(gè)數(shù)組,數(shù)組里全是指針變量,在32位
arm上,大于約等于max*int, 數(shù)組指針就是1個(gè)指向數(shù)組的指針,在32位arm上就是4byte.
static int__sound_insert_unit(struct sound_unit * s, struct sound_unit **list,
conststruct file_operations *fops, int index, int low, int top)
{ //傳入的參數(shù)依次為: s,&chains[3], fops, dev, 3, 131
……………………………。.
if (index 《 0) { /* first free */ //index 傳入為 -1, 故進(jìn)入此分支
while (*list &&(*list)-》unit_minor//*list 就等于chains[3]值是否為空,為空
list=&((*list)-》next);
while(n
{
/* Found a hole ? */
if(*list==NULL ||(*list)-》unit_minor》n) //因?yàn)榈谝淮巫?cè)list為空,跳出
break;
list=&((*list)-》next);
n+=SOUND_STEP;
}
if(n》=top)
return -ENOENT;
} else {
……………………………。.
}
s-》unit_minor=n; //直接賦值退出
s-》unit_fops=fops;
s-》next=*list;
*list=s;
static int__sound_insert_unit(struct sound_unit * s, struct sound_unit **list,conststruct file_operations *fops, int index, int low, int top){ //傳入的參數(shù)依次為: s,&chains[3], fops, dev, 3, 131……………………………。.if (index 《 0) { /* first free */ //index 傳入為 -1, 故進(jìn)入此分支while (*list &&(*list)-》unit_minornext);while(nunit_minor》n) //因?yàn)榈谝淮巫?cè)list為空,跳出break;list=&((*list)-》next);n+=SOUND_STEP;}if(n》=top)return -ENOENT;} else {……………………………。.}s-》unit_minor=n; //直接賦值退出s-》unit_fops=fops;s-》next=*list;*list=s;
接下來返回到sound_insert_unit, 通過__register_chrdev將s, 注冊(cè)到系統(tǒng)上,這
里/dev/snd/下就出現(xiàn)dsp名字了,但奇怪的時(shí),這里傳入的fops不是s-》fops,而是系統(tǒng)公
用的全局soundcore_fops, 在打開dsp時(shí)接著分析。
r = __register_chrdev(SOUND_MAJOR,s-》unit_minor, 1, s-》name,
&soundcore_fops);
r = __register_chrdev(SOUND_MAJOR,s-》unit_minor, 1, s-》name,&soundcore_fops);
打開設(shè)備流程
由于注冊(cè)的時(shí)候傳入的是soundcore_fops, 故打開設(shè)備時(shí)會(huì)進(jìn)入soundcore_fops的
open函數(shù)。Soundcore_fops結(jié)構(gòu)體如下。
static const struct file_operationssoundcore_fops =
{
/*We must have an owner or the module locking fails */
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = soundcore_open,
};
static const struct file_operationssoundcore_fops ={/*We must have an owner or the module locking fails */.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = soundcore_open,};
在這里進(jìn)入soundcore_open函數(shù), 現(xiàn)在我們就跟進(jìn)去分析。
static int soundcore_open(struct inode*inode, struct file *file)
{
…………………
if(s)
new_fops= fops_get(s-》unit_fops);
/*在這里獲得__sound_insert_unit注冊(cè)的fops, 就是我們?cè)谧?cè)dsp時(shí)傳入的fops. */
if(preclaim_oss && !new_fops) { //這里的new_fops是有值的,所有不會(huì)進(jìn)入此分支
spin_unlock(&sound_loader_lock);
…………。.
if(new_fops) {
…………………。.
conststruct file_operations *old_fops = file-》f_op;
file-》f_op= new_fops; //在這里偷天換日,將系統(tǒng)的fops轉(zhuǎn)換為s-》fops
spin_unlock(&sound_loader_lock);
if(file-》f_op-》open)
err= file-》f_op-》open(inode,file);
if(err) {
fops_put(file-》f_op);
file-》f_op= fops_get(old_fops);
}
fops_put(old_fops);
unlock_kernel();
returnerr;
}
static int soundcore_open(struct inode*inode, struct file *file){…………………if(s)new_fops= fops_get(s-》unit_fops);/*在這里獲得__sound_insert_unit注冊(cè)的fops, 就是我們?cè)谧?cè)dsp時(shí)傳入的fops. */if(preclaim_oss && !new_fops) { //這里的new_fops是有值的,所有不會(huì)進(jìn)入此分支spin_unlock(&sound_loader_lock);…………。.if(new_fops) {…………………。.conststruct file_operations *old_fops = file-》f_op;file-》f_op= new_fops; //在這里偷天換日,將系統(tǒng)的fops轉(zhuǎn)換為s-》fopsspin_unlock(&sound_loader_lock);if(file-》f_op-》open)err= file-》f_op-》open(inode,file);if(err) {fops_put(file-》f_op);file-》f_op= fops_get(old_fops);}fops_put(old_fops);unlock_kernel();returnerr;}
在這里就發(fā)現(xiàn)在open設(shè)置時(shí),系統(tǒng)將設(shè)備的fops轉(zhuǎn)換為dsp注冊(cè)時(shí)的fops, 偷天換
日啊, linux kernel還是蠻神奇的。
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App






















評(píng)論