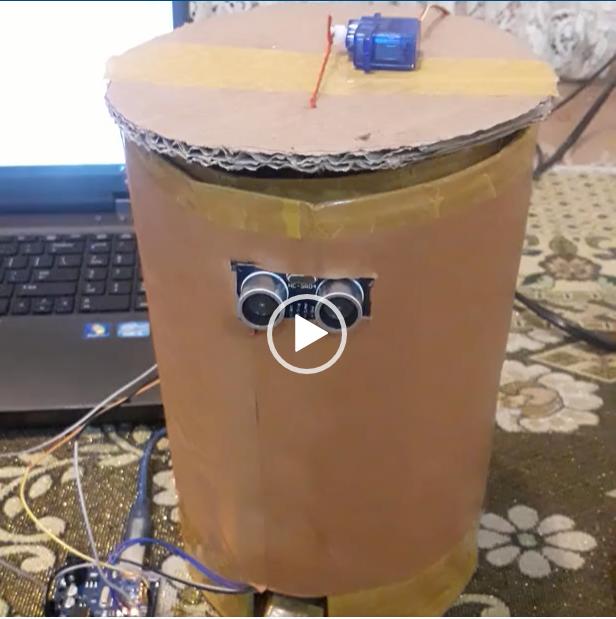
智能垃圾桶(dustbin)是傳統垃轉存設備的替代者。本項目采用基于MCU的Arduino Uno開發板,通過伺服馬達和超聲波傳感器,實現了對傳統垃圾桶的智能化升級改造。

1.項目介紹
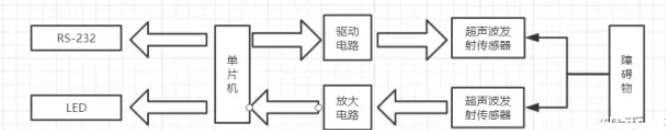
項目中的超聲波傳感器安置于垃圾桶的頂部,感測來跡象的狀態,其閾值設置成一個特別電平。Arduino編程邏輯如下:當有人靠近垃圾桶前方并伸手丟垃圾時,伺服馬達開始動作,并打開垃圾桶的蓋子,讓人把廢物丟進垃圾桶里。
由于住戶不用動手開蓋,并在離開時自動關閉,避免了傳統垃圾桶蓋子長期打開散發氣味、危害環境的弊端,還能培養住戶和小孩養成良好衛生習慣,保持環境干凈、整潔。
通常,垃圾箱分為干、濕、可回收、有毒害四類。本項目通過檢測人手的存在決定箱蓋的打開、閉合,還能夠識別丟進來的垃圾的種類,并區分為可生物降解,獲非降解兩類。
?
2.物料介紹
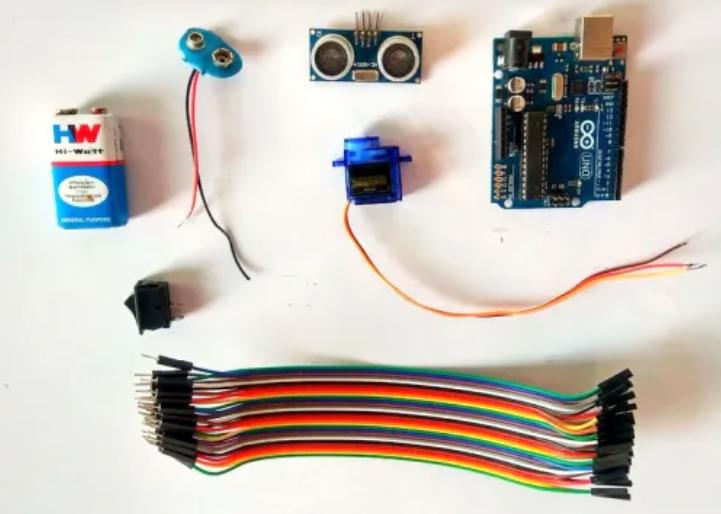
項目物料清單如下:
12v電源適配器
Arduino Uno開發板
Arduino Nano
HC-SR04超聲波傳感器
微型伺服馬達
面包板
工具及軟件:示波器、可變電源、數字萬用表、烙鐵、PCB打孔機
(1)超聲波傳感器
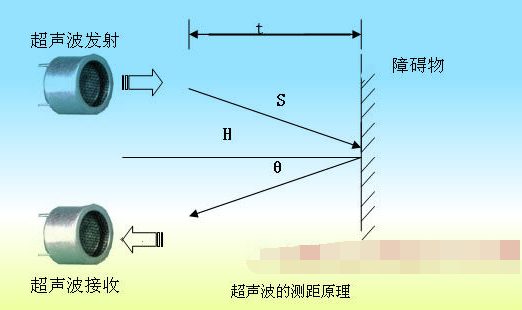
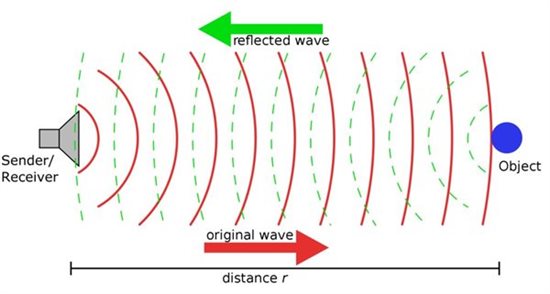
超聲波傳感器工作時會發出一個超出人類聽覺范圍的超聲波,其換能器相當于話筒,可接收超聲波信號并轉換成電信號。超聲波是振動頻率高于20kHz的機械波,具有頻率高、波長短、繞射現象小、方向性好等特點。
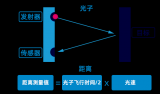
本項目與其他一樣,也使用單換能器來發送脈沖合接收回聲。如圖2所示,傳感器向某一方向發射超聲波時開始計時,超聲波碰到障礙物時返回,根據時間差和超聲波速度可以估算出發射位置到障礙物的距離。

項目使用的HC-SRO4傳感器模塊的四個引腳分別為:Vcc(5V電源)、觸發引腳、回聲引腳、接地(0V)。工作時,采用IO觸發測距10us的高電平信號,模塊自動發送8個40khz的方波,自動檢測是否有回聲。如果有回聲,通過IO輸出一高電平,高電平持續的時間就是超聲波從發射到返回的時間。HC-SRO4性能參數如下:
工作使用電壓:DC5V
靜態電流:小于2mA
電平輸出:高5V
電平輸出:底0V
感應角度:不大于15度
探測距離:2-450cm
高精度:可達0.3cm
(2)伺服馬達
伺服馬達是可以讓物體精確轉動的電氣元件,可以控制速度,位置精度非常準確。伺服電機轉子轉速受輸入信號控制,并能快速反應,在自動控制系統中,用作執行元件,且具有機電時間常數小、線性度高等特性,可把所收到的電信號轉換成電動機軸上的角位移或角速度輸出。
?
伺服馬達分為直流和交流兩大類,當信號電壓為零時無自轉現象,轉速隨著轉矩的增加而勻速下降。Micro Servo 9G伺服馬達參數如下:
重量: 9g
尺寸: 22.2 x 11.8 x 31mm approx.
失速轉矩: 1.8kgf·cm
運行速度: 0.1s/60度
工作電壓: 4.8V(~5V)
死區寬度: 10μs
工作溫度: 0–55oC
模擬力矩: 4.8V@1.80kg-cm)
旋轉范圍: 180°
脈沖周期: ca. 20ms
脈沖寬度: 500-2400μs
(3)Arduino UNO
Arduino是一個構架電子項目的開源平臺,包括一個物理可編程電路板和一套開發環境軟件(IDE),IDE可在PC運行,用來向Arduino板子寫入代碼或上傳代碼。

Arduino的Uno版本更加普及,適合藝術家、設計師、發燒友和各種愛好DIY的人群,可用來控制按鈕、LEDs、馬達、喇叭、GPS單元、照相機,甚至于手機和電視機。
Arduino有很多種類,但大多數板子上面的元器件是一樣的。以下按標號逐一解釋:
標號1:USB座。可通過USB電纜連接電腦或者電源,為Arduino UNO供電。從PC向Arduino開發板上傳代碼,也是通過這個USB電纜進行的。
標號3:GND引腳。Arduino有多個接地引腳,功能是一樣的。
標號4:5V電源。提供5V電壓。
標號5:3.3V電源。提供3.3V電壓。
標號6:模擬輸入引腳(A0--A5),用來讀取來自模擬傳感器(如溫度傳感器)的信號,并轉換成我們能夠識別的數字。
標號7:數字輸入引腳(0--13),用以數字輸入(如按鈕被按下)信號,或者輸出數字信號(如驅動一個LED)。
標號8:PWM引腳 (3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11)。本質上屬于數字引腳,也可用作PWM。可用來模擬某些輸出,如LED的亮度變化。
標號9:AREF引腳,表示模擬參考,大多數情況下不用,有時用來設置一個作為上限的外部模擬電壓。
標號10:復位按鈕。按個案件非常有用,按下就立即接地,并重啟任何上傳到Arduino的代碼。
標號11:電源LED指示器。只要將Arduino接上電源,這個LED就一直點亮。如果不亮,馬上檢查電路,看看哪里出錯了?
標號12:TX RX LEDs指示燈,點亮表示正在接收或發射數據。
標號13:主控IC芯片,來自愛特梅爾的ATmega。
標號14:穩壓芯片。
3.項目目標
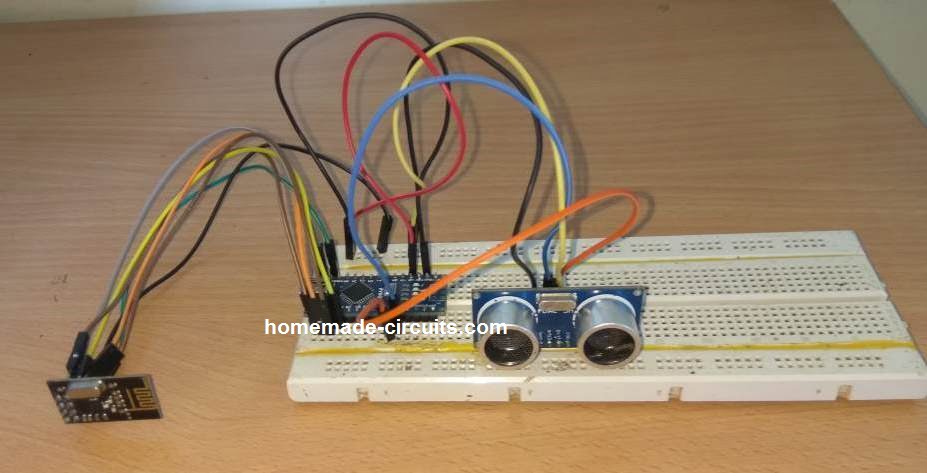
該項目的目的是建立一個原型,在有人準備扔垃圾的時候自動打開垃圾箱蓋子,并檢測剛扔進來垃圾的種類,具體參考原理圖。Arduino連接方法如下:
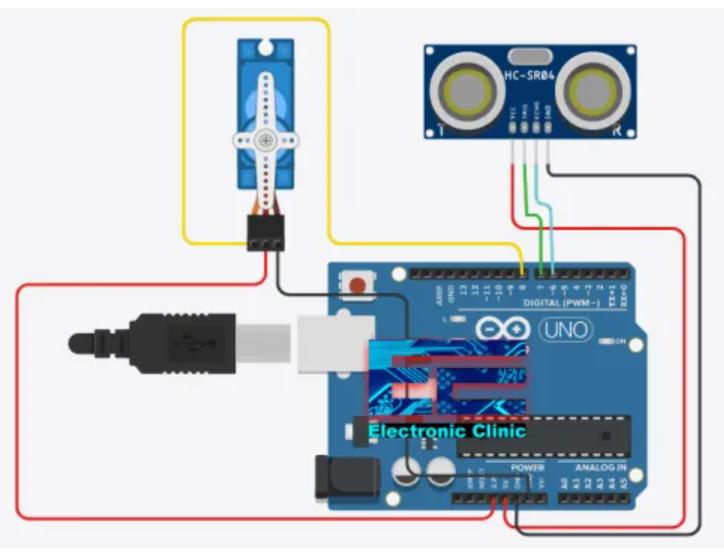
HC-SRO4傳感器模塊引腳VCC連接到Arduino引腳+5VDC,引腳Trig連接到Arduino引腳7,引腳Echo連接到Arduino引腳6,引腳GND連接到Arduino引腳GND。
伺服馬達SG-90的Red引腳連接Arduino 3.3v,Black引腳連接Arduino GND,Orange引腳連接Arduino Pin 8。
4.代碼編程
按照上述說明把Arduino與超聲波傳感器、伺服馬達連接好后,就開始上傳代碼。
該智能垃圾箱的伺服數據庫為:
// Download Servo Library
//https://www.electroniclinic.com/arduino-libraries-download-and-projects-they-are-used-in-project-codes/
#include?
// Defines Tirg and Echo pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor
const int trigPin = 6;
const int echoPin = 7;
// Variables for the duration and the distance
long duration;
int distance;
Servo myServo; // Creates a servo object for controlling the servo motor
void setup() {
?pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // Sets the trigPin as an Output
?pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // Sets the echoPin as an Input
?Serial.begin(9600);
?myServo.attach(9); // Defines on which pin is the servo motor attached
}
void loop() {
?// rotates the servo motor from 15 to 165 degrees
?for (int i = 15; i <= 165; i++) {
? ?myServo.write(i);
? ?delay(30);
? ?distance = calculateDistance();// Calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor for each degree
? ?Serial.print(i); // Sends the current degree into the Serial Port
? ?Serial.print(","); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
? ?Serial.print(distance); // Sends the distance value into the Serial Port
? ?Serial.print("."); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
?}
?// Repeats the previous lines from 165 to 15 degrees
?for (int i = 165; i > 15; i--) {
? ?myServo.write(i);
? ?delay(30);
? ?distance = calculateDistance();
? ?Serial.print(i);
? ?Serial.print(",");
? ?Serial.print(distance);
? ?Serial.print(".");
?}
}
// Function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor
int calculateDistance() {
?digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
?delayMicroseconds(2);
?// Sets the trigPin on HIGH state for 10 micro seconds
?digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
?delayMicroseconds(10);
?digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
?duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds
?distance = duration * 0.034 / 2;
?return distance;
}
開始編程前,我們先添加 Servo.h 頭文件,
#include
接下來,定義觸發和回聲引腳。HC-SR04超聲波傳感器的觸發和回聲引腳分別連接于Arduino的pins 6、7。
const int trigPin = 6;
const int echoPin = 7;
// Variables for the duration and the distance
long duration;
int distance;
Servo myServo; // Creates a servo object for controlling the servo motor
setup() function runs only one time with the Arduino board is turned ON.
void setup() {
?pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // Sets the trigPin as an Output
?pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // Sets the echoPin as an Input
?Serial.begin(9600);
?myServo.attach(9); // Defines on which pin is the servo motor attached
}
void loop() {
?// rotates the servo motor from 15 to 165 degrees
?for (int i = 15; i <= 165; i++) {
? ?myServo.write(i);
? ?delay(30);
? ?distance = calculateDistance();// Calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor for each degree
? ?Serial.print(i); // Sends the current degree into the Serial Port
? ?Serial.print(“,”); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
? ?Serial.print(distance); // Sends the distance value into the Serial Port
? ?Serial.print(“.”); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
?}
?
?// Repeats the previous lines from 165 to 15 degrees
?for (int i = 165; i > 15; i–) {
? ?myServo.write(i);
? ?delay(30);
? ?distance = calculateDistance();
? ?Serial.print(i);
? ?Serial.print(“,”);
? ?Serial.print(distance);
? ?Serial.print(“.”);
?}
}
// Function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor
int calculateDistance() {
?digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
?delayMicroseconds(2);
?// Sets the trigPin on HIGH state for 10 micro seconds
?digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
?delayMicroseconds(10);
?digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
?duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds
?distance = duration * 0.034 / 2;
?return distance;
審核編輯:符乾江
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App











































評論