本來計劃使用 ART-Pi Smart 進行車標識別的,但是現在實際測試發現攝像頭采集的數據顯示有大概率抖動的現象發生,所以實現了將攝像頭采集的數據以 bmp 圖片格式存儲,然后發送到電腦端使用 tflite 格式的模型數據進行測試。
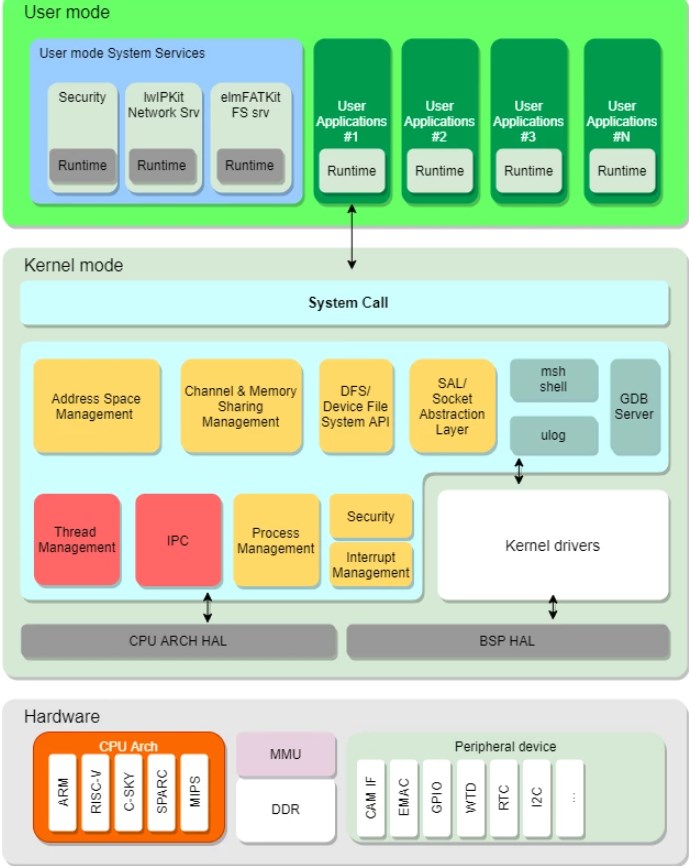
第一部分,系統概述
該項目實現了在 ART-Pi Smart 上通過 OV5640 攝像頭采集視頻數據,并以 bmp 格式圖片保存在設備端,然后借助 ART-Pi Smart webserver 服務將生成的 bmp 圖片下載到 PC,然后在 PC 端使用訓練的 tflite 模型對下載的 bmp 圖片進行預測輸出結果。
硬件框圖:
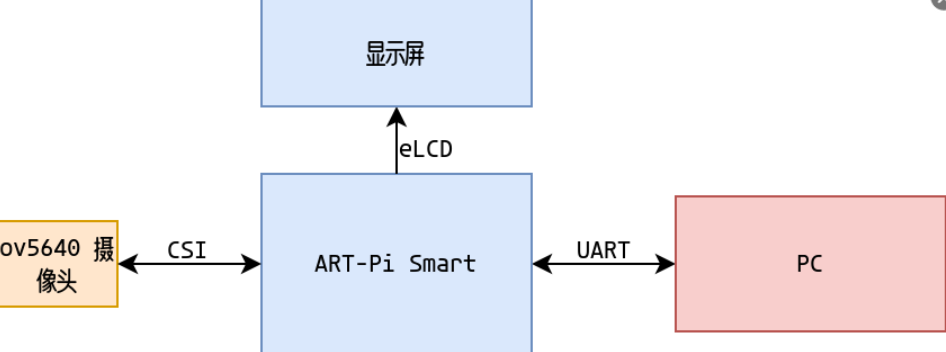
軟件框圖:
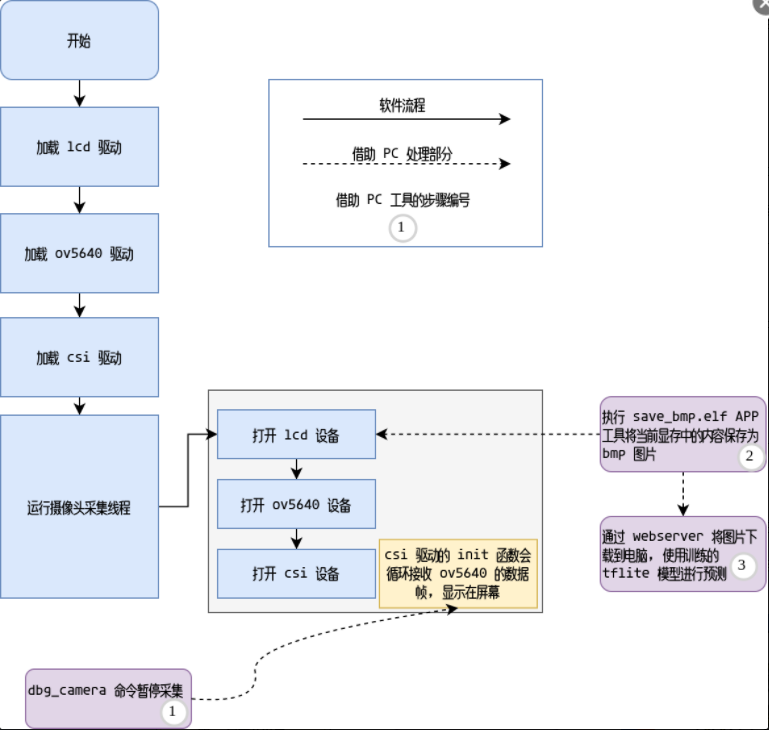
第二部分,系統流程
為了實現預期的目的,將系統流程分為如下幾個階段:
1、使用官方 demo 移植 tflite 到 ART-Pi Smart, 針對這部分內容可以查看文章?在 ART-Pi Smart 上運行 TensorFlow Lite
2、移植 TensorFLow 基礎的圖像分類?mnist?的 demo 到 ART-Pi Smart,針對這部分內容可以查看文章
3、使用 Kicad 設計 ov5640 轉結板,并開發 ov5640 攝像頭驅動,在開發這部分軟件的過程中,遇到了問題,具體細節可以查看問題ov5640 顯示效果不穩定
4、使用攝像頭采集數據判斷是否有車輛信息
本節重點描述系統流程的第 4 部分,訓練自己的模型檢測是否有車輛信息,這部分主要分為如下步驟:
1、從網上下載包含有車輛的圖片數據集和沒有車輛的數據集合(這部分內容,我選擇了一些包含有花朵的數據集),通過 python 將其批量轉換為屏幕分辨率的圖片,這部分代碼大概是這樣的:
!/usr/bin/env python

源數據的目錄

如果指定有源文件目錄,使用指定的源文件目錄

生成轉換后的源文件的目錄

最多轉換 1000 張圖片
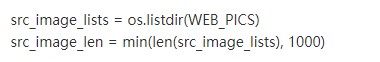
修改原始圖片的分辨率
for i in range(src_image_len):
current_image_name = src_image_lists[i]
full_current_image_name = os.path.join(WEB_PICS, current_image_name)
target_image_name = current_image_name.split('.')[0]+'_convert.bmp'
full_target_image_name = os.path.join(TAREGT_PICS, target_image_name)
raw_image =Image.open(full_current_image_name)
image_L = raw_image.convert('L')
image = image_L.resize((480,272))
image.save(full_target_image_name)
print(np.array(image, dtype=np.float32, order=’C’).shape)
exit()
如圖所示,四個目錄分別是原始帶有車輛和沒有車輛的數據集目錄和轉換后的數據集目錄。
2.標定帶有車輛的圖片和沒有車輛的圖片信息,使用 tensorflow 進行訓練,這部分代碼大概是這樣的:
``` python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# 車標分類算法
from PIL import Image
import os
MODELS_DIR = 'models/'
if not os.path.exists(MODELS_DIR):
os.mkdir(MODELS_DIR)
MODEL_TF = MODELS_DIR + 'model'
MODEL_NO_QUANT_TFLITE = MODELS_DIR + 'model_no_quant.tflite'
MODEL_TFLITE = MODELS_DIR + 'model.tflite'
MODEL_TFLITE_MICRO = MODELS_DIR + 'model.cc'
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
TRAIN_IMAGES_COUNTS = 1000
whole_train_images = np.ones((2 * TRAIN_IMAGES_COUNTS , 480, 272), dtype=np.float32)
whole_train_labels = np.ones((2 * TRAIN_IMAGES_COUNTS , ), dtype=np.float32)
#test_images = np.ones((2 * TEST_IMAGES_COUNTS , 480, 272), dtype=np.float32)
#test_labels = np.ones((2 * TEST_IMAGES_COUNTS , ), dtype=np.float32)
CAR_CONVERT_PICS = 'cars_train_convert_sets'
FLOWER_TAREGT_PICS = 'flowers_convert_sets'
# 矩陣行列交換
def transpose_2d(data):
# transposed = list(zip(*data))
# [(1, 5, 9), (2, 6, 10), (3, 7, 11), (4, 8, 12)]
# 注意 zip 本身返回的數據類型為 tuple 元組
# 其中符號 * 號可以對元素進行解壓或展開
transposed = list(map(list, zip(*data)))
return transposed
whole_train_sets_index = 0
def merge_whole_train_sets(src, type):
global whole_train_sets_index
src_image_lists = os.listdir(src)
for i in range(TRAIN_IMAGES_COUNTS):
full_current_image_name = os.path.join(src, src_image_lists[i])
#print(full_current_image_name)
raw_image = Image.open(full_current_image_name)
#print(type(raw_image.convert('RGB')))
temp_whole_train_images = np.array(raw_image, dtype=np.float32)
whole_train_images[whole_train_sets_index] = np.array(transpose_2d(temp_whole_train_images), dtype=np.float32)
whole_train_labels[whole_train_sets_index] = type
whole_train_sets_index = whole_train_sets_index + 1
merge_whole_train_sets(CAR_CONVERT_PICS, 1)
merge_whole_train_sets(FLOWER_TAREGT_PICS, 0)
print(whole_train_labels)
print(type(whole_train_images), whole_train_images.shape)
print(type(whole_train_labels), whole_train_labels.shape)
train_images, test_images = train_test_split(whole_train_images, train_size=0.8, random_state=10)
train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(whole_train_labels, train_size=0.8, random_state=10)
print(type(train_images), type(train_labels))
print(train_images.shape, train_labels.shape)
class_names = ['nocar', 'car']
if False:
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5,5,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
plt.show()
#exit()
#train_images = train_images
#test_images = test_images
#train_images = np.array(train_images, dtype=np.float32)
#plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
#for i in range(25):
# plt.subplot(5,5,i+1)
# plt.xticks([])
# plt.yticks([])
# plt.grid(False)
# plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
# plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
#plt.show()
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(480, 272)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(2)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 如果模型已經存在,加載整個模型
if os.path.exists(MODELS_DIR) and os.path.exists(MODEL_TF) and 0 != len(os.listdir(MODEL_TF)):
try:
#model.load_weights(MODEL_TF + 'saved_model.pb')
model = keras.models.load_model(MODEL_TF)
except:
print("load weights failed")
exit()
# 訓練模型
else:
print(f"{MODEL_TF} no exist ???")
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10)
# 查看 model 概要
print(model.summary())
# 測試模型
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2)
print(' Test accuracy:', test_acc)
probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model,
tf.keras.layers.Softmax()])
predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images)
print(type(test_images), test_images.shape, " red")
print(predictions[0])
#exit()
# 測試自定義圖片
from PIL import Image
import sys
IMG_SRC = 'flowers/image_1111.jpg'
IMG_TARGET = IMG_SRC.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0] + '_gry_test' + '.bmp'
print(IMG_TARGET)
raw_image = Image.open(IMG_SRC)
image = raw_image.resize((480, 272))
image_gray = image.convert('L')
image_gray_array = np.array(image_gray, dtype=np.float32)
image_gray_array = np.array(transpose_2d(image_gray_array), dtype=np.float32).reshape(1,480,272)
#image_gray_array = image_gray_array / 255.0
image_gray.save(IMG_TARGET)
predictions = probability_model.predict(image_gray_array)
print("red prefictions")
print(predictions[0])
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.imshow(test_images[0], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
print(test_labels[0], "oh no red")
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.imshow(raw_image, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.show()
#exit()
#plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
#plt.xticks([])
#plt.yticks([])
#plt.grid(False)
#plt.imshow(test_images[0], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
#plt.show()
# Save the model to disk
model.save(MODEL_TF)
# Convert the model to the TensorFlow Lite format without quantization
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(MODEL_TF)
model_no_quant_tflite = converter.convert()
# Save the model to disk
open(MODEL_NO_QUANT_TFLITE, "wb").write(model_no_quant_tflite)
# Convert the model to the TensorFlow Lite format with quantization
def representative_dataset():
for i in range(500):
# 強制轉換為 float32 類型
array = np.array(train_images[i], dtype=np.float32)
#print(array.shape, "red dbg")
#print(type(train_images[0].dtype), type(array[0].dtype), type(array), len(array))
yield([array])
# Set the optimization flag.
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
# Enforce integer only quantization
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
converter.inference_input_type = tf.float32
converter.inference_output_type = tf.float32
# Provide a representative dataset to ensure we quantize correctly.
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset
# 轉換為 tflite 模型
model_tflite = converter.convert()
# Save the model to disk
open(MODEL_TFLITE, "wb").write(model_tflite)
該函數可以訓練模型導出 model.tflite 到 models 目錄:

因為輸入的 tensor 有 480*272 個,所以導致模型特別巨大,發現直接編譯出的 rtthread.bin 有 16MB 左右,通過 tftp 下載后無法正常運行,就只能使用這個模型在 PC 端對 ov5640 采集的圖片進行識別了。
1、開發 save_bmp.elf 工具,支持將當前顯存的內容保存到 bmp 圖片中,這部分代碼大概這樣,下述 demo 簡單完成了使用顯存內容對原始 bmp 圖片的重寫:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2006-2022, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2022-05-05 iysheng The first version
*/
#include
#include
#include"rtdef.h"
#include
#include"rt_lcd.h"
typedefunsignedcharuint8_t;
typedefunsignedshortuint16_t;
typedefunsignedintuint32_t;
typedefintint32_t;
#define LCD_WIDTH 480
#define LCD_HEIGHT 272
#define LCD_BUF_SIZE (LCD_WIDTH * LCD_HEIGHT)
rt_uint16_t pixel_ptr[LCD_BUF_SIZE];
rt_device_t lcd = NULL;
struct fb_fix_screeninfo f_info;
struct fb_var_screeninfo v_info;
int rt_smart_lcdinit(void)
{
rt_err_t ret =-1;
lcd = rt_device_find("lcd");
if(!lcd)return1;
ret = rt_device_open(lcd, RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR);
if(-1==ret)return1;
rt_device_control(lcd, FBIOGET_FSCREENINFO,&f_info);
printf("screen: %s - 0x%08x, size %d ", f_info.id,(unsignedint)f_info.smem_start, f_info.smem_len);
rt_device_control(lcd, FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO,&v_info);
printf("screen: bpp %d, width - %d, height - %d ", v_info.bits_per_pixel, v_info.xres, v_info.yres);
return ret;
}
#pragma pack(1)
struct bmp_header {
uint16_t file_type;// File type always BM which is 0x4D42
uint32_t file_size;// Size of the file (in bytes)
uint16_t reserved1;// Reserved, always 0
uint16_t reserved2;// Reserved, always 0
uint32_t offset_data;// Start position of pixel data (bytes from the beginning of the file)
};
struct windows_bmp_info_header {
uint32_t size;// Size of this header (in bytes)
int32_t width;// width of bitmap in pixels
int32_t height;// width of bitmap in pixels
uint16_t planes;// No. of planes for the target device, this is always 1
uint16_t bit_count;// No. of bits per pixel
uint32_t compression;// 0 or 3 - uncompressed. THIS PROGRAM CONSIDERS ONLY UNCOMPRESSED BMP images
uint32_t size_image;// 0 - for uncompressed images
int32_t x_pixels_per_meter;
int32_t y_pixels_per_meter;
uint32_t colors_used;// No. color indexes in the color table. Use 0 for the max number of colors allowed by bit_count
uint32_t colors_important;// No. of colors used for displaying the bitmap. If 0 all colors are required
};
#define RED_TFLITE_CONVERT 10
int get_bmp_at(struct fb_fix_screeninfo *finfo,struct fb_var_screeninfo *vinfo,struct windows_bmp_info_header *header,uint8_t*buffer,uint8_t bytes)
{
int32_t x, y, i =0;
uint16_t pix_tmp =0;
vinfo->xres =0;
vinfo->yres =0;
for(y = header->height; y >0; y--)
{
for(x =0; x < header->width; x++)
{
if(1== bytes)
{
buffer[i++]=*((uint16_t*)finfo->smem_start +(y -1+ vinfo->yres)* LCD_WIDTH + vinfo->xres + x);
}
elseif(2== bytes)
{
pix_tmp =*((uint16_t*)finfo->smem_start +(y -1+ vinfo->yres)* LCD_WIDTH + vinfo->xres + x);
buffer[i]= pix_tmp;
buffer[i +1]= pix_tmp >>8;
i +=2;
}
else
{
printf("error: no support this format ");
return-1;
}
}
}
/* TODO flush */
rt_device_control(lcd, RED_TFLITE_CONVERT, NULL);
return0;
}
void show_hex(uint8_t* buffer,uint16_t buffer_len,char*title)
{
uint16_t i =0;
printf("[%s](%hu)", title, buffer_len);
for(i =0; i < buffer_len; i++)
{
printf("%x ", buffer[i]);
}
printf(" ");
}
uint8_t bmp9696[480*272*2];
int main(int argc,char**argv)
{
FILE *fp;
/* 屏幕顯示起始地址 */
__attribute__((unused))int display_pos;
struct bmp_header t_bmp_header;
struct windows_bmp_info_header t_bmp_info_header;
int num;
if(0!= rt_smart_lcdinit())
{
printf("Failed init lcd. ");
return-3;
}
else
{
printf("init lcd ok ");
}
if(argc ==2)
{
printf("use default display width height and addr ");
}
elseif(argc ==3)
{
printf("ruse default display width height ");
}
elseif(argc ==4)
{
printf("use default display addr ");
}
elseif(argc ==5)
{
display_pos = atoi(argv[4]);
}
else
{
printf("Usage:show_bmp xxx.bmp 96 96 [pos]! ");
return-1;
}
fp = fopen(argv[1],"r+");
if(!fp)
{
printf("Failed open file:%s as:r+ ", argv[1]);
return-2;
}
num = fread(&t_bmp_header,1,sizeof(t_bmp_header), fp);
if(num !=sizeof(t_bmp_header))
{
printf("Read data len mismatch, please check:%d ", num);
return-3;
}
else
{
show_hex((uint8_t*)&t_bmp_header, num,"dbg_header");
printf("size=%u offset=%u ", t_bmp_header.file_size, t_bmp_header.offset_data);
}
display_pos = t_bmp_header.offset_data;
printf("size header:%u infoheader:%u ",sizeof(t_bmp_header),sizeof(t_bmp_info_header));
num = fread(&t_bmp_info_header,1,sizeof(t_bmp_info_header), fp);
if(num !=sizeof(t_bmp_info_header))
{
printf("Read data len mismatch, please check:%d ", num);
return-4;
}
else
{
printf("width=%u height=%u ", t_bmp_info_header.width, t_bmp_info_header.height);
}
/* seek offset positon */
fseek(fp, t_bmp_header.offset_data, SEEK_SET);
get_bmp_at(&f_info,&v_info,&t_bmp_info_header, bmp9696, t_bmp_info_header.bit_count /8);
num = fwrite(bmp9696,1, t_bmp_info_header.width * t_bmp_info_header.height * t_bmp_info_header.bit_count >>3, fp);
if(num != t_bmp_info_header.width * t_bmp_info_header.height * t_bmp_info_header.bit_count >>3)
{
printf("bmp raw data mismatch. ");
return-5;
}
else
{
printf("save bmp ok");
fclose(fp);
}
return0;
}
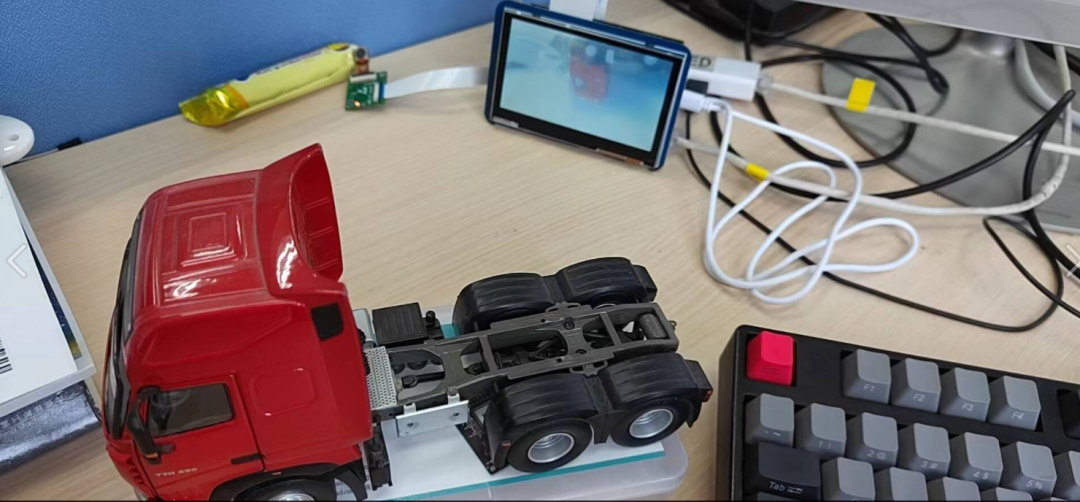
2、實驗,我使用了一個卡車模型進行采集,現場是這樣的:

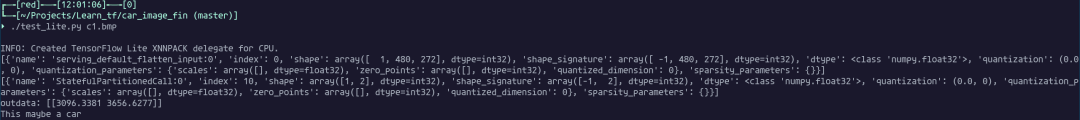
采集回來的圖片是這樣的:
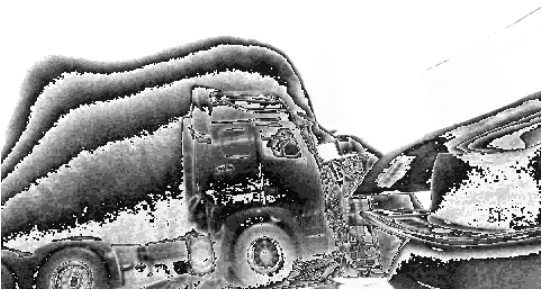
隱約可以從這個灰度圖中看出來卡車模型的輪廓,接下來使用 tflite 的模型對這個圖片進行預測,結果可以看出來識別到這個圖片中包含有車:
為了做對比,再采集一張有花朵的圖片,進行預測,現場是這樣的:
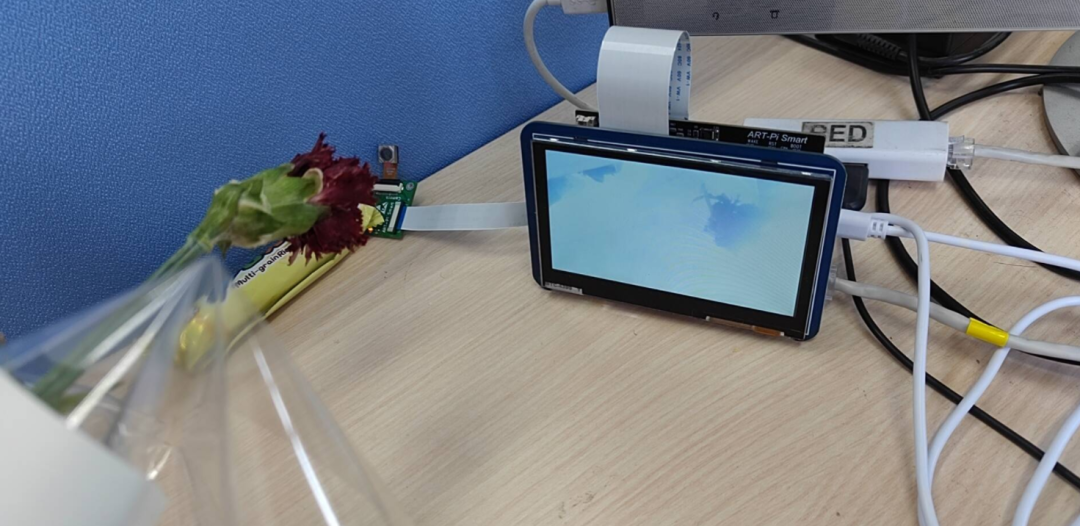

對攝像頭采集的圖片進行捕捉,保存到一個灰度 bmp 圖片:
結果是:

可以看出正確識別除了是花還是汽車。
至此本次項目暫時告一段落了,通過這次試用,主要收獲有兩個方面:
1、通過實際對機器學習遷移到嵌入式設備端這個過程的接觸,對在邊緣節點進行機器學習有了一個基礎的認識;
2、通過這次對 ov5640 攝像頭的調試,對 CSI 接口攝像頭的圖像采集以及顯示有了一個更深入的理解;
目前還有部分未完成的工作,對攝像頭采集的圖像效果不是特別滿意,目前分析可能是 ART-Pi Smart 到轉接板之間排線有點長(我選的是10cm的)對顯示信號(有高頻 50MHz 附近的 PCLK 時鐘)有干擾,轉接板沒有處理好高頻信號導致的,看一下轉接板 PCB 和 3D 是這樣的。
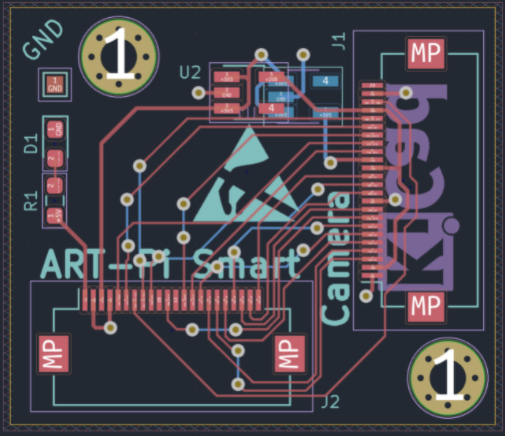
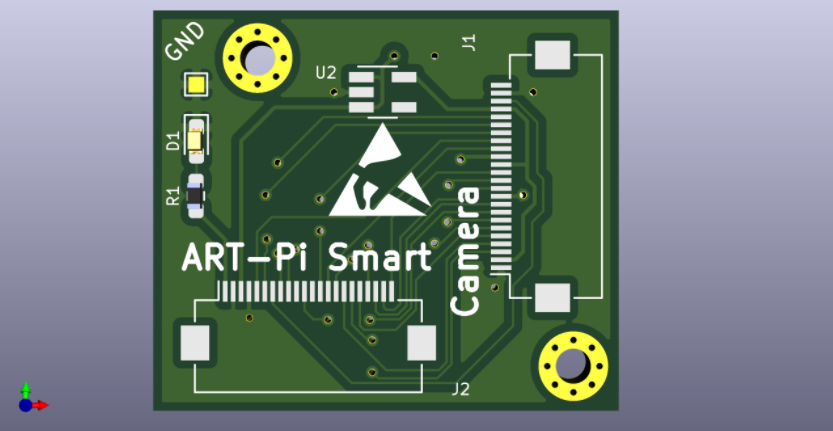
審核編輯:劉清
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App






















評論