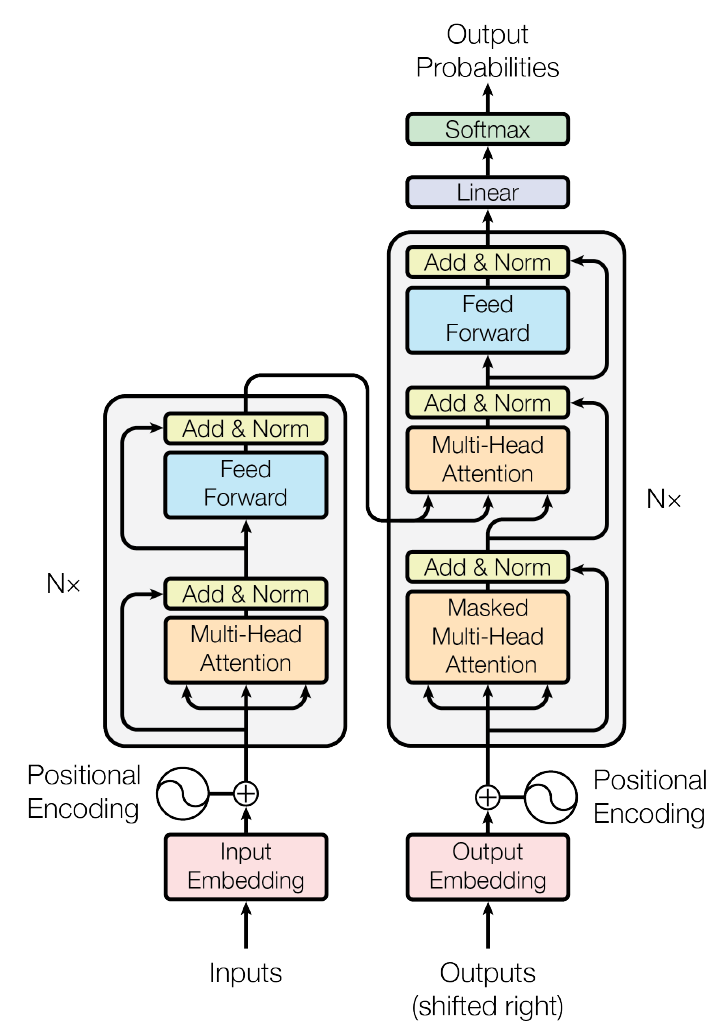
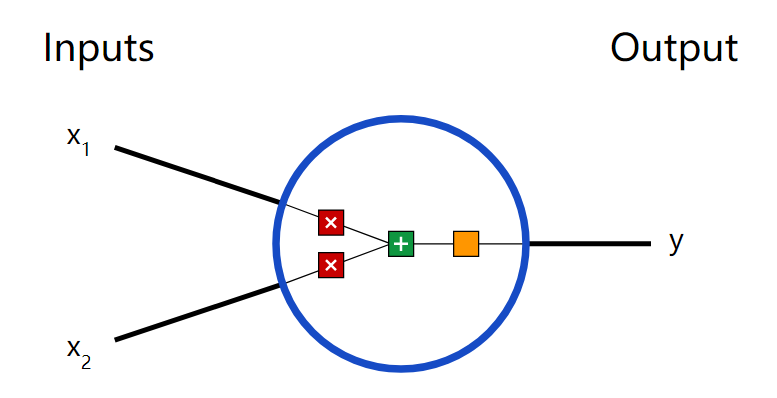
當前層輸出為Ij,f為非線性轉化函數,又稱為激活函數,定義如下:
即每一層的輸出為:
這樣就可以通過輸入值正向得到每一層的輸出值。
2、根據誤差反向傳送 對于輸出層:其中Tk是真實值,Ok是預測值
對于隱藏層:
權重更新:其中l為學習率
偏向更新:
3、終止條件
偏重的更新低于某個閾值;
預測的錯誤率低于某個閾值;
達到預設一定的循環次數;
4、非線性轉化函數
上面提到的非線性轉化函數f,一般情況下可以用兩種函數:
(1)tanh(x)函數:
tanh(x)=sinh(x)/cosh(x)
sinh(x)=(exp(x)-exp(-x))/2
cosh(x)=(exp(x)+exp(-x))/2
(2)邏輯函數,本文上面用的就是邏輯函數
五、BP神經網絡的python實現
需要先導入numpy模塊
import numpy as np
定義非線性轉化函數,由于還需要用到給函數的導數形式,因此一起定義
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
def tanh_deriv(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x)*np.tanh(x)
def logistic(x):
return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x))
def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x)*(1-logistic(x))
設計BP神經網絡的形式(幾層,每層多少單元個數),用到了面向對象,主要是選擇哪種非線性函數,以及初始化權重。layers是一個list,里面包含每一層的單元個數。
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, layers, activation='tanh'):
"""
:param layers: A list containing the number of units in each layer.
Should be at least two values
:param activation: The activation function to be used. Can be
"logistic" or "tanh"
"""
if activation == 'logistic':
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv
self.weights = []
for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1):
self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1))-1)*0.25)
self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1]))-1)*0.25)
實現算法
def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
X = np.atleast_2d(X)
temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1]+1])
temp[:, 0:-1] = X
X = temp
y = np.array(y)
for k in range(epochs):
i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0])
a = [X[i]]
for l in range(len(self.weights)):
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l])))
error = y[i] - a[-1]
deltas = [error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])]
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1):
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T)*self.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse()
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta)
實現預測
def predict(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0]+1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l]))
return a
我們給出一組數進行預測,我們上面的程序文件保存名稱為BP
from BP import NeuralNetwork
import numpy as np
nn = NeuralNetwork([2,2,1], 'tanh')
x = np.array([[0,0], [0,1], [1,0], [1,1]])
y = np.array([1,0,0,1])
nn.fit(x,y,0.1,10000)
for i in [[0,0], [0,1], [1,0], [1,1]]:
print(i, nn.predict(i))
結果如下:
([0, 0], array([ 0.99738862]))
([0, 1], array([ 0.00091329]))
([1, 0], array([ 0.00086846]))
([1, 1], array([ 0.99751259]))
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App






















評論