?
這個問題看起來十分刁鉆,不過稍有常識的人都知道,制定 C 標準的那幫語言律師也不是吃白飯的,對這種奇奇怪怪的問題一定會有定義。我們翻閱 C17 標準 草案 N2176,在?7.22.3?節里,有如下說法:The order and contiguity of storage allocated by successive calls to the aligned_alloc, calloc, malloc, and realloc functions is unspecified. The pointer returned if the allocation succeeds is suitably aligned so that it may be assigned to a pointer to any type of object with a fundamental alignment requirement and then used to access such an object or an array of such objects in the space allocated (until the space is explicitly deallocated). The lifetime of an allocated object extends from the allocation until the deallocation. Each such allocation shall yield a pointer to an object disjoint from any other object. The pointer returned points to the start (lowest byte address) of the allocated space. If the space cannot be allocated, a null pointer is returned. If the size of the space requested is zero, the behavior is implementation-defined: either a null pointer is returned to indicate an error, or the behavior is as if the size were some nonzero value, except that the returned pointer shall not be used to access an object.在這里,標準委員會明確規定了:當?
malloc?接到的參數為 0 時,其行為是由實現定義的(implementation-defined)。“由實現定義的行為”這個詞就提醒我們,在實際編程時如果要考慮到程序在多個運行環境下進行運行時,不能對?malloc?返回的數值進行任何假設。換言之,沒事兒不要吃飽了撐的在實際編程中寫下?malloc(0)?這種天怒人怨的代碼。但是,這個無意義的問題吸引了我的興趣。因此筆者開始查閱?glibc?的源代碼,依此了解在?glibc?下,mallloc(0)?的行為。在?glibc2.27/malloc/malloc.c?中,有如下注釋:/* malloc(size_t n) Returns a pointer to a newly allocated chunk of at least n bytes, or null if no space is available. Additionally, on failure, errno is set to ENOMEM on ANSI C systems. If n is zero, malloc returns a minumum-sized chunk. (The minimum size is 16 bytes on most 32bit systems, and 24 or 32 bytes on 64bit systems.) On most systems, size_t is an unsigned type, so calls with negative arguments are interpreted as requests for huge amounts of space, which will often fail. The maximum supported value of n differs across systems, but is in all cases less than the maximum representable value of a size_t. */注釋已經說得很清楚了,當我們執行?
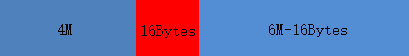
malloc(0)?時,我們實際會拿到一個指向一小塊內存的指針,這個指針指向的(分配給我們的)內存的大小是由機器決定的。細讀代碼,可以發現,將讀入的內存大小進行轉換是由宏?checked_request2size?實現的。相關的宏定義如下:/* pad request bytes into a usable size -- internal version */ #define request2size(req) (((req) + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK < MINSIZE) ? MINSIZE : ((req) + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) /* Same, except also perform an argument and result check. First, we check that the padding done by request2size didn't result in an integer overflow. Then we check (using REQUEST_OUT_OF_RANGE) that the resulting size isn't so large that a later alignment would lead to another integer overflow. */ #define checked_request2size(req, sz) ({ (sz) = request2size (req); if (((sz) < (req)) || REQUEST_OUT_OF_RANGE (sz)) { __set_errno (ENOMEM); return 0; } })也就是說,我們能申請到的數值最小為?
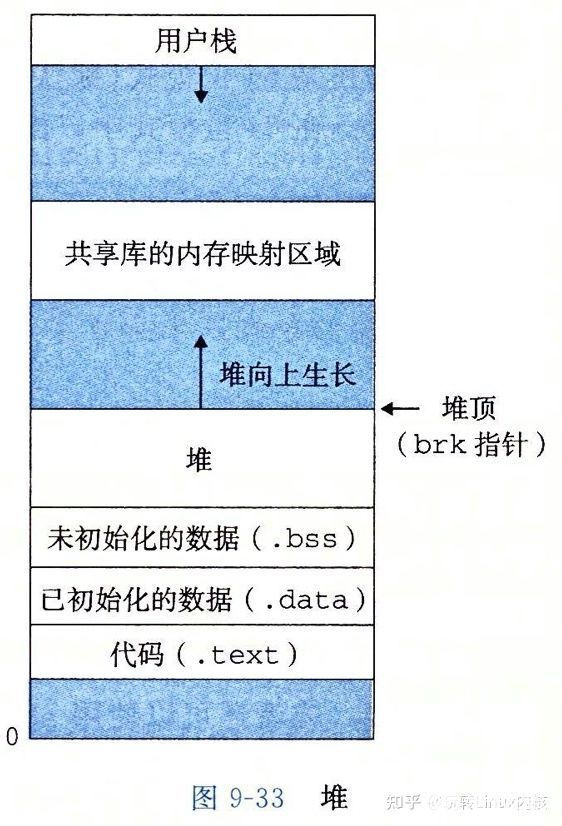
MINSIZE?,這個?MINSIZE?的相關定義如下:/* The smallest possible chunk */ #define MIN_CHUNK_SIZE (offsetof(struct malloc_chunk, fd_nextsize)) /* The smallest size we can malloc is an aligned minimal chunk */ #define MINSIZE (unsigned long)(((MIN_CHUNK_SIZE+MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK))/* The corresponding bit mask value. */ #define MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1) /* MALLOC_ALIGNMENT is the minimum alignment for malloc'ed chunks. It must be a power of two at least 2 * SIZE_SZ, even on machines for which smaller alignments would suffice. It may be defined as larger than this though. Note however that code and data structures are optimized for the case of 8-byte alignment. */ #define MALLOC_ALIGNMENT (2 * SIZE_SZ < __alignof__ (long double) ? __alignof__ (long double) : 2 * SIZE_SZ) #ifndef INTERNAL_SIZE_T # define INTERNAL_SIZE_T size_t #endif /* The corresponding word size. */ #define SIZE_SZ (sizeof (INTERNAL_SIZE_T)) /* This struct declaration is misleading (but accurate and necessary). It declares a "view" into memory allowing access to necessary fields at known offsets from a given base. See explanation below. */ struct malloc_chunk { INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */ INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */ struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */ struct malloc_chunk* bk; /* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */ struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */ struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize; }; // GCC 提供 /* Offset of member MEMBER in a struct of type TYPE. */ #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) __builtin_offsetof (TYPE, MEMBER)至此,我們就可以根據這些計算出使用?
glibc?在我們的電腦上運行時?malloc?出的最小空間的大小了。計算完后,還可以根據?malloc_usable_size?判斷自己的計算是否正確,樣例代碼如下:#include
glibc?下,執行?malloc?會得到一個指向分配給我們的大小為?24?字節的內存空間的指針。但這只是在?glibc?下的結果,在其他 C 標準庫實現內,可能你會得到一個空指針。因為標準中提到了,對于?malloc(0)?這種故意挑事的代碼,實現時可以返回一個空指針作為回禮。
審核編輯:湯梓紅
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App


























評論