Teachable Machine 嵌入式神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò) – Arduino 也可以做視覺分類!
Google Teachable Machine 最近推出了新的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)導(dǎo)出方案,需要使用 Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense 搭配 OV7670 相機(jī)模塊,就可以讓Arduino 透過(guò)匯出的 tensorflow lite 檔案來(lái)做到邊緣裝置端的”實(shí)時(shí)”影像分類。
說(shuō)是實(shí)時(shí),但都在Arduino 上執(zhí)行了,當(dāng)然不可能快到哪里去,圖片也是黑白的,這都是針對(duì) Arduino 的運(yùn)算能力來(lái)考慮,且 Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense 與 OV7670 相機(jī)模塊這兩個(gè)買起來(lái)也快接近 Raspberry Pi 了。另外,ESP32cam 搭配 tensorflow lite 很早就能做到深度學(xué)習(xí)視覺分類應(yīng)用,但用 teachable machine 可以自行訓(xùn)練所要目標(biāo),也是不錯(cuò)的選擇。老話一句,看您的項(xiàng)目需求來(lái)決定使用哪些軟硬件喔!
本文會(huì)帶您完成相關(guān)的軟硬件環(huán)境設(shè)定,并操作? Teachable Machine 透過(guò)相機(jī)模塊來(lái)搜集照片、訓(xùn)練神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò),最后導(dǎo)出檔案給 Arduino 執(zhí)行實(shí)時(shí)影像(灰階)分類!
以下操作步驟根據(jù) teachable Machine 網(wǎng)站說(shuō)明
https://github.com/googlecreativelab/teachablemachine-community/blob/master/snippets/markdown/tiny_image/GettingStarted.md
硬件
Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense / Nano 33 BLE
目前指定只能用這片板子,其他板子編譯會(huì)有問題,看看之后有沒有機(jī)會(huì)在別的板子上執(zhí)行啰,詳細(xì)規(guī)格請(qǐng)參考原廠網(wǎng)站。
https://store-usa.arduino.cc/products/arduino-nano-33-ble-sense
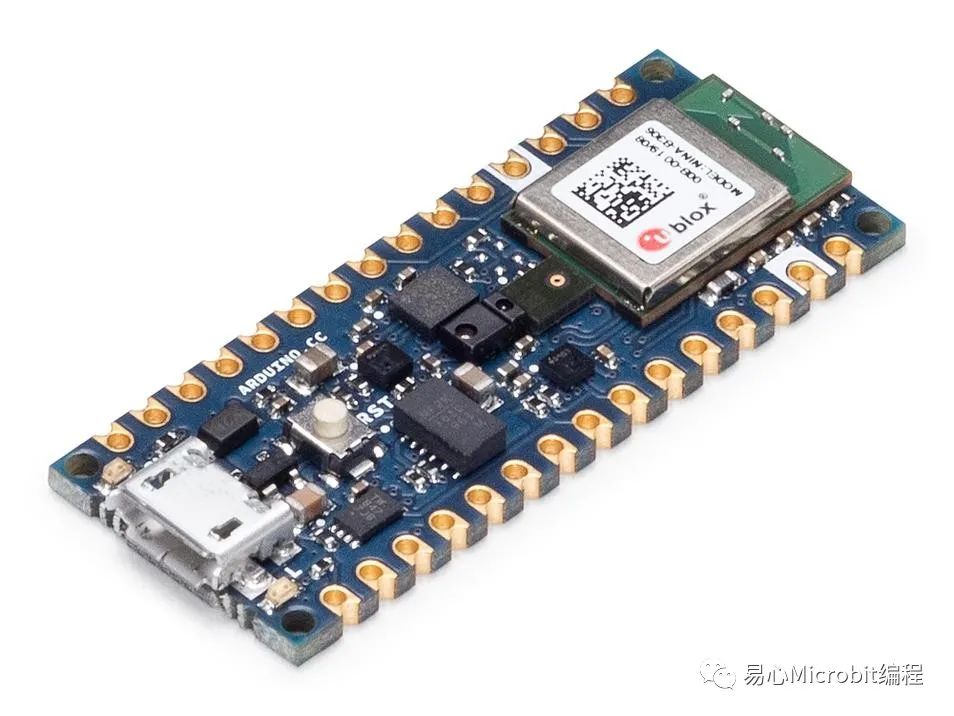

以下是實(shí)物照片,板子都愈來(lái)愈小呢(視力挑戰(zhàn))

重要信息有寫在盒裝背面,當(dāng)然看原廠網(wǎng)站是最快的。
https://store-usa.arduino.cc/products/arduino-nano-33-ble-sense

Ov7670 相機(jī)模塊
由 OmniVision 推出的相機(jī)模塊,本范例會(huì)把它接在Arduino上,并直接從 Teachable Machine 來(lái)擷取黑白影像作為訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)集。
規(guī)格請(qǐng)看這里。
http://web.mit.edu/6.111/www/f2016/tools/OV7670_2006.pdf
實(shí)體照片如下


接下來(lái)是大工程,使用母母杜邦線并根據(jù)下表完成接線,請(qǐng)細(xì)心完成啰。
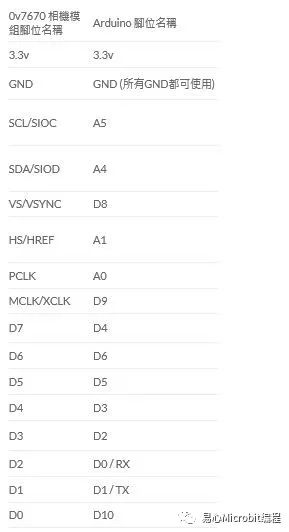
完成如下圖
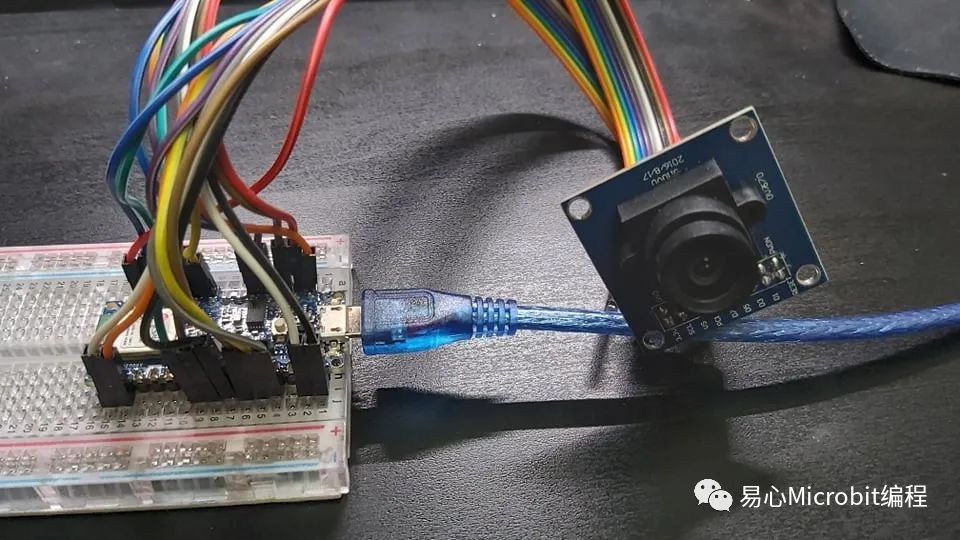
軟件– Arduino IDE
請(qǐng)先取得 Arduino IDE,我使用 Arduino 1.8.5。OV7670 相機(jī)模塊需要匯入一些函式庫(kù),請(qǐng)根據(jù)以下步驟操作:
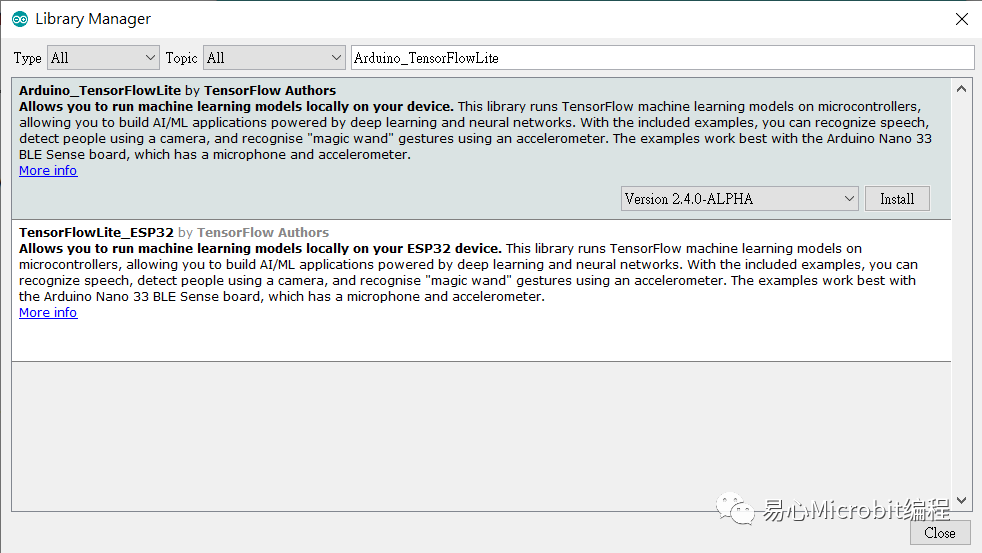
1.安裝Arduino_TensorFlowLite 函式庫(kù):Arduino IDE,請(qǐng)開啟 Tools -> Manage Libraries,并搜尋Arduino_TensorFlowLite.,請(qǐng)選擇 Version 2.4.0-ALPHA 之后的版本,點(diǎn)選安裝。
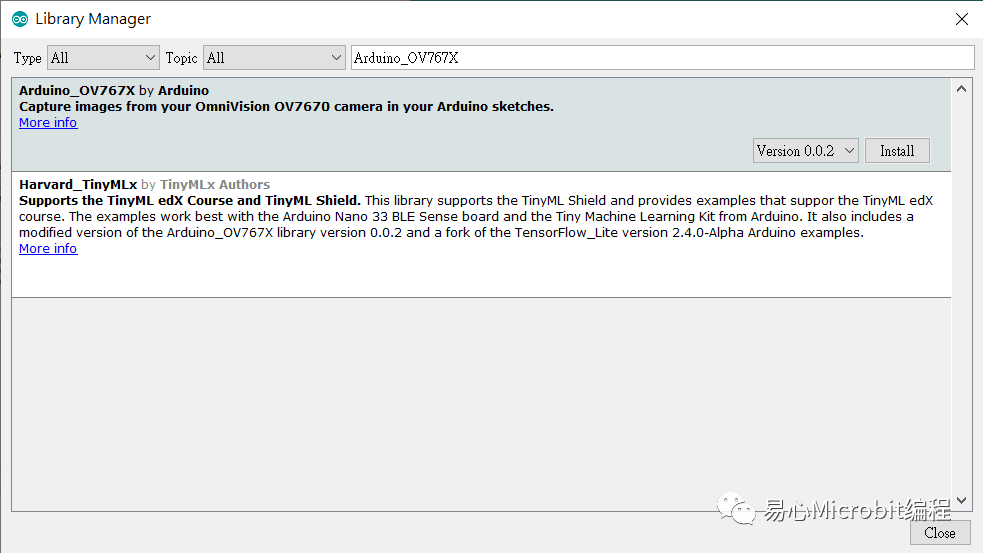
2.安裝 Arduino_OV767X 函式庫(kù):搜尋Arduino_OV767X 并安裝。
軟件– Processing
Processing 是用來(lái)連接 Arduino 與 TeachableMachine。請(qǐng)先下載 Processing IDE 3.X 版本。
https://processing.org/download/?PHPSESSID=8e6890fd30e3476408b69f203c217284
下載好 Processing IDE 之后,請(qǐng)開啟 Sketch -> Add Library -> Manage Libraries,并搜尋ControlP5 與 Websockets,點(diǎn)選安裝就完成了
軟件– Teachable Machine
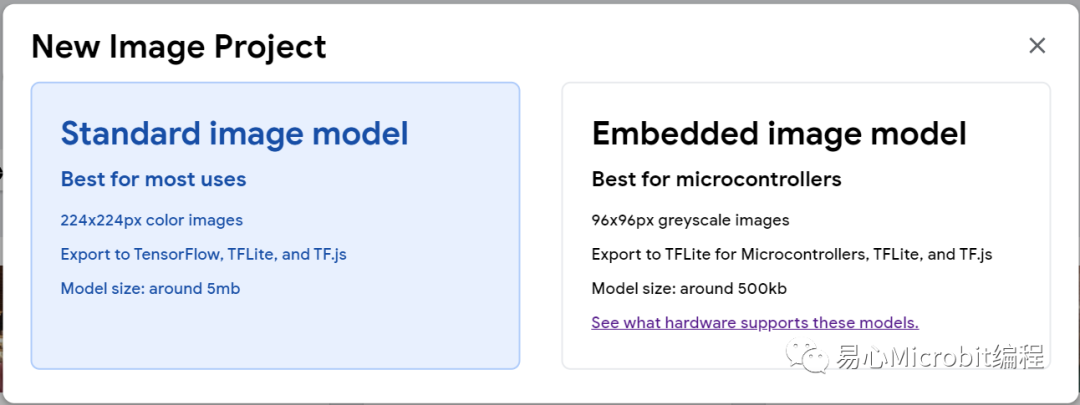
根據(jù)網(wǎng)站說(shuō)明,embedded model 是標(biāo)準(zhǔn)影像分類神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型的迷你版,因此可在微控制器上運(yùn)行。
這應(yīng)該是最簡(jiǎn)單的地方啦,但在操作 TM 之前要先完成上述的軟硬件設(shè)定。完成之后請(qǐng)根據(jù)以下步驟操作:
1.下載 TMUploader ArduinoSketch,解壓縮之后于Arduino IDE 開啟同名的 .ino 檔。板子類型要選擇 Arduino Nano 33,COM port 也要正確設(shè)定否則將無(wú)法刻錄。本程序負(fù)責(zé)把 Arduino 所拍攝的影像送往 Processing。
https://github.com/googlecreativelab/teachablemachine-community/tree/master/snippets/markdown/tiny_image/tiny_templates/TMUploader
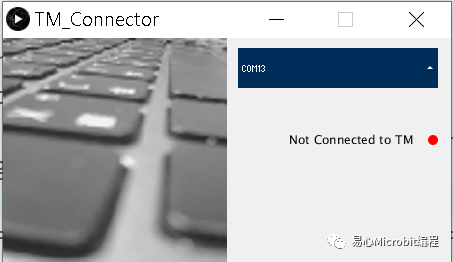
2.下載 TMConnectorProcessing Sketch, 解壓縮之后于 Arduino IDE 開啟同名的 .pde 檔。點(diǎn)選左上角的執(zhí)行(Play)鍵,會(huì)看到如下的畫面,并列出可用的 COM port 與聯(lián)機(jī)狀態(tài)。
https://github.com/googlecreativelab/teachablemachine-community/tree/master/snippets/markdown/tiny_image/tiny_templates/TMConnector
3.請(qǐng)由畫面中來(lái)選擇您的 Arduino,如果列出很多裝置不知道怎么選的話,可由 Arduino IDE 中來(lái)交叉比對(duì)。順利的話就會(huì)在 Processing 執(zhí)行畫面中看到相機(jī)的實(shí)時(shí)預(yù)覽畫面。如果畫面停頓或是沒有畫面,請(qǐng)檢查接線是否都接對(duì)了。如果畫面有更新但是模糊,請(qǐng)轉(zhuǎn)動(dòng)相機(jī)模塊前端圓環(huán)來(lái)調(diào)整焦距。
4.回到 Teachable Machine 網(wǎng)站,新增一個(gè) ImageProject 專案。先點(diǎn)選 Device,再點(diǎn)選 [Attempt to connect to device] 選項(xiàng),順利的話應(yīng)該就可以看到 OV7670的畫面了。
收集資料與訓(xùn)練
接下來(lái)的步驟就一樣了,請(qǐng)用您的照相機(jī)來(lái)搜集想要訓(xùn)練的圖片吧,圖片格式為 96 x 96 灰階。請(qǐng)用相機(jī)對(duì)準(zhǔn)想要辨識(shí)的物體,從 [webcam] 選項(xiàng)來(lái)收集照片。請(qǐng)注意,即便用 [Upload] 選項(xiàng)去上傳彩色照片,訓(xùn)練完的模型一樣只能接受單色(灰階)輸入。請(qǐng)盡量讓數(shù)據(jù)收集與后續(xù)測(cè)試時(shí)使用同一個(gè)相機(jī)模塊 (原場(chǎng)考照的概念~)
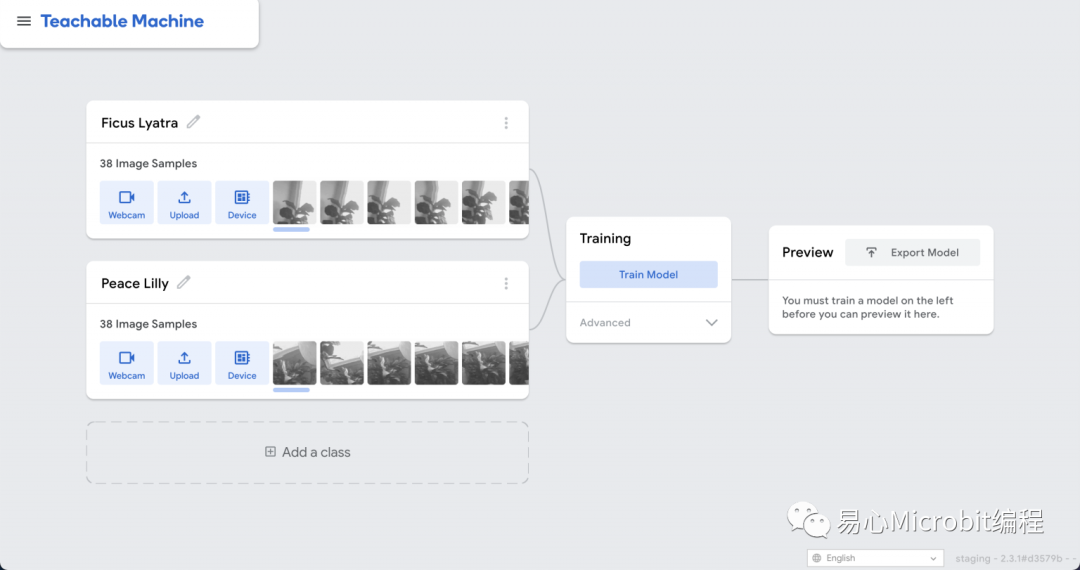
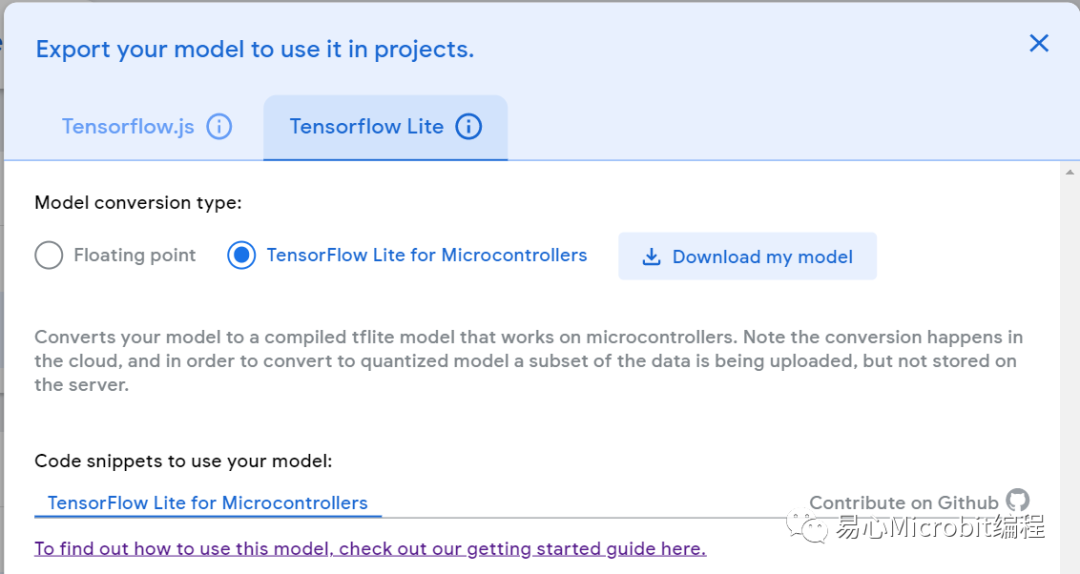
訓(xùn)練完成(很快)之后,于 Teachable Machine 右上角點(diǎn)選 [Export Model],于彈出畫面中選擇 Tensorflow Lite 并勾選下方的 Tensorflow Lite for Microcontrollers ,最后點(diǎn)選 [Download myModel] 就好了!轉(zhuǎn)檔需要稍等一下(有可能要幾分鐘),完成就會(huì)下載一個(gè) converted_tinyml.zip,檔名如果不對(duì),就代表之前的選項(xiàng)選錯(cuò)了喔
解壓縮可以看到 converted_tinyml 相關(guān)內(nèi)容
執(zhí)行于 Arduino
關(guān)閉所有 Processing app,因?yàn)槲覀儠簳r(shí)不需要收集照片了,且這樣占住 COM port 而無(wú)法上傳 Arduino 程序。上傳完成,請(qǐng)開啟 Arduino IDE 的 Serial Monitor,就會(huì)看到每一個(gè)畫面的辨識(shí)結(jié)果與信心指數(shù) (-128 to 127),請(qǐng)回顧本文一開始的執(zhí)行影片就知道啰,happy making !
TMUploader Arduino 程序
#include
#include
#include"ImageProvider.h"
voidsetup() {
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);?? // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltagelevel)
delay(400);?????????????????????? // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);??? // turn the LED off by making the voltageLOW
delay(400);?????????????????????? // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);?? // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltagelevel)
delay(400);???? ??????????????????// wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);??? // turn the LED off by making the voltageLOW
delay(400);?????????????????????? // wait for a second
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial);
}
constint kNumCols = 96;
constint kNumRows = 96;
constint kNumChannels = 1;
constint bytesPerFrame = kNumCols * kNumRows;
// QVGA: 320x240 X 2 bytes per pixel (RGB565)
uint8_tdata[kNumCols * kNumRows * kNumChannels];
voidflushCap() {
for (int i = 0; i < kNumCols * kNumRows *kNumChannels; i++) {
data[i] = 0;
}
}
voidloop() {
//? Serial.println(000"creatingimage");
GetImage(kNumCols, kNumRows, kNumChannels,data);
//? Serial.println("got image");
Serial.write(data, bytesPerFrame);
//? flushCap();
}
TMConnectorProcessing 程序
importprocessing.serial.*;
importjava.nio.ByteBuffer;
importjava.nio.ByteOrder;
importwebsockets.*;
importjavax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter;
importcontrolP5.*;
importjava.util.*;
SerialmyPort;
WebsocketServerws;
// mustmatch resolution used in the sketch
finalint cameraWidth = 96;
finalint cameraHeight = 96;
finalint cameraBytesPerPixel = 1;
finalint bytesPerFrame = cameraWidth * cameraHeight * cameraBytesPerPixel;
PImagemyImage;
byte[] frameBuffer= new byte[bytesPerFrame];
String[]portNames;
ControlP5cp5;
ScrollableListportsList;
booleanclientConnected = false;
voidsetup()
{
size(448, 224);
pixelDensity(displayDensity());
frameRate(30);
cp5 = new ControlP5(this);
portNames = Serial.list();
portNames = filteredPorts(portNames);
ws = new WebsocketServer(this, 8889,"/");
portsList =cp5.addScrollableList("portSelect")
.setPosition(235, 10)
.setSize(200, 220)
.setBarHeight(40)
.setItemHeight(40)
.addItems(portNames);
portsList.close();
// wait for full frame of bytes
//myPort.buffer(bytesPerFrame);??
//myPort = new Serial(this, "COM5",9600);
//myPort = new Serial(this,"/dev/ttyACM0", 9600);
//myPort = new Serial(this, "/dev/cu.usbmodem14201",9600);??
myImage = createImage(cameraWidth,cameraHeight, RGB);
noStroke();
}
voiddraw()
{?
background(240);
image(myImage, 0, 0, 224, 224);
drawConnectionStatus();
}
voiddrawConnectionStatus() {
fill(0);
textAlign(RIGHT, CENTER);
if (!clientConnected) {
text("Not Connected to TM", 410,100);
fill(255, 0, 0);
} else {
text("Connected to TM", 410,100);
fill(0, 255, 0);
}
ellipse(430, 102, 10, 10);
}
voidportSelect(int n) {
String selectedPortName = (String) cp5.get(ScrollableList.class,"portSelect").getItem(n).get("text");
try {
myPort = new Serial(this, selectedPortName,9600);
myPort.buffer(bytesPerFrame);
}
catch (Exception e) {
println(e);
}
}
booleanstringFilter(String s) {
return (!s.startsWith("/dev/tty"));
}
intlastFrame = -1;
String[] filteredPorts(String[] ports) {
int n = 0;
for (String portName : ports) if(stringFilter(portName)) n++;
String[] retArray = new String[n];
n = 0;
for (String portName : ports) if(stringFilter(portName)) retArray[n++] = portName;
return retArray;
}
voidserialEvent(Serial myPort) {
// read the saw bytes in
myPort.readBytes(frameBuffer);
//println(frameBuffer);
// access raw bytes via byte buffer
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(frameBuffer);
bb.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
int i = 0;
while (bb.hasRemaining()) {
//0xFF & to treat byte as unsigned.
int r = (int) (bb.get() & 0xFF);
myImage.pixels[i] = color(r, r, r);
i++;
//println("adding pixels");
}
if (lastFrame == -1) {
lastFrame = millis();
}
else {
int frameTime = millis() - lastFrame;
print("fps: ");
println(frameTime);
lastFrame = millis();
}
myImage.updatePixels();
myPort.clear();
String data = DatatypeConverter.printBase64Binary(frameBuffer);
ws.sendMessage(data);
}
voidwebSocketServerEvent(String msg) {
if (msg.equals("tm-connected"))clientConnected = true;
}
編輯:黃飛
?
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App





















評(píng)論